Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 6
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
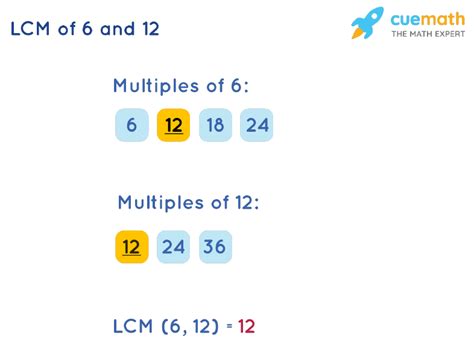
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 12 and 6: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The concept of the Least Common Multiple (LCM) is a fundamental cornerstone in number theory, with wide-ranging applications in various fields, from scheduling problems to simplifying fractions. Understanding LCMs is crucial for anyone venturing into the world of mathematics, and this comprehensive guide will explore the LCM of 12 and 6 in detail, providing a solid foundation for grasping more complex scenarios.
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
Before delving into the specific LCM of 12 and 6, let's establish a clear understanding of what an LCM represents. The Least Common Multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that can be divided evenly by all the numbers in the set without leaving a remainder.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, hence the LCM(2,3) = 6.
Finding the LCM of 12 and 6: Three Proven Methods
There are several efficient methods for determining the LCM of two numbers, and we'll explore three commonly used techniques to calculate the LCM(12, 6):
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This method, while straightforward, can become cumbersome for larger numbers. It involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found.
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72...
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple is 12. Therefore, LCM(12, 6) = 12.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method offers a more elegant and efficient solution, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization and multiply them together:
LCM(12, 6) = 2² x 3 = 4 x 3 = 12
This method is particularly useful for understanding the fundamental structure of numbers and their relationships.
Method 3: Using the Formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
This method utilizes the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of the two numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. We can find the GCD using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization.
-
Finding the GCD of 12 and 6 using prime factorization:
- 12 = 2² x 3
- 6 = 2 x 3
- The common prime factors are 2 and 3. The lowest power of 2 is 2¹, and the lowest power of 3 is 3¹. Therefore, GCD(12, 6) = 2 x 3 = 6.
-
Applying the formula:
- LCM(12, 6) = (|12 x 6|) / GCD(12, 6) = 72 / 6 = 12
This formula provides a concise and powerful way to calculate the LCM, especially when dealing with larger numbers where listing multiples becomes impractical.
Understanding the Relationship Between LCM and GCD
The relationship between the LCM and GCD is fundamental in number theory. The formula LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b) highlights this intrinsic connection. Understanding this relationship allows for a deeper appreciation of the structure and properties of integers. It emphasizes that the LCM and GCD are not independent entities but are intimately linked through the product of the two numbers.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of the Least Common Multiple extends far beyond abstract mathematical exercises. It finds practical applications in numerous real-world scenarios:
1. Scheduling Problems:
Imagine two buses arrive at a bus stop at different intervals. One bus arrives every 12 minutes, and the other every 6 minutes. To determine when both buses will arrive simultaneously, you need to find the LCM(12, 6). As we've established, the LCM is 12. Therefore, both buses will arrive together every 12 minutes.
2. Fraction Simplification:
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is essential for finding a common denominator. This simplifies the process and allows for accurate calculations.
3. Gear Ratios and Rotational Mechanics:
In mechanical engineering, LCM is crucial in calculating gear ratios and determining when different gears will align perfectly.
4. Cyclic Processes and Synchronization:
Many processes in nature and engineering are cyclical. Finding the LCM helps determine when these cycles will synchronize or coincide.
5. Music Theory and Harmonies:
LCM plays a role in music theory, especially in determining harmonic intervals and when different musical phrases will align rhythmically.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method remains particularly efficient. For example, to find the LCM(12, 6, 18):
-
Prime factorization:
- 12 = 2² x 3
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 18 = 2 x 3²
-
LCM(12, 6, 18) = 2² x 3² = 4 x 9 = 36
The formula LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b) is not directly applicable to more than two numbers, but the prime factorization method provides a general and effective approach.
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM
Understanding the Least Common Multiple is essential for anyone working with numbers and their relationships. Whether you're tackling mathematical problems, solving real-world scheduling dilemmas, or simplifying fractions, the LCM provides a powerful tool for efficient and accurate calculations. By mastering the various methods for finding the LCM, you equip yourself with a valuable skillset applicable across diverse fields. The detailed explanation and examples provided in this guide should provide a strong foundation for further exploration of number theory and its applications. Remember, the LCM is not just an abstract concept; it's a practical tool that helps us understand and navigate the numerical world around us. The simple case of finding the LCM of 12 and 6, as explored in detail here, provides a stepping stone to understanding more complex LCM calculations and their wide-ranging applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Eigenvectors Of A 3x3 Matrix
Mar 20, 2025
-
Describing Words That Start With D
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Gas Is Most Abundant In Earths Atmosphere
Mar 20, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Starting With T H O
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Elbow Is An Example Of What Type Of Joint
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
