What Is The Purpose Of The Commutator
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
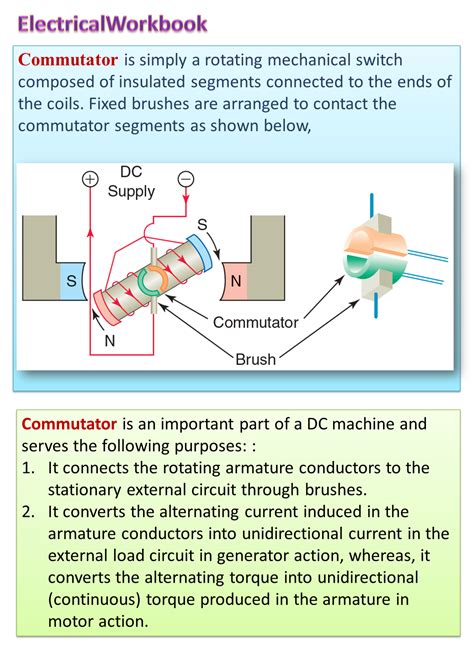
Table of Contents
What is the Purpose of the Commutator? A Deep Dive into DC Motor Functionality
The humble commutator. Often overlooked, this seemingly simple component is the heart of a direct current (DC) motor's ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical rotational energy. Understanding its purpose is key to grasping the fundamental workings of these ubiquitous machines. This article will delve into the intricacies of the commutator, exploring its function, construction, operation, and importance in various applications.
The Fundamental Role: Rectifying AC to DC
At its core, the commutator's primary purpose is to mechanically rectify alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This might seem counterintuitive – why would a DC motor need AC rectification? The answer lies in the way the motor's magnetic fields interact.
Understanding the Magnetic Field Interaction
A DC motor relies on the interaction between a rotating armature (containing the motor windings) and a stationary magnetic field (created by permanent magnets or electromagnets). The current flowing through the armature windings generates its own magnetic field. The interaction between these two magnetic fields creates a torque, causing the armature to rotate.
However, to maintain consistent rotational direction, the direction of the current flowing through the armature windings must be periodically reversed. This is where the commutator steps in. Without it, the motor would experience a constantly reversing torque, leading to no net rotation.
The Commutator as a Mechanical Switch
Imagine the armature windings as a simple coil of wire. As the armature rotates, the position of the coil relative to the magnetic field changes. To maintain consistent torque, the direction of current flow through the coil needs to reverse at precisely the right moments. The commutator achieves this by acting as a rotating switch, reversing the current direction as the armature rotates.
The Construction of a Commutator
A commutator is essentially a cylindrical structure segmented into a series of insulated copper bars or segments. These segments are carefully arranged and insulated from each other to prevent short circuits. Each segment is connected to a specific point in the armature winding.
Connecting the Commutator to the Armature
The connection between the commutator segments and the armature windings is crucial. The precise arrangement ensures that as the armature rotates, the current flow through the windings is reversed at the appropriate instants, maintaining consistent rotational torque. This connection process is highly precise and often involves careful soldering or welding techniques.
Brushes and the Electrical Connection
The commutator doesn't operate in isolation. It works in conjunction with carbon brushes. These brushes maintain electrical contact with the rotating commutator segments. As the commutator rotates, the brushes move from one segment to another, switching the current direction in the armature windings. The brushes are strategically positioned to ensure the proper timing of the current reversals.
Importance of Insulation
The insulation between the commutator segments is absolutely critical. If the segments were to short-circuit, the motor would fail. The insulation material must be able to withstand high temperatures and voltages, ensuring the commutator's reliable operation. Regular inspection and maintenance of the commutator and brushes are essential to prevent short circuits and ensure optimal motor performance.
The Operational Mechanism: A Step-by-Step Analysis
Let's break down the operational mechanism of a commutator in a DC motor.
-
Initial Current Flow: Initially, current flows through a specific set of armature windings via a particular pair of commutator segments and brushes. This creates a magnetic field that interacts with the stator's magnetic field, producing a torque.
-
Rotation and Segment Change: As the armature begins to rotate, the commutator segments also rotate. The brushes maintain continuous contact with the rotating commutator segments.
-
Current Reversal: At a specific point in the rotation, the brushes transition from one set of commutator segments to the next. This effectively switches the current flow through the armature windings. The current reversal occurs precisely at the point where the torque would otherwise begin to reverse, maintaining consistent rotational direction.
-
Continuous Rotation: This process repeats continuously as the commutator rotates. The current is periodically reversed in the armature windings, resulting in a continuous and unidirectional torque, leading to continuous rotation of the motor.
Why is the Commutator Important? Applications and Significance
The commutator plays a crucial role in a wide range of DC motor applications, impacting our daily lives in countless ways.
Essential for DC Motor Operation
Without the commutator, DC motors wouldn't function correctly. It's the essential component that enables the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical rotational energy. Its function is central to the operation of these motors.
Powering Various Devices
DC motors are found in a multitude of applications, from small devices like electric toothbrushes and toys to larger applications such as industrial machinery, electric vehicles, and power tools. The commutator ensures the smooth and efficient operation of all these devices.
Advantages of DC Motors with Commutators
DC motors with commutators offer several advantages:
- Precise speed control: The speed of DC motors can be precisely controlled by adjusting the current flowing through the armature windings.
- High starting torque: DC motors typically exhibit high starting torque, making them suitable for applications that require significant initial force.
- Simple construction and maintenance: Compared to other types of motors, DC motors with commutators are relatively simple to construct and maintain.
Limitations of Commutators
While commutators are essential, they also present certain limitations:
- Mechanical wear: The brushes and commutator segments are subject to mechanical wear and tear, requiring periodic replacement.
- Spark generation: The switching action of the commutator can generate sparks, which can be problematic in certain environments.
- Limited lifespan: Due to mechanical wear, commutators have a limited lifespan.
The Future of Commutators: Innovation and Alternatives
While commutators have been a cornerstone of DC motor technology for decades, research continues into alternative technologies that might eventually replace them.
Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) represent a significant advancement, eliminating the need for brushes and commutators. Instead, electronic commutation is employed, offering several advantages, including longer lifespan, higher efficiency, and reduced maintenance. However, BLDC motors typically require more complex control circuitry.
Advances in Commutator Technology
Despite the emergence of brushless technology, research is also ongoing to improve commutator designs. This includes the development of materials that enhance durability, reduce wear, and minimize sparking.
Conclusion: The Commutator's Enduring Importance
Despite the advancement of brushless motor technology, the commutator remains an integral component in many DC motors, particularly in applications where cost and simplicity are paramount. Its role in transforming alternating current into unidirectional torque is fundamental to the operation of these motors, powering a vast array of devices that shape our modern world. Understanding its purpose, construction, and operational mechanism is crucial for anyone working with DC motors or studying electrical engineering. While its future might see increasing competition from brushless designs, the commutator's legacy as a pivotal component in motor technology remains secure for the foreseeable future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Bromine
Mar 25, 2025
-
63 Kg Is How Many Pounds
Mar 25, 2025
-
X 2 X 3 X 2 X 3
Mar 25, 2025
-
Two Stroke Engine Four Stroke Engine Difference
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is Ph Of Pure Water
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Purpose Of The Commutator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
