What Are The Factors Of 112
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
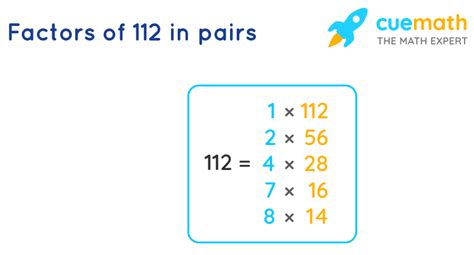
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 112? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization and Divisibility
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the process unlocks a deeper understanding of number theory and its applications. This article delves into the fascinating world of factors, focusing specifically on the number 112. We'll explore different methods to find its factors, discuss prime factorization, and touch upon related mathematical concepts. By the end, you'll not only know all the factors of 112 but also grasp the underlying principles that govern this fundamental area of mathematics.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we jump into finding the factors of 112, let's establish a clear definition. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. In simpler terms, if you can divide a number by another number without getting a fraction or decimal, the second number is a factor of the first. Divisibility is the property of a number being perfectly divisible by another number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Method 1: Finding Factors of 112 through Systematic Division
The most straightforward method to find the factors of 112 is through systematic division. We start by checking each whole number, starting from 1, to see if it divides 112 evenly.
- 1: 112 divided by 1 is 112. Therefore, 1 and 112 are factors.
- 2: 112 divided by 2 is 56. Therefore, 2 and 56 are factors.
- 4: 112 divided by 4 is 28. Therefore, 4 and 28 are factors.
- 7: 112 divided by 7 is 16. Therefore, 7 and 16 are factors.
- 8: 112 divided by 8 is 14. Therefore, 8 and 14 are factors.
Notice that as we continue to divide, we'll eventually reach numbers we've already encountered. This indicates we've found all the factors.
Therefore, the factors of 112 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 16, 28, 56, and 112.
Method 2: Prime Factorization – A More Elegant Approach
While the systematic division method works, prime factorization offers a more efficient and insightful approach, particularly for larger numbers. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.).
Let's find the prime factorization of 112:
- Start by dividing 112 by the smallest prime number, 2: 112 ÷ 2 = 56
- Divide 56 by 2: 56 ÷ 2 = 28
- Divide 28 by 2: 28 ÷ 2 = 14
- Divide 14 by 2: 14 ÷ 2 = 7
- 7 is a prime number, so we stop here.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 112 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 7, or 2<sup>4</sup> x 7.
From Prime Factorization to All Factors
Once we have the prime factorization, finding all factors becomes significantly easier. We can systematically combine the prime factors to generate all possible factors.
Considering the prime factorization 2<sup>4</sup> x 7:
- Using only powers of 2: 2<sup>0</sup> = 1, 2<sup>1</sup> = 2, 2<sup>2</sup> = 4, 2<sup>3</sup> = 8, 2<sup>4</sup> = 16
- Combining powers of 2 with 7: 1 x 7 = 7, 2 x 7 = 14, 4 x 7 = 28, 8 x 7 = 56, 16 x 7 = 112
This method confirms that the factors of 112 are indeed 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 16, 28, 56, and 112.
Understanding the Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number is fundamental in various mathematical applications:
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): Finding the GCD of two or more numbers involves comparing their prime factorizations. The GCD is the product of the common prime factors raised to their lowest power.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): Similarly, finding the LCM involves comparing prime factorizations. The LCM is the product of all prime factors raised to their highest power.
- Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization helps in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms by canceling out common factors in the numerator and denominator.
- Cryptography: Prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors forms the basis of the security of these systems.
Beyond the Factors: Exploring Divisibility Rules
Knowing the factors of 112 also allows us to understand its divisibility properties. Divisibility rules are shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by another number without performing the actual division. Some relevant divisibility rules include:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, or 8). 112 is divisible by 2 because its last digit is 2.
- Divisibility by 4: A number is divisible by 4 if its last two digits are divisible by 4. The last two digits of 112 are 12, which is divisible by 4.
- Divisibility by 7: There isn't a simple divisibility rule for 7, but we know from our factorization that 112 is divisible by 7.
- Divisibility by 8: A number is divisible by 8 if its last three digits are divisible by 8. The last three digits of 112 are 112, which is divisible by 8 (112 ÷ 8 = 14).
Applications of Factorization in Real-World Scenarios
While seemingly abstract, understanding factors and factorization has practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
- Geometry: When dealing with area and volume calculations, determining factors can be useful in finding dimensions of shapes with specific areas or volumes. For example, if you have a rectangular area of 112 square units, you can find possible dimensions by using its factors (e.g., 14 units by 8 units).
- Resource Allocation: Dividing resources equitably often requires finding factors. If you have 112 items to distribute equally among groups, the factors of 112 determine the possible number of groups and the number of items per group.
- Project Management: Breaking down large projects into smaller, manageable tasks involves using factorization principles.
Conclusion: Factors of 112 and Beyond
This in-depth exploration of the factors of 112 has illuminated not just the specific factors (1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 16, 28, 56, and 112) but also the broader mathematical concepts underlying the process. Prime factorization, in particular, stands out as a powerful tool with far-reaching implications in various fields. By understanding these principles, we gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and interconnectedness of mathematics and its practical relevance in our daily lives. From simple arithmetic to complex algorithms, the concept of factors remains a cornerstone of mathematical understanding. The next time you encounter a number, consider its factors – you might be surprised by the insights you uncover.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Glass A Good Insulator Of Electricity
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is The Number 7 A Prime Number
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Demand Curve Faced By A Monopoly Is
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is 6 A Multiple Of 3
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is Lcm Of 9 And 12
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 112 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
