What Is The Purpose Of Commutator
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
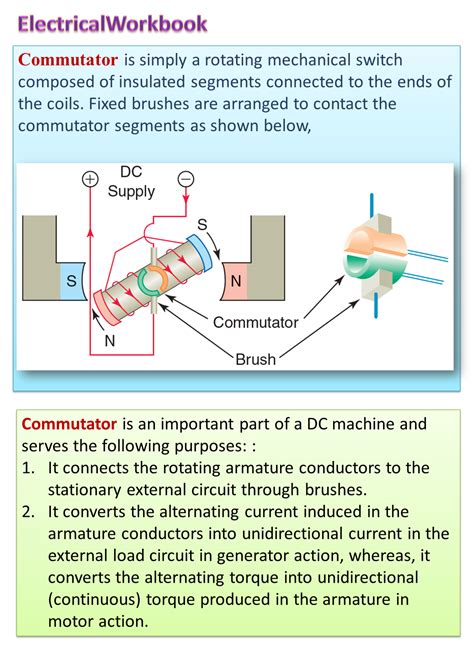
Table of Contents
What is the Purpose of a Commutator? A Deep Dive into DC Motor Functionality
The commutator, a seemingly simple component, plays a crucial role in the operation of direct current (DC) motors. Understanding its purpose is key to grasping the fundamental principles behind these ubiquitous machines. This article will delve deep into the intricacies of the commutator, exploring its function, construction, and significance in converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. We’ll also touch upon its limitations and the emergence of brushless DC motors as an alternative.
Understanding the Commutator's Primary Function: Rectification
At its core, the commutator's purpose is electrical rectification. In a DC motor, the current needs to flow in a specific direction to generate continuous rotational motion. However, the armature, the rotating part of the motor, contains coils that generate alternating current (AC). The commutator acts as a mechanical rectifier, converting this AC into DC to ensure unidirectional torque. This continuous unidirectional torque is what enables the motor shaft to rotate consistently in one direction.
The Role of the Brushes
The commutator doesn't work in isolation. It works in tandem with carbon brushes, which are stationary conductive contacts that press against the rotating commutator segments. These brushes act as the interface between the external DC power source and the rotating armature. As the armature rotates, the commutator segments make and break contact with the brushes, effectively switching the current direction within the armature windings.
The Process of Commutation
This switching process, known as commutation, is remarkably precise. The timing of the switching is directly related to the position of the armature coils within the magnetic field. As the coils reach a point where they would naturally start producing a counter-torque, the commutator switches the current, reversing the direction of current flow in that specific coil. This ensures the torque remains consistent and unidirectional, preventing the motor from stalling or oscillating.
Commutator Construction: A Closer Look
A commutator is typically constructed from a series of copper segments, carefully insulated from each other. These segments are precisely arranged in a cylindrical shape on the rotor shaft. The number of segments is directly related to the number of armature coils in the motor. Each segment is connected to a specific coil in the armature winding. This arrangement ensures that the current is consistently directed to the appropriate coils to generate the desired rotational force.
Insulation and Material Selection: Crucial Considerations
The insulation between the commutator segments is of critical importance. It must withstand high voltage and current, along with the significant centrifugal forces experienced during rotation. Materials used for the commutator segments are chosen for their high conductivity, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. Copper is a common choice due to its excellent electrical conductivity and relatively good mechanical properties.
The Significance of Commutation in DC Motor Operation
The precise and timed commutation achieved by the commutator is fundamentally important for efficient DC motor operation. Without it, the generated torque would fluctuate, leading to jerky motion and inefficient energy conversion. The smooth and consistent rotation produced by the commutator is essential for various applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Advantages of Commutator-Based DC Motors:
- Simple Design: Commutator motors, compared to other motor types, often have a relatively simple and robust design.
- High Starting Torque: They are capable of producing high starting torque, making them suitable for applications requiring rapid acceleration.
- Speed Control: Their speed can be easily controlled by varying the voltage or current supplied to the motor.
- Wide Range of Applications: Their versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications in various industries.
Limitations of Commutators and the Rise of Brushless Motors
While commutators are effective, they are not without their limitations. The physical contact between the brushes and the commutator segments leads to several challenges:
- Mechanical Wear: The continuous friction between the brushes and the commutator leads to wear and tear, reducing the lifespan of the motor. This necessitates periodic maintenance and replacement of brushes.
- Spark Generation: The making and breaking of contact between the brushes and the commutator segments can generate sparks, which can cause interference and damage the insulation over time.
- Limited Speed: The physical limitations of the commutator system restrict the maximum speed attainable by the motor.
- Maintenance Requirements: The need for periodic brush replacement and commutator maintenance contributes to higher operating costs.
These limitations have driven the development of brushless DC motors, which eliminate the commutator and brushes altogether. In brushless motors, electronic switching circuits replace the mechanical commutator, resulting in higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and improved speed control.
Understanding the Different Types of Commutators
While the basic principle remains the same, commutators can vary in design depending on the specific requirements of the application. These variations primarily focus on mitigating the drawbacks associated with standard commutators.
Segment Design and Material:
Variations in the shape, size and material of the commutator segments are incorporated to optimize for specific application needs. For instance, using materials with higher thermal conductivity can help to dissipate heat more effectively, reducing the risk of overheating. Similarly, different segment shapes can improve the contact with the brushes, enhancing the reliability of the motor.
Advanced Commutation Techniques:
Some modern DC motors employ sophisticated commutation techniques to further enhance their efficiency and performance. These techniques may incorporate advanced control algorithms or specialized materials to minimize sparking and wear. These improvements aim to extend the lifespan and reliability of commutator-based motors while addressing some of their inherent shortcomings.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of the Commutator
Despite the rise of brushless motors, the commutator remains a significant component in many DC motors. Its simple yet effective design provides a reliable and cost-effective solution for a wide range of applications where high starting torque, simple speed control, and robust operation are paramount. Understanding the purpose and function of the commutator is essential for anyone working with or studying electrical machinery. While the future may favor brushless technologies for some applications, the commutator's legacy continues, underscoring its enduring importance in the field of electrical engineering. The ongoing development of improved materials and commutation techniques suggests that commutator-based motors will continue to find applications where their advantages outweigh the limitations. Understanding both the strengths and limitations of this simple yet ingenious device remains crucial for anyone working in the realm of electrical motors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Orbitals With The Same Energy Are Called
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Chambers Are In A Frogs Heart
Mar 23, 2025
-
Chemical Bonds From Weakest To Strongest
Mar 23, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 21 And 49
Mar 23, 2025
-
A Polynomial With Only One Term
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Purpose Of Commutator . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
