What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 3 4 5
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
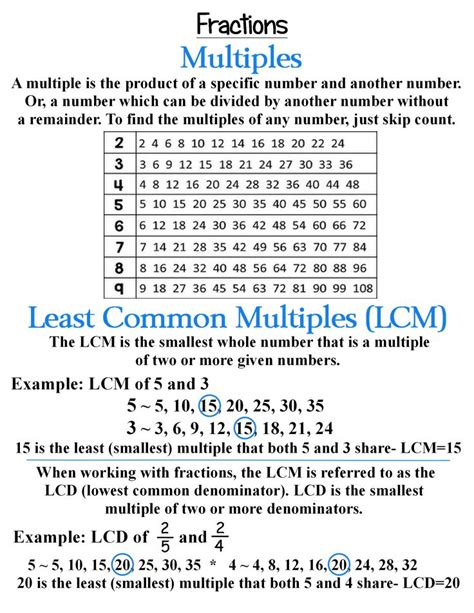
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 3, 4, and 5? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, but understanding the underlying concepts unlocks a world of mathematical elegance and practical applications. This article will delve deep into determining the LCM of 3, 4, and 5, exploring various methods, explaining the theoretical underpinnings, and showcasing the significance of LCM in diverse fields.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors. This concept is fundamental in mathematics, appearing in various areas, from simplifying fractions to solving complex scheduling problems.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 3, 4, and 5
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM, each offering a unique perspective and level of computational complexity. Let's explore the most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This straightforward method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 51, 54, 57, 60...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60...
By inspecting the lists, we observe that the smallest number appearing in all three lists is 60. Therefore, the LCM of 3, 4, and 5 is 60. While this method is intuitive for small numbers, it becomes cumbersome and inefficient for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method leverages the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers. The steps are as follows:
-
Find the prime factorization of each number:
- 3 = 3
- 4 = 2 x 2 = 2²
- 5 = 5
-
Identify the highest power of each prime factor:
- The prime factors are 2, 3, and 5.
- The highest power of 2 is 2².
- The highest power of 3 is 3.
- The highest power of 5 is 5.
-
Multiply the highest powers together:
- LCM(3, 4, 5) = 2² x 3 x 5 = 4 x 3 x 5 = 60
This method is significantly more efficient than listing multiples, particularly when dealing with larger numbers. It provides a systematic approach that avoids the potential for overlooking common multiples.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) are intimately related. The relationship is expressed by the formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
While this formula is generally used for two numbers, it can be extended to multiple numbers using iterative application. First, find the LCM of two numbers, then find the LCM of that result and the third number, and so on. However, for finding the LCM of 3, 4, and 5, the prime factorization method is more straightforward.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. Its applications are diverse and impactful:
1. Fraction Simplification
Finding the LCM of denominators is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions. By converting fractions to a common denominator (the LCM), we can easily perform arithmetic operations.
2. Scheduling Problems
LCM plays a vital role in solving scheduling problems. For instance, if three buses depart from a station at intervals of 3, 4, and 5 hours respectively, the LCM determines when they will all depart at the same time again. In this case, the buses will depart simultaneously every 60 hours.
3. Cyclic Processes
Many real-world phenomena exhibit cyclical behavior. Understanding the LCM allows us to predict when these cycles will align. This has applications in various fields, including engineering, astronomy, and even music.
4. Modular Arithmetic
LCM is fundamental in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with applications in cryptography and computer science. It helps in determining the periodicity of sequences and solving congruence equations.
5. Number Theory Research
The LCM is a cornerstone in advanced number theory research, influencing the study of prime numbers, divisibility, and other fascinating properties of integers.
Expanding on the Concept: LCM of Larger Sets of Numbers
While we've focused on the LCM of 3, 4, and 5, the methods discussed can be extended to calculate the LCM of any set of integers. The prime factorization method remains particularly efficient, even for larger sets. For example, to find the LCM of 6, 8, 10, and 12:
-
Prime factorization:
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 8 = 2³
- 10 = 2 x 5
- 12 = 2² x 3
-
Highest powers:
- 2³
- 3
- 5
-
Multiplication:
- LCM(6, 8, 10, 12) = 2³ x 3 x 5 = 8 x 3 x 5 = 120
Conclusion: The Significance of the LCM
The seemingly simple problem of finding the LCM of 3, 4, and 5 reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From basic arithmetic to advanced number theory and real-world scheduling problems, the LCM plays a vital, albeit often unseen, role. Understanding this fundamental concept empowers us to tackle more complex mathematical challenges and appreciate the interconnectedness of various branches of mathematics. The ability to efficiently compute the LCM, particularly through the prime factorization method, is a valuable tool for anyone working with numbers, highlighting the importance of mastering fundamental mathematical principles. The LCM isn't merely a number; it's a key that unlocks deeper understanding and problem-solving capabilities across various domains.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write 30 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Boiling Point For Kelvin
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 12
Mar 17, 2025
-
Plants That Make Their Own Food Are Called
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 11 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 3 4 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
