Is 69 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
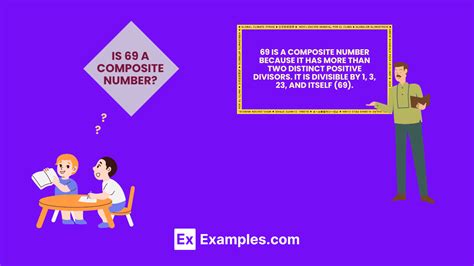
Table of Contents
Is 69 a Prime Number or a Composite Number? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The question, "Is 69 a prime number or a composite number?" might seem simple at first glance. However, exploring this seemingly straightforward query opens doors to a fascinating world of number theory, delving into the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. Understanding the difference between prime and composite numbers is crucial for grasping more advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive article will not only answer the question definitively but also provide a thorough understanding of prime and composite numbers, exploring related concepts and their significance.
Understanding Prime and Composite Numbers
Before we delve into the specifics of the number 69, let's establish a clear understanding of the definitions:
Prime Numbers: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and the number itself. Examples of prime numbers include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. The prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers.
Composite Numbers: A composite number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number. This means it has at least one positive divisor other than 1 and itself. Composite numbers can be expressed as the product of two or more prime numbers. Examples include 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 9 (3 x 3), and 10 (2 x 5).
The Number 1: It's important to note that the number 1 is neither prime nor composite. It's a unique number with only one divisor, itself.
Determining if 69 is Prime or Composite
Now, let's tackle the question at hand: Is 69 a prime or composite number? To determine this, we need to check if 69 has any divisors other than 1 and 69.
We can start by checking the divisibility rules for small prime numbers:
- Divisibility by 2: 69 is not divisible by 2 because it's an odd number.
- Divisibility by 3: The divisibility rule for 3 states that a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. In this case, 6 + 9 = 15, and 15 is divisible by 3. Therefore, 69 is divisible by 3.
Since 69 is divisible by 3 (69 = 3 x 23), it has a divisor other than 1 and itself. This conclusively proves that 69 is a composite number.
Factorization of 69
The prime factorization of 69 is 3 x 23. Both 3 and 23 are prime numbers. This factorization confirms that 69 is a composite number because it's expressed as a product of two prime numbers.
The Significance of Prime and Composite Numbers
The distinction between prime and composite numbers is far more than a simple classification. It forms the bedrock of several crucial areas within mathematics:
1. Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This fundamental principle underpins many other mathematical concepts and algorithms.
2. Cryptography
Prime numbers play a vital role in modern cryptography. Many encryption algorithms rely on the difficulty of factoring very large composite numbers into their prime factors. The security of online transactions and sensitive data often depends on this principle.
3. Number Theory Research
Prime numbers are a central focus of ongoing research in number theory. Many unsolved problems, like the twin prime conjecture and the Riemann hypothesis, are directly related to the properties and distribution of prime numbers.
4. Generating Random Numbers
Prime numbers are used in algorithms for generating pseudorandom numbers, crucial for simulations, statistical analysis, and other computational tasks.
Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding prime and composite numbers leads to exploring related mathematical concepts:
1. Prime Factorization
This is the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. It's a fundamental tool in number theory and has applications in various fields.
2. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
These concepts, closely related to prime factorization, are essential for simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and other mathematical operations.
3. Sieve of Eratosthenes
This ancient algorithm efficiently identifies prime numbers up to a specified limit. It's a classic example of an elegant and effective mathematical technique.
Practical Applications Beyond Mathematics
The concepts of prime and composite numbers extend beyond theoretical mathematics and find practical applications in various fields:
-
Computer Science: Hashing algorithms, data structures, and cryptographic systems heavily rely on prime numbers for their efficiency and security.
-
Engineering: Prime numbers find applications in signal processing, coding theory, and error detection.
-
Cryptography: As mentioned earlier, prime numbers are the cornerstone of modern encryption techniques, securing sensitive data online and offline.
Conclusion: 69 is Definitely Composite
To reiterate, the number 69 is definitively a composite number. Its divisibility by 3, and its prime factorization (3 x 23), clearly demonstrate this fact. Understanding the properties of prime and composite numbers is not just a matter of academic interest; it forms the foundation of many crucial mathematical concepts and real-world applications. From the security of online transactions to the advancement of number theory, the seemingly simple distinction between prime and composite numbers holds immense significance. This detailed exploration should have provided a thorough understanding of the topic, highlighting its importance and relevance in various fields. The seemingly simple question "Is 69 a prime number or a composite number?" thus serves as a gateway to a much richer and more complex world of mathematical exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Solid Has A Definite Shape And Volume
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 32 Out Of 40
Mar 27, 2025
-
Words With Ie In Them 5 Letters
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Are The Pros Of Fossil Fuels
Mar 27, 2025
-
An Object Following A Straight Line Path At Constant Speed
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 69 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
