What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
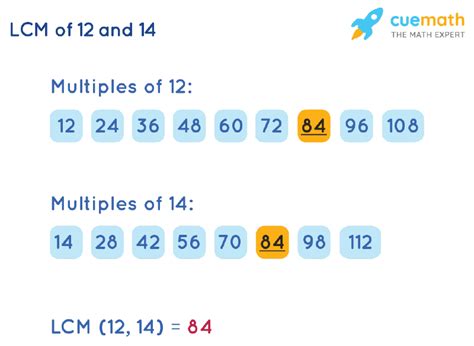
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 14 and 12? A Deep Dive into Finding LCMs
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and different methods for calculating it can significantly enhance your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of determining the LCM of 14 and 12, exploring various techniques and their applications. We'll move beyond a simple answer to fully grasp the why behind the calculation.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 14 and 12, let's establish a solid understanding of what LCM actually represents. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving any remainder. It's a fundamental concept used extensively in various mathematical fields and real-world applications, from scheduling tasks to simplifying fractions.
Key Differences Between LCM and GCD
It's crucial to distinguish LCM from the greatest common divisor (GCD). While LCM finds the smallest common multiple, GCD identifies the largest number that divides both integers without leaving a remainder. These two concepts are inversely related; understanding one clarifies the other. For instance, the GCD of 14 and 12 is 2, while, as we will see, their LCM is significantly larger.
Methods for Calculating LCM
Several effective methods exist to calculate the LCM of two or more numbers. Let's explore the most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 14: 14, 28, 42, 56, 70, 84, 98, 112, 126, 140...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120, 132, 144...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple is 84. This method is simple but becomes inefficient for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 7: 7¹ = 7
Now, multiply these highest powers together: 4 x 3 x 7 = 84
This method is far more efficient than listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers or multiple numbers.
3. Formula Using GCD
The LCM and GCD of two numbers are related through a simple formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
Where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers.
Since we already know that the GCD of 14 and 12 is 2, we can use this formula:
LCM(14, 12) x 2 = 14 x 12 LCM(14, 12) = (14 x 12) / 2 = 168 / 2 = 84
This method is efficient if you've already calculated the GCD. Finding the GCD can be done using the Euclidean algorithm, which is particularly efficient for larger numbers.
Applications of LCM
Understanding and applying LCM extends far beyond the realm of abstract mathematics. Here are some real-world applications:
1. Scheduling and Timing
Imagine you have two machines that complete cycles every 14 and 12 minutes respectively. To find out when both machines will complete a cycle simultaneously, you would calculate the LCM of 14 and 12. The LCM (84) represents the time interval (in minutes) after which both machines will be at the beginning of a cycle concurrently.
2. Fraction Operations
LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To find a common denominator, you need to find the LCM of the denominators.
For example, to add 1/14 and 1/12, the LCM (84) becomes the common denominator:
(6/84) + (7/84) = 13/84
3. Music and Rhythm
In music, LCM is used to determine the least common multiple of note durations to synchronize different rhythms. This is fundamental in understanding musical harmony and composition.
4. Gear Ratios and Mechanical Engineering
In mechanical systems, gear ratios often involve finding the least common multiple of gear teeth to determine synchronous rotation or to calculate the speed ratios between different components of a machine.
5. Project Management and Scheduling
LCM can be instrumental in planning and coordinating tasks with different timelines. Determining the earliest time when multiple projects can be completed simultaneously often involves finding their LCM.
Beyond the Basics: Extending the Concept of LCM
While we've focused on finding the LCM of two numbers, the concept extends to any number of integers. The principles remain the same: find the prime factorization of each number, and then build the LCM using the highest power of each prime factor present in any of the factorizations.
The prime factorization method provides a systematic and efficient approach, especially beneficial when dealing with a larger set of numbers. For instance, to find the LCM of 14, 12, and 21, we'd factorize each and find the highest power of 2, 3, and 7 respectively, then multiply them together.
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM
Finding the least common multiple of 14 and 12 is more than just an arithmetic exercise; it's a gateway to understanding fundamental mathematical concepts with wide-ranging applications. By mastering the different calculation methods, you equip yourself not only to solve problems efficiently but also to appreciate the underlying logic and the connections between seemingly disparate mathematical ideas. Whether you're working with fractions, coordinating schedules, or tackling complex engineering problems, the LCM is a powerful tool that enhances your problem-solving capabilities. Remember the various methods discussed – listing multiples, prime factorization, and utilizing the GCD relationship – to choose the most efficient approach depending on the numbers involved. This deep understanding ensures you are well-prepared to tackle a broad range of mathematical challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Difference Between A Mixture And A Solution
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Type Of Rock Can Contain Fossils
Mar 17, 2025
-
Write The Chemical Formula For Chloric Acid
Mar 17, 2025
-
5 Letter Words With O W
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Number Of Elements In A Set Is Called The
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
