What Is The Prime Factorization Of 400
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
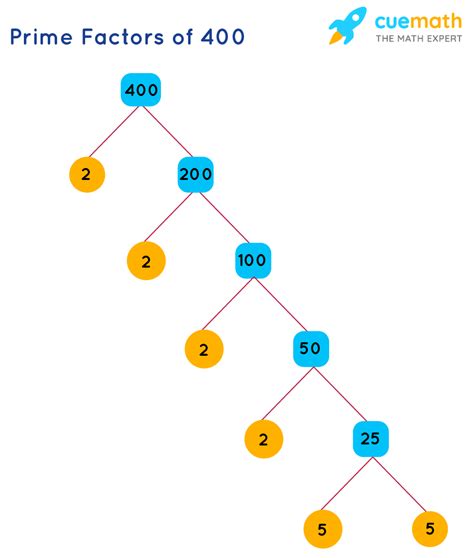
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 400? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 400?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself might be quickly obtained, understanding the process and the underlying concepts of prime numbers and factorization provides a solid foundation for more complex mathematical explorations. This article will not only provide the answer but delve deep into the "why" and "how," exploring related concepts and showcasing the practical applications of prime factorization.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 400, let's establish a clear understanding of what prime numbers are. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The sequence of prime numbers is infinite, a fact that has captivated mathematicians for centuries.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Uniqueness: Each prime number is unique and distinct from all others.
- Building Blocks: Prime numbers are considered the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers. This is the core concept behind prime factorization.
What is Factorization?
Factorization (or factoring) is the process of breaking down a composite number (a number greater than 1 that is not prime) into smaller numbers that when multiplied together, result in the original number. These smaller numbers are called factors. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Because 2 x 2 x 3 = 12, 2 and 3 are considered prime factors of 12.
Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The prime factorization of a number is the unique representation of that number as a product of its prime factors. This is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be expressed uniquely as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order of the factors). This theorem is fundamental to many areas of mathematics and has profound implications.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 400
Now, let's apply these concepts to find the prime factorization of 400. There are several methods to achieve this:
Method 1: Repeated Division
This is a straightforward method. We repeatedly divide 400 by the smallest prime number possible until we are left with 1.
- Divide by 2: 400 ÷ 2 = 200
- Divide by 2: 200 ÷ 2 = 100
- Divide by 2: 100 ÷ 2 = 50
- Divide by 2: 50 ÷ 2 = 25
- Divide by 5: 25 ÷ 5 = 5
- Divide by 5: 5 ÷ 5 = 1
Therefore, the prime factorization of 400 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 5 x 5, which can be written more concisely as 2⁴ x 5².
Method 2: Factor Tree
A factor tree is a visual representation of the factorization process. We start with 400 and branch out, repeatedly factoring until all branches end in prime numbers.
400
/ \
200 2
/ \
100 2
/ \
50 2
/ \
25 2
/ \
5 5
Again, this leads us to the prime factorization of 400 as 2⁴ x 5².
Why is Prime Factorization Important?
Understanding prime factorization is not just an academic exercise; it has significant practical applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Many modern encryption methods rely heavily on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The security of online transactions and sensitive data often depends on this.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers play a critical role in algorithm design and data structures. Prime factorization is used in hash table design and other computational techniques.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is a cornerstone of number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers. It's fundamental to understanding concepts like modular arithmetic and Diophantine equations.
-
Mathematics Education: Learning about prime factorization helps students develop their understanding of number systems, operations, and logical reasoning. It's a building block for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Beyond 400: Exploring Prime Factorization of Other Numbers
Let's briefly explore the prime factorization of a few other numbers to further solidify our understanding:
- 100: 2² x 5²
- 1000: 2³ x 5³
- 144: 2⁴ x 3²
- 2520: 2³ x 3² x 5 x 7
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The seemingly abstract concept of prime factorization finds its way into everyday applications, though often hidden beneath the surface. Consider these examples:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization helps in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms by identifying common factors in the numerator and denominator.
-
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) and Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): Understanding prime factorization is essential for efficiently calculating the LCM and GCD of numbers, which are crucial in solving various problems related to ratios, proportions, and scheduling tasks.
-
Coding and Algorithms: Efficient algorithms for finding prime factors are crucial in cryptography and other areas of computer science, impacting the speed and security of various digital systems.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those interested in delving deeper, here are some advanced concepts related to prime factorization:
-
The Riemann Hypothesis: This unsolved problem in mathematics concerns the distribution of prime numbers and is one of the most important open problems in mathematics.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm provides an efficient method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
-
Miller-Rabin Primality Test: This probabilistic algorithm efficiently checks whether a given number is prime or composite, crucial for cryptographic applications.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 400, while seemingly a simple calculation, represents a gateway to a vast and intricate world of mathematical exploration. Understanding prime numbers, factorization, and the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic provides a solid foundation for various applications in mathematics, computer science, and cryptography. The seemingly simple act of breaking down a number into its prime components reveals profound implications for our understanding of numbers and their properties. From secure online transactions to efficient algorithms, the significance of prime factorization extends far beyond the classroom, shaping the digital landscape and influencing our daily lives in countless ways.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Muscles Is Voluntary
Mar 25, 2025
-
How To Find The Experimental Probability
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Grooved Wheel With A Rope Running Along The Groove
Mar 25, 2025
-
Can An Even Number Be A Prime Number
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Are The Factors Of 112
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 400 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
