What Is The S I Unit For Temperature
Juapaving
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
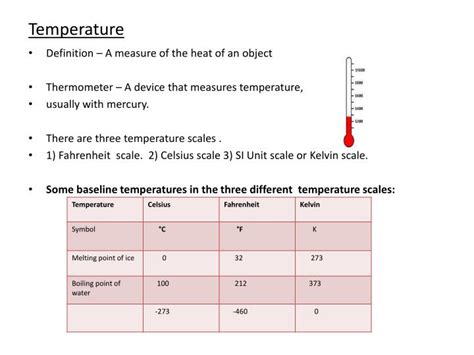
Table of Contents
What is the SI Unit for Temperature? A Deep Dive into Kelvin and its Applications
The world of physics relies heavily on standardized units of measurement to ensure consistency and accuracy in scientific communication and experimentation. Among the fundamental physical quantities, temperature holds a significant position, influencing countless physical phenomena. So, what is the SI unit for temperature? The answer is Kelvin (K). This seemingly simple answer, however, opens the door to a much deeper understanding of temperature scales, their history, and their critical applications across various scientific disciplines.
Understanding Temperature and its Measurement
Before diving into the specifics of Kelvin, let's establish a foundational understanding of temperature itself. Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses the degree of hotness or coldness of a substance. It's a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles (atoms and molecules) within a substance. Higher temperature signifies greater kinetic energy, meaning particles move more rapidly. Conversely, lower temperatures indicate slower particle movement.
This understanding of temperature at a microscopic level is crucial because it forms the basis for the thermodynamic temperature scale, which is ultimately anchored in Kelvin. Other temperature scales, like Celsius and Fahrenheit, are derived from Kelvin and defined relative to specific reference points.
The Kelvin Scale: A Thermodynamic Perspective
The Kelvin scale, named after the renowned physicist Lord Kelvin (William Thomson), is the absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. This means it's based on the fundamental laws of thermodynamics and defines a temperature of absolute zero as its zero point. Absolute zero represents the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases; the lowest possible temperature.
This absolute nature is what makes Kelvin the preferred SI unit for temperature. Using a scale anchored at absolute zero provides a more fundamental and consistent framework for scientific calculations, especially in thermodynamics and related fields. Unlike Celsius and Fahrenheit, Kelvin doesn't use arbitrary reference points like the freezing and boiling points of water.
Key Characteristics of the Kelvin Scale:
- Absolute Zero: 0 K (zero Kelvin) corresponds to absolute zero, where all molecular motion theoretically stops. Note that it's practically impossible to reach absolute zero.
- No Negative Values: The Kelvin scale only comprises positive values, eliminating the need to deal with negative temperatures, simplifying many calculations.
- Interval Size: The size of one Kelvin degree is identical to one Celsius degree. This means a temperature change of 1 K is equal to a temperature change of 1 °C.
- Relationship to Celsius: The conversion between Kelvin and Celsius is straightforward: K = °C + 273.15. Therefore, 0 °C is equivalent to 273.15 K.
Why Kelvin is the SI Unit: Advantages and Applications
The designation of Kelvin as the SI unit for temperature underscores its advantages in various scientific and engineering applications:
-
Consistency in Scientific Calculations: The absolute nature of the Kelvin scale removes ambiguity and simplifies calculations involving thermodynamic properties like entropy, internal energy, and enthalpy. These properties often exhibit complex relationships with temperature, and using Kelvin avoids errors stemming from arbitrary scale conventions.
-
Precision in Scientific Measurements: Kelvin’s absolute zero reference point allows for highly precise measurements of temperature differences and changes. This precision is essential in various high-precision scientific experiments and engineering applications.
-
Universally Accepted Standard: As the SI unit, Kelvin ensures a common language among scientists worldwide, promoting clarity and avoiding confusion caused by different temperature scales. This is especially crucial in international collaborations and the dissemination of scientific findings.
-
Applications in Astrophysics and Cosmology: The incredibly low temperatures encountered in space, often close to absolute zero, require the Kelvin scale for meaningful measurements and understanding of cosmological phenomena.
-
Importance in Material Science: Many material properties, such as thermal expansion and conductivity, exhibit strong temperature dependencies. Using Kelvin allows for accurate modeling and prediction of material behavior across a wide range of temperatures.
-
Critical Role in Cryogenics: Cryogenics involves the production and application of extremely low temperatures. The Kelvin scale is indispensable in this field, enabling the precise control and measurement of temperatures in cryogenic processes and experiments.
-
Applications in Meteorology and Climatology: While Celsius is often used for reporting everyday temperatures, Kelvin plays a critical role in climate modeling, atmospheric studies, and the understanding of global warming. Accurate temperature measurements in Kelvin are necessary for simulating climate systems and predicting future climate change scenarios.
-
Essential in Chemical Engineering: Chemical reactions are highly sensitive to temperature. Kelvin ensures accurate monitoring and control of reaction temperatures, allowing for optimized chemical processes and the synthesis of desired products.
-
Use in Nuclear Physics: Nuclear reactions, like nuclear fusion, involve extremely high temperatures. The Kelvin scale provides a consistent way to measure and analyze the temperatures involved in these processes.
Other Temperature Scales: Celsius and Fahrenheit
While Kelvin is the SI unit, other temperature scales, such as Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F), are commonly used in everyday life and certain specialized fields.
Celsius Scale:
The Celsius scale, previously known as the centigrade scale, is based on the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure. 0 °C is defined as the freezing point of water, and 100 °C is its boiling point. The Celsius scale is widely used for everyday temperature measurements and many scientific applications.
Fahrenheit Scale:
The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, uses different reference points. 32 °F is defined as the freezing point of water, and 212 °F as its boiling point. The Fahrenheit scale is mainly used in the United States and some other countries.
Converting between Temperature Scales
The conversion between different temperature scales is crucial for ensuring compatibility and consistency in scientific data. Here are the formulas for conversion:
- Kelvin to Celsius: °C = K - 273.15
- Celsius to Kelvin: K = °C + 273.15
- Celsius to Fahrenheit: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
- Fahrenheit to Celsius: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
- Kelvin to Fahrenheit: °F = (K × 9/5) - 459.67
- Fahrenheit to Kelvin: K = (°F + 459.67) × 5/9
The Importance of Accurate Temperature Measurement
Accurate temperature measurement is paramount across numerous disciplines. The use of appropriate instruments and calibrated devices is crucial for obtaining reliable data. Different types of thermometers, such as liquid-in-glass thermometers, thermocouples, and thermistors, are employed depending on the temperature range and application. Regular calibration and maintenance of these instruments are essential to ensure accurate and reliable temperature measurements.
Conclusion: Kelvin's Enduring Significance
The Kelvin scale, with its grounding in thermodynamics and absolute zero, stands as the fundamental and universally accepted SI unit for temperature. Its absolute nature simplifies calculations, enhances precision in measurements, and promotes consistency in scientific communication. While other temperature scales like Celsius and Fahrenheit hold their practical applications, the significance of Kelvin remains paramount in scientific research, engineering, and various other disciplines that rely on precise temperature measurements and understanding. Its continued use underscores its importance in advancing our comprehension of the physical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Relationship Between The Following Compounds
Mar 30, 2025
-
5 Letter Words Starting With A P
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Many Hundreds Are In 7000
Mar 30, 2025
-
Write 72 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 30, 2025
-
How To Find The Latus Rectum Of A Parabola
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The S I Unit For Temperature . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
