What Are The Prime Factors Of 57
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 4 min read
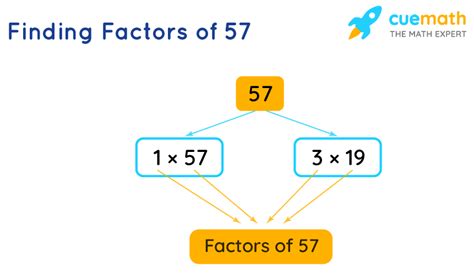
Table of Contents
What are the Prime Factors of 57? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Finding the prime factors of a number might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers like 57. However, understanding the process behind prime factorization is crucial for grasping fundamental concepts in number theory and algebra. This article will not only reveal the prime factors of 57 but also delve into the broader world of prime numbers, factorization methods, and their applications.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 57, let's refresh our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number.
Prime numbers are the building blocks of all other whole numbers. This fundamental concept is the cornerstone of number theory. The infinitude of primes – the fact that there are infinitely many prime numbers – is a fascinating and significant theorem in mathematics.
Methods for Finding Prime Factors
Several methods exist to find the prime factors of a number. Let's explore a few:
1. Trial Division
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We systematically test for divisibility by prime numbers, starting with the smallest prime number, 2. If the number is divisible, we divide it and continue the process with the quotient until we reach 1.
For example, let's find the prime factors of 12:
- 12 ÷ 2 = 6
- 6 ÷ 2 = 3
- 3 ÷ 3 = 1
Therefore, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3, or 2² x 3.
2. Factor Tree
A factor tree is a visual representation of the prime factorization process. We start with the original number and branch out, dividing by prime factors until only prime numbers remain at the ends of the branches.
Let's use the factor tree method for the number 24:
24
/ \
2 12
/ \
2 6
/ \
2 3
The prime factorization of 24 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 3, or 2³ x 3.
3. Division by Prime Numbers
This method systematically divides the number by prime numbers until the result is 1. We record the prime numbers used in the division. This method is essentially a refined version of trial division.
For instance, to factorize 36:
- 36 ÷ 2 = 18
- 18 ÷ 2 = 9
- 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- 3 ÷ 3 = 1
The prime factorization of 36 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 3, or 2² x 3².
Finding the Prime Factors of 57
Now, let's apply these methods to find the prime factors of 57. We can start with trial division:
- 57 is not divisible by 2 (it's not an even number).
- 57 is not divisible by 3 (5 + 7 = 12, which is divisible by 3). 57 ÷ 3 = 19
- 19 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 57 is 3 x 19.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization might seem like a purely mathematical exercise, but it has significant applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: The security of many encryption methods, such as RSA encryption, relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors. The larger the numbers, the more computationally intensive the factorization becomes.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms related to prime numbers and factorization are crucial in various computer science applications, including hashing, data structures, and algorithm design.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization forms the basis for many theorems and concepts in number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties and relationships of numbers.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a critical role in error-correcting codes, which are used to ensure data integrity in communication systems.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime factorization concepts extend to more abstract algebraic structures, contributing to a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships.
Beyond 57: Exploring Larger Numbers
While finding the prime factors of 57 is relatively straightforward, the process can become significantly more complex for larger numbers. For very large numbers, specialized algorithms, like the general number field sieve, are employed to efficiently determine their prime factors. These algorithms are computationally intensive and require powerful computing resources.
Conclusion: The Importance of Primes
The prime factors of 57, 3 and 19, are seemingly simple numbers. However, their identification exemplifies the fundamental importance of prime numbers in mathematics and their unexpected applications in various fields. Understanding prime factorization is not just an exercise in arithmetic; it’s a key to unlocking deeper mathematical insights and technological advancements. The seemingly simple act of breaking down a number into its prime components unveils a profound connection to the building blocks of our number system and its intricate applications in the modern world. The journey of finding the prime factors of 57, therefore, serves as a gateway to a much wider and fascinating exploration of number theory and its impact on our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Diagram Of An Animal And Plant Cell
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Environment And Ecosystem
Mar 29, 2025
-
How To Find Average Speed With Two Speeds
Mar 29, 2025
-
A Subset Of A Population Is Called A
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Ultimate Source Of Energy For Most Organisms Is
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Prime Factors Of 57 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
