What Is The Rule Of Adding Integers
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
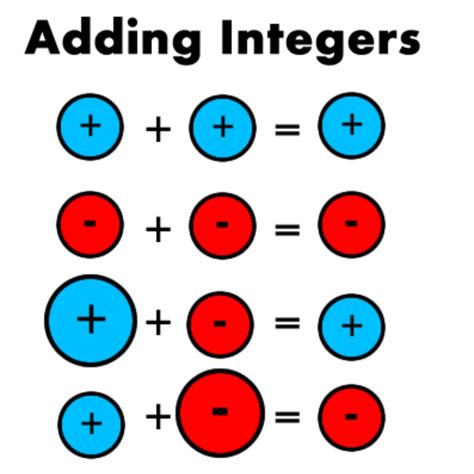
Table of Contents
What is the Rule of Adding Integers? A Comprehensive Guide
Adding integers might seem simple at first glance, but a solid understanding of the underlying rules is crucial for mastering more advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of integer addition, covering various methods, strategies, and practical applications. We'll explore the rules governing positive and negative integers, tackle different scenarios, and provide ample examples to solidify your understanding. Whether you're a student brushing up on your math skills or an adult looking to refresh your knowledge, this guide will serve as a valuable resource.
Understanding Integers: A Quick Refresher
Before diving into the rules of addition, let's briefly revisit the definition of integers. Integers are whole numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero. They are represented on a number line, with zero at the center, positive integers to the right, and negative integers to the left. Examples of integers include: -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. Understanding the number line is key to visualizing integer addition.
The Number Line: Your Visual Aid
The number line is an invaluable tool for understanding integer addition. It provides a visual representation of the magnitude and direction of numbers. When adding integers, you can visualize movement along the number line. Positive integers represent movement to the right, and negative integers represent movement to the left.
The Fundamental Rules of Adding Integers
The core rules for adding integers revolve around the signs of the numbers being added. Let's break down the different scenarios:
1. Adding Two Positive Integers
Adding two positive integers is straightforward; simply add their absolute values (the numerical value without the sign).
Example: 5 + 3 = 8
This is equivalent to moving 5 units to the right on the number line, and then moving another 3 units to the right, resulting in a final position of 8.
2. Adding Two Negative Integers
Adding two negative integers also involves adding their absolute values, but the result will be negative.
Example: -5 + (-3) = -8
On the number line, this means moving 5 units to the left, and then moving another 3 units to the left, ending at -8. Remember the parentheses are crucial here to avoid confusion.
3. Adding a Positive and a Negative Integer
This scenario requires more careful consideration. The key is to find the difference between the absolute values of the two integers. The sign of the result is determined by the integer with the larger absolute value.
Scenario A: Positive Integer has a larger absolute value
Example: 5 + (-3) = 2
Here, we subtract the absolute value of the negative integer (3) from the absolute value of the positive integer (5), resulting in 2. The result is positive because the positive integer had the larger absolute value. On the number line, you move 5 units to the right and then 3 units to the left, ending at 2.
Scenario B: Negative Integer has a larger absolute value
Example: -5 + 3 = -2
Here, we subtract the absolute value of the positive integer (3) from the absolute value of the negative integer (5), resulting in 2. The result is negative because the negative integer had the larger absolute value. On the number line, you move 5 units to the left and then 3 units to the right, ending at -2.
4. Adding Zero to an Integer
Adding zero to any integer does not change its value. This is known as the additive identity property.
Example: 5 + 0 = 5 and -5 + 0 = -5
Advanced Techniques and Strategies for Adding Integers
While the fundamental rules are essential, mastering integer addition often involves tackling more complex scenarios. Let's explore some strategies:
1. Using the Number Line for Multiple Additions
When adding multiple integers, the number line provides a clear visual approach. Start at zero and move left or right based on the sign and value of each integer.
Example: -2 + 5 + (-3) + 4
- Start at 0.
- Move 2 units left (-2).
- Move 5 units right (+5).
- Move 3 units left (-3).
- Move 4 units right (+4).
The final position on the number line will be your answer.
2. Rearranging Terms for Easier Calculation (Commutative Property)
The commutative property of addition states that you can change the order of the integers without affecting the sum. This can be incredibly helpful when dealing with a string of positive and negative integers. Rearrange the numbers to group positive integers together and negative integers together, making the addition process simpler.
Example: -5 + 8 + (-3) + 2
Rearrange: 8 + 2 + (-5) + (-3) = 10 + (-8) = 2
3. Using the Associative Property
The associative property of addition allows you to group integers in different ways without altering the sum. This is particularly useful when dealing with longer addition problems.
Example: (-2 + 5) + (-3 + 4) = 3 + 1 = 4
4. Breaking Down Complex Problems
For very large or complex addition problems, breaking them down into smaller, more manageable chunks can improve accuracy and efficiency.
Example: -125 + 78 + 150 + (-35)
Break it down:
- (-125 + 150) = 25
- (78 + (-35)) = 43
- 25 + 43 = 68
Real-World Applications of Adding Integers
Understanding integer addition is not confined to the classroom; it has numerous real-world applications:
1. Financial Management
Adding integers is fundamental to tracking income and expenses. Positive integers represent income, while negative integers represent expenses. Adding them helps to determine net income or loss.
Example: Calculating profit: Income ($1000) + (-$500 expenses) = $500 profit
2. Temperature Changes
Changes in temperature often involve integer addition. A rise in temperature is a positive integer, and a drop is a negative integer.
Example: The temperature started at 5°C and dropped by 8°C, then rose by 3°C. The final temperature is 5 + (-8) + 3 = 0°C
3. Elevation Changes
In geography and surveying, calculating elevation changes requires adding integers. Positive integers represent an increase in elevation, and negative integers represent a decrease.
Example: Hiking a trail: Initial elevation (1000m) + (+200m climb) + (-150m descent) = 1050m final elevation
4. Accounting and Bookkeeping
Accounting relies heavily on integer addition for balancing accounts, tracking debits and credits, and ensuring financial accuracy.
5. Game Scoring
Many games involve scoring systems where points can be gained (positive integers) or lost (negative integers). Adding these integers determines a player's final score.
Conclusion: Mastering Integer Addition for Future Success
Mastering the rules of adding integers is not merely about rote memorization; it's about understanding the underlying principles and developing efficient strategies. This knowledge forms the bedrock for more complex mathematical concepts, including algebra, calculus, and beyond. By practicing the techniques outlined in this guide, you will not only improve your integer addition skills but also develop a stronger foundation for your mathematical journey. Remember to utilize the number line as a visual aid, explore different strategies, and practice regularly to solidify your understanding. The ability to confidently add integers will open doors to a wider range of mathematical applications and problem-solving capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Displacement Is Which Of The Following Types Of Quantities
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 5 And 20
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Advantage Of Ac Over Dc
Mar 24, 2025
-
A Rhombus With 4 Right Angles
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Are The Prime Factors Of 57
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Rule Of Adding Integers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
