What Is The Prime Factorization 24
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
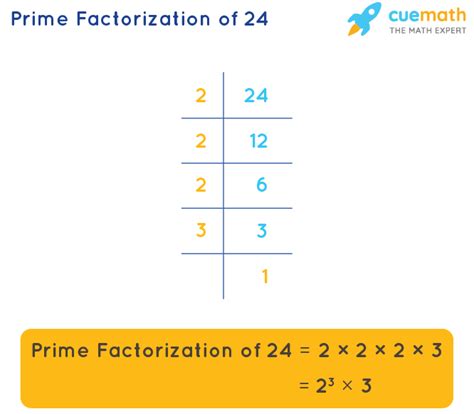
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 24? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 24?" opens the door to a fascinating exploration of fundamental concepts in mathematics: prime numbers and factorization. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the underlying principles provides a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. This article will not only answer the question but will also delve into the theoretical underpinnings, providing a comprehensive understanding of prime factorization and its applications.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before diving into the prime factorization of 24, let's define the key term: prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In simpler terms, a prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself.
Some examples of prime numbers include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number. The sequence of prime numbers is infinite, a fact proven by Euclid centuries ago. The distribution of prime numbers is a subject of ongoing research in number theory, with many unsolved mysteries remaining.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Uniqueness: Each prime number is unique and cannot be expressed as a product of smaller numbers.
- Building Blocks: Prime numbers are considered the fundamental building blocks of all other natural numbers.
Factorization: Breaking Down Numbers
Factorization is the process of breaking down a composite number (a number that is not prime) into its prime number components. Every composite number can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers. This unique representation is called the prime factorization of the number.
For example, let's consider the number 12. We can factorize 12 as follows:
- 12 = 2 x 6
- 12 = 2 x 2 x 3
Notice that we've broken down 12 into its prime factors: 2 and 3. The prime factorization of 12 is therefore 2² x 3.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 24
Now, let's address the central question: What is the prime factorization of 24?
We can approach this using different methods:
Method 1: Repeated Division
We can repeatedly divide 24 by the smallest prime number possible until we reach 1.
- Divide by 2: 24 ÷ 2 = 12
- Divide by 2 again: 12 ÷ 2 = 6
- Divide by 2 again: 6 ÷ 2 = 3
- Divide by 3: 3 ÷ 3 = 1
We are left with only prime numbers: 2, 2, 2, and 3. Therefore, the prime factorization of 24 is 2³ x 3.
Method 2: Factor Tree
A factor tree is a visual representation of the factorization process.
24
/ \
2 12
/ \
2 6
/ \
2 3
Following the branches down, we arrive at the prime factors 2, 2, 2, and 3. Again, this gives us the prime factorization of 24 as 2³ x 3.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The fact that every composite number has a unique prime factorization is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This theorem is a cornerstone of number theory and has significant implications in various mathematical fields. Its uniqueness ensures that there's only one correct prime factorization for any given number. This consistency is crucial for many mathematical operations and proofs.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization might seem like a purely theoretical concept, but it has many practical applications:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are fundamental to many modern encryption techniques, such as RSA cryptography, which is widely used to secure online transactions. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components forms the basis of the security of these systems.
-
Computer Science: Prime factorization plays a role in algorithms related to efficient computation and data structures.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is a cornerstone of many areas of number theory, including the study of modular arithmetic, Diophantine equations, and the Riemann Hypothesis.
-
Coding Theory: Error detection and correction codes often utilize properties of prime numbers and factorization.
Beyond 24: Practicing Prime Factorization
Understanding the prime factorization of 24 provides a solid foundation for tackling larger numbers. Let's try a few more examples to solidify our understanding:
Example 1: Prime Factorization of 36
Following the same methods, we can find the prime factorization of 36:
36 = 2 x 18 = 2 x 2 x 9 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2² x 3²
Example 2: Prime Factorization of 100
100 = 2 x 50 = 2 x 2 x 25 = 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 = 2² x 5²
Example 3: Prime Factorization of 1000
1000 = 10 x 100 = 2 x 5 x 2 x 5 x 10 = 2 x 5 x 2 x 5 x 2 x 5 = 2³ x 5³
Conclusion: The Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple question of finding the prime factorization of 24 leads to a deeper appreciation for prime numbers and their fundamental role in mathematics. Understanding prime factorization isn't just about performing calculations; it's about grasping the underlying structure of numbers and appreciating their importance in various fields, from cryptography to computer science and beyond. The ability to efficiently find the prime factorization of a number is a valuable skill with significant applications in a variety of areas. Mastering this concept lays the groundwork for further exploration in the fascinating world of number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Melting Of Wax A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Is Carbon Tetrachloride Ionic Or Covalent
Mar 16, 2025
-
Write The Formula For Sulfurous Acid
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Raw Materials Required For Photosynthesis
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization 24 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
