What Is The Prime Factorization Of 13
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
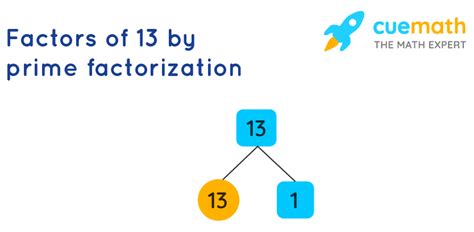
Table of Contents
- What Is The Prime Factorization Of 13
- Table of Contents
- What is the Prime Factorization of 13? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
- Understanding Prime Numbers
- What is Factorization?
- The Prime Factorization of 13
- Beyond 13: Exploring Prime Factorization Techniques
- 1. Trial Division
- 2. Factorization Algorithms for Larger Numbers
- The Significance of Prime Factorization
- 1. Cryptography
- 2. Computer Science
- 3. Number Theory
- Conclusion: The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is the Prime Factorization of 13? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The question, "What is the prime factorization of 13?" might seem deceptively simple. However, understanding the answer requires a solid grasp of fundamental number theory concepts, specifically prime numbers and factorization. This article will not only answer the question directly but delve into the broader context of prime factorization, exploring its significance in mathematics and computer science.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 13, let's define the core concept: prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible without a remainder by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, and so on. Notice that 2 is the only even prime number, as all other even numbers are divisible by 2.
Key Characteristics of Prime Numbers:
- Divisibility: A prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This is a fundamental theorem in number theory, proven by Euclid centuries ago.
- Unique Factorization: Every integer greater than 1 can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers (ignoring the order). This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
What is Factorization?
Factorization is the process of breaking down a composite number (a number that is not prime) into its prime factors. This means expressing the number as a product of prime numbers. For example, the factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3, or 2² x 3. Each of these factors (2 and 3) is a prime number.
The Prime Factorization of 13
Now, let's return to our original question: What is the prime factorization of 13?
The answer is straightforward: 13.
Why? Because 13 is itself a prime number. It fulfills the definition: it's a natural number greater than 1, and its only divisors are 1 and 13. Therefore, its prime factorization is simply the number itself. There's no further decomposition into smaller prime factors possible.
Beyond 13: Exploring Prime Factorization Techniques
While the prime factorization of 13 is trivial, understanding the methods for factoring larger numbers is crucial. Several techniques exist, ranging from simple trial division to sophisticated algorithms used in cryptography:
1. Trial Division
This is the most basic method. You systematically test for divisibility by prime numbers, starting with the smallest prime number, 2. If a prime number divides the number evenly, you record it as a factor and repeat the process with the resulting quotient until you're left with 1.
Example: Let's find the prime factorization of 36:
- Divide 36 by 2: 36 = 2 x 18
- Divide 18 by 2: 18 = 2 x 9
- Divide 9 by 3: 9 = 3 x 3
- Therefore, the prime factorization of 36 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 3, or 2² x 3².
Trial division is straightforward for small numbers but becomes computationally expensive for very large numbers.
2. Factorization Algorithms for Larger Numbers
For larger numbers, more advanced algorithms are necessary. These algorithms are crucial in cryptography, where the difficulty of factoring large numbers is the basis of many encryption systems. Some notable algorithms include:
- Pollard's rho algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm that is relatively efficient for finding small prime factors.
- Quadratic sieve: A deterministic algorithm that is more efficient than trial division for larger numbers.
- General number field sieve (GNFS): The most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers. It's used to break RSA encryption with extremely large keys.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization might seem like a purely mathematical exercise, but it has profound implications in various fields:
1. Cryptography
As mentioned earlier, the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors is the cornerstone of many widely used encryption systems, including RSA. The security of these systems relies on the fact that it's computationally infeasible to factor extremely large numbers (hundreds or thousands of digits) within a reasonable timeframe using currently available algorithms.
2. Computer Science
Prime numbers and factorization algorithms play a significant role in computer science, particularly in:
- Hashing: Prime numbers are often used in hashing algorithms to minimize collisions and improve efficiency.
- Random Number Generation: Prime numbers are essential in generating pseudo-random numbers, which are widely used in simulations, cryptography, and other applications.
3. Number Theory
Prime factorization is fundamental to number theory, forming the basis for many theorems and conjectures. The distribution of prime numbers, their properties, and their relationships with other numbers are areas of ongoing research and exploration. The Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics, is directly related to the distribution of prime numbers.
Conclusion: The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 13, while simple, underscores a fundamental truth in mathematics: every integer greater than 1 can be expressed uniquely as a product of prime numbers. This unique factorization theorem forms the basis of numerous mathematical concepts and has far-reaching applications in various fields. While finding the prime factors of small numbers is straightforward, the challenge of factoring large numbers has significant implications for cryptography and computer science, ensuring the ongoing study and refinement of efficient factorization algorithms. The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 13?" thus serves as a gateway to a rich and fascinating area of mathematics with profound practical relevance. Understanding prime numbers and factorization is crucial for anyone interested in mathematics, computer science, or cryptography.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Every Square Is A Rectangle
Mar 21, 2025
-
Fourth Period Of The Periodic Table
Mar 21, 2025
-
Common Multiple Of 11 And 15
Mar 21, 2025
-
Daughter Cells Produced In Meiosis Are Identical
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Organelle Is Enclosed By A Double Membrane
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 13 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
