What Is The Name Of The Covalent Compound Ncl3
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
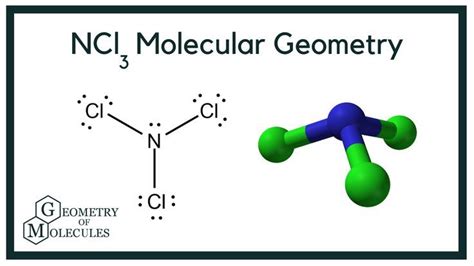
Table of Contents
What is the Name of the Covalent Compound NCl3?
Nitrogen trichloride. That's the simple answer. But understanding the naming convention, the properties, and the fascinating chemistry behind this covalent compound requires a deeper dive. This article will explore everything you need to know about NCl3, from its basic nomenclature to its synthesis, properties, and dangers.
Understanding Covalent Compounds and Nomenclature
Before diving into the specifics of NCl3, let's establish a foundational understanding of covalent compounds and their naming conventions. Covalent compounds are formed when two or more non-metal atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Unlike ionic compounds, which involve the transfer of electrons, covalent compounds share electrons, forming covalent bonds.
The naming of covalent compounds follows a set of specific rules:
-
The element furthest to the left on the periodic table is named first. In cases where both elements are in the same group, the element lower down is named first.
-
The name of the second element is modified to end in "-ide."
-
Greek prefixes (mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-, hepta-, octa-, nona-, deca-) are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule. The prefix "mono-" is often omitted for the first element unless necessary to distinguish between different compounds.
Decoding the Name: Nitrogen Trichloride
Now, let's apply these rules to NCl3.
- Nitrogen (N) is to the left of Chlorine (Cl) on the periodic table. Therefore, it's named first.
- Chlorine (Cl) is modified to become "chloride".
- There is one nitrogen atom, so we omit the prefix "mono-".
- There are three chlorine atoms, so we use the prefix "tri-".
Combining these components, we get the name Nitrogen Trichloride.
Properties of Nitrogen Trichloride (NCl3)
Nitrogen trichloride is a volatile, oily, and highly reactive compound. It's characterized by several key properties:
- Appearance: It's a pale yellow liquid.
- Odor: It has a pungent, irritating odor, often described as similar to bleach or chloramine.
- Density: Less dense than water.
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, but readily soluble in non-polar solvents.
- Boiling Point: Relatively low boiling point, making it easily vaporized.
- Reactivity: Extremely reactive and unstable. It is highly sensitive to shock and light, prone to explosive decomposition.
Chemical Properties and Reactions:
NCl3 exhibits several crucial chemical properties:
- Hydrolysis: Reacts readily with water, producing toxic ammonia (NH3) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl). This reaction is exothermic.
- Decomposition: It can spontaneously decompose explosively, especially when exposed to light, heat, or shock. This decomposition produces nitrogen gas (N2) and chlorine gas (Cl2), both hazardous substances.
- Reactions with Reducing Agents: It acts as a strong oxidizing agent, readily reacting with reducing agents.
- Reactions with Metals: It can react with certain metals, producing metal chlorides and nitrogen gas.
Synthesis of Nitrogen Trichloride
The synthesis of NCl3 involves a carefully controlled reaction to avoid unwanted explosions. Typically, it is prepared by the reaction of chlorine gas with ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) or an ammonium salt in an acidic medium. The reaction is complex and needs to be carefully monitored and conducted in a controlled environment with appropriate safety measures. Note that the detailed procedures are highly specialized and should only be performed by trained chemists with proper safety equipment and protocols.
Dangers and Safety Precautions
Nitrogen trichloride is an extremely hazardous substance. Its volatile nature, explosive decomposition potential, and production of toxic byproducts necessitate stringent safety precautions:
- Explosion Hazard: The primary danger is its inherent instability and propensity for explosive decomposition. Even minor shocks or exposure to light can trigger an explosion.
- Toxicity: The compound itself is toxic, and its decomposition products (chlorine gas and ammonia) are also highly toxic and corrosive.
- Exposure Risks: Inhalation of NCl3 vapor or exposure to its decomposition products can cause severe respiratory irritation, lung damage, and even death. Skin contact can result in burns and irritation.
Handling NCl3 requires specialized training and expertise. It should only be handled in a well-ventilated fume hood, under controlled conditions, and with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, eye protection, and respiratory protection. Never attempt to synthesize or handle NCl3 without the proper training and safety precautions.
Applications (Limited Due to its Instability)
Despite its inherent dangers, NCl3 has found extremely limited applications. Its instability largely restricts its use. In the past, it has been explored for its bleaching properties, but its extreme reactivity and danger outweigh any potential benefits.
Comparison with Other Nitrogen Halides
Nitrogen forms a series of halides, including NF3, NBr3, and NI3. While they share some similarities, they differ significantly in their stability and properties. NCl3 is notably less stable than NF3, which is relatively inert. NBr3 and NI3 are even less stable than NCl3, exhibiting even greater explosive tendencies.
Ecological Considerations
The highly reactive nature of NCl3 means it's unlikely to persist in the environment for an extended period. Its decomposition products, however, (chlorine and ammonia) are significant environmental pollutants, potentially impacting water quality and air quality. Therefore, it is crucial to prevent its release into the environment.
Conclusion: Respecting the Power of Nitrogen Trichloride
Nitrogen trichloride (NCl3), while simply named, is a compound of considerable complexity and danger. Its volatile nature and explosive tendencies necessitate extreme caution. Understanding its properties, synthesis, and associated risks is crucial for anyone working with or studying this fascinating, yet formidable, chemical compound. The name "Nitrogen Trichloride" itself simply reflects the composition; it doesn't encapsulate the potential hazard it presents. This underscores the importance of proper training, safety protocols, and respect for the inherent dangers of working with reactive chemicals. Always prioritize safety when dealing with any chemical, particularly highly reactive ones like NCl3. Remember, knowledge and caution are the best defenses against the risks associated with this compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Circuit Diagram Full Wave Center Tap Rectifier Unregulated
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 6
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 18 And 24
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Normative Statement
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 5
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Name Of The Covalent Compound Ncl3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
