Common Multiple Of 11 And 15
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
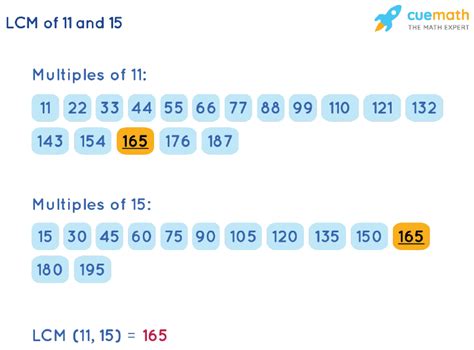
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of the Least Common Multiple of 11 and 15: A Deep Dive
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and exploring different methods unlocks a deeper appreciation of number theory. This article delves into the fascinating world of LCMs, focusing specifically on the LCM of 11 and 15. We'll explore various approaches, examining their efficiency and providing a comprehensive understanding of the process. This exploration will go beyond a simple calculation, connecting it to broader mathematical concepts and showcasing its practical applications.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the LCM of 11 and 15, let's solidify our understanding of what an LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors.
For instance, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18...
The common multiples are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The least common multiple is 6.
Prime Factorization: The Foundation of LCM Calculation
Prime factorization is a crucial technique for finding the LCM of any two numbers, including 11 and 15. It involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors – numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves.
Let's break down 11 and 15:
- 11: 11 is a prime number itself. Its prime factorization is simply 11.
- 15: 15 can be factored as 3 x 5. Both 3 and 5 are prime numbers.
Now that we have the prime factorizations, we can proceed to calculate the LCM using the prime factorization method.
Calculating the LCM of 11 and 15 using Prime Factorization
The prime factorization method involves comparing the prime factors of the numbers. We select the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization and multiply them together.
In our case:
- The prime factors of 11 are just 11 (to the power of 1).
- The prime factors of 15 are 3 and 5 (both to the power of 1).
Therefore, the LCM(11, 15) = 11 x 3 x 5 = 165.
Therefore, the least common multiple of 11 and 15 is 165.
Alternative Methods for Finding the LCM
While prime factorization is a robust and fundamental method, other techniques can be employed to calculate the LCM, particularly for smaller numbers.
The Listing Method: A Simple Approach (But Less Efficient)
This method involves listing out the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. While straightforward for smaller numbers, it becomes increasingly inefficient as the numbers get larger.
For 11 and 15:
- Multiples of 11: 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 110, 121, 132, 143, 154, 165...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165...
The smallest common multiple is 165.
Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): A More Advanced Approach
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) of two numbers are related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers themselves. This relationship provides an alternative way to calculate the LCM.
First, we need to find the GCD of 11 and 15. Since 11 is a prime number and 15 is not divisible by 11, the GCD(11, 15) = 1.
Then, we can use the formula:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
Substituting the values:
LCM(11, 15) = (11 x 15) / 1 = 165
This method confirms our previous result.
Real-World Applications of LCM
Understanding LCMs isn't just an academic exercise; it has practical applications in various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses departing from the same station, one every 11 minutes and the other every 15 minutes. The LCM (165 minutes) represents the time when both buses will depart simultaneously again.
-
Fractions: Finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions. This ensures a common denominator for easy calculation.
-
Project Management: In project management, determining the LCM of different task durations can help in scheduling and resource allocation.
Beyond the Basics: Extending the Concept
The concept of LCM extends beyond two numbers. We can calculate the LCM of three or more numbers using similar principles. The prime factorization method remains a powerful tool for finding the LCM of any number of integers.
For example, to find the LCM of 11, 15, and 7:
- Prime factorization of 11: 11
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
- Prime factorization of 7: 7
LCM(11, 15, 7) = 11 x 3 x 5 x 7 = 1155
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM of 11 and 15 and Beyond
This in-depth exploration of the LCM of 11 and 15 highlights the importance of understanding fundamental mathematical concepts. We've explored different methods for calculating the LCM, emphasizing the efficiency and versatility of the prime factorization method. Furthermore, we’ve showcased the practical applications of LCMs in various real-world scenarios. By mastering these concepts, you equip yourself with valuable tools applicable in numerous fields, extending far beyond simple arithmetic. Remember, the journey of learning mathematics is an ongoing process of discovery and application, and understanding the LCM is a significant step in that journey. The seemingly simple question of "What is the LCM of 11 and 15?" opens a door to a rich tapestry of mathematical ideas and practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Baking Soda The Same As Sodium Carbonate
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is 70 A Prime Or Composite Number
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Does Not Dissolve In Water
Mar 22, 2025
-
Based On The Law Of Conservation Of Energy
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is Electric Field A Vector Quantity
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Multiple Of 11 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
