A Rhombus With 4 Right Angles
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
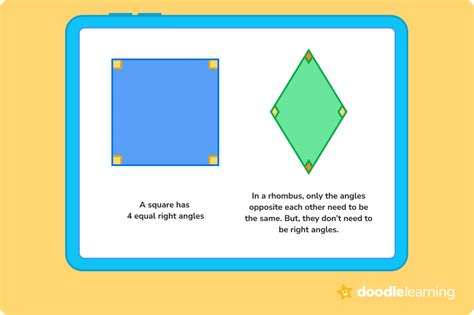
Table of Contents
A Rhombus with 4 Right Angles: Exploring the Square
A rhombus, by definition, is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length. However, the angles within a rhombus can vary. This leads to an interesting question: what happens when a rhombus possesses four right angles? The answer, quite simply, is that it becomes a square. This seemingly straightforward statement opens the door to a deeper exploration of geometric properties, their relationships, and the significance of precise definitions in mathematics.
Understanding the Properties of a Rhombus
Before diving into the implications of a rhombus with four right angles, let's solidify our understanding of a rhombus's fundamental properties:
-
Four Equal Sides: This is the defining characteristic of a rhombus. All four sides are congruent, meaning they have the same length. This characteristic distinguishes it from other quadrilaterals like rectangles or parallelograms.
-
Opposite Sides are Parallel: Like parallelograms, the opposite sides of a rhombus are parallel to each other. This parallelism contributes to many of the rhombus's geometric relationships.
-
Opposite Angles are Equal: The angles opposite each other within a rhombus are congruent. This is a direct consequence of the parallel sides.
-
Consecutive Angles are Supplementary: Any two angles that share a side (consecutive angles) add up to 180 degrees. This is another crucial property stemming from the parallel sides.
-
Diagonals Bisect Each Other: The diagonals of a rhombus intersect at a point that divides each diagonal into two equal segments.
-
Diagonals are Perpendicular Bisectors: The diagonals not only bisect each other but also intersect at a right angle (90 degrees). This perpendicularity is a key distinguishing feature.
The Transition from Rhombus to Square
Now, let's consider the crucial addition: four right angles. When we introduce the constraint that all four angles of a rhombus measure 90 degrees, a significant transformation occurs. The rhombus's properties, combined with the new right angle constraint, inevitably lead to a square.
This is because:
-
Right Angles and Equal Sides: A quadrilateral with four right angles is, by definition, a rectangle. However, because our shape also retains the rhombus's property of having four equal sides, it fulfills the requirements of a square. A square is a special case of both a rhombus and a rectangle.
-
Geometric Proof: We can rigorously prove this using geometric principles. Consider a rhombus ABCD, where AB = BC = CD = DA. If we add the condition that ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90°, then we have a rectangle with four equal sides. This automatically satisfies the definition of a square.
The Square: A Unique Quadrilateral
The square inherits all the properties of a rhombus and adds some unique characteristics of its own:
-
All Sides Equal: As with the rhombus, all four sides are congruent.
-
All Angles Equal (90°): This is the defining characteristic differentiating it from other quadrilaterals.
-
Diagonals are Equal: Unlike a general rhombus, the diagonals of a square are equal in length.
-
Diagonals Bisect Angles: Each diagonal bisects the angles it connects. This results in four congruent isosceles right-angled triangles formed by the diagonals.
-
Area Calculation: The area of a square is simply the side length squared (s²). This straightforward formula makes area calculations exceptionally easy.
-
Symmetry: The square exhibits a high degree of symmetry, possessing both rotational and reflectional symmetry.
Implications and Applications
The fact that a rhombus with four right angles is a square has numerous implications across various fields:
-
Geometry and Trigonometry: The square serves as a fundamental building block in geometric constructions and proofs. Its properties are extensively used in trigonometry, particularly with respect to right-angled triangles.
-
Engineering and Architecture: Squares and their properties are essential in engineering and architecture for designing stable and symmetrical structures. From building foundations to tiling patterns, the square's predictable properties are invaluable.
-
Computer Graphics and Programming: Squares are frequently used in computer graphics and programming to represent objects and define spatial relationships.
-
Tessellations and Patterns: Squares perfectly tessellate (tile a plane without gaps or overlaps), making them a cornerstone in creating various repeating patterns and designs in art and design.
Exploring Further: Beyond the Square
While the transformation from a rhombus to a square might seem straightforward, it highlights the importance of precise definitions and the interconnectedness of geometric properties. Exploring variations and related concepts can deepen our understanding:
-
Exploring other quadrilaterals: Comparing and contrasting the properties of squares with other quadrilaterals like rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and kites allows for a richer appreciation of their unique characteristics.
-
Higher dimensions: The concept of a square can be extended to higher dimensions. A cube, for example, is the three-dimensional equivalent of a square.
-
Non-Euclidean Geometry: Investigating the properties of squares in non-Euclidean geometries, where parallel lines can intersect, reveals fascinating departures from traditional Euclidean geometry.
-
Mathematical proofs and theorems: The properties of squares are frequently used as cornerstones in various mathematical proofs and theorems, highlighting their fundamental importance.
Conclusion: The Significance of Precise Definitions
The seemingly simple statement that a rhombus with four right angles is a square encapsulates a powerful lesson in the importance of precise definitions in mathematics. The combination of rhombus properties and the addition of right angles leads to an elegant and predictable result. This highlights the interconnectedness of geometric concepts and their wide-ranging applications across various disciplines. From simple geometric constructions to complex engineering designs, the square's unique properties continue to play a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world around us. The exploration of this seemingly simple geometric figure offers a compelling glimpse into the beauty and precision of mathematics. By understanding the subtle yet significant differences between quadrilaterals, we gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of geometric principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Group Of Nonmetals Is The Most Reactive
Mar 28, 2025
-
99 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Percent Is Equivalent To 3 8
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 75
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is A Subset Of A Real Number
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Rhombus With 4 Right Angles . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
