What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 25 And 15
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
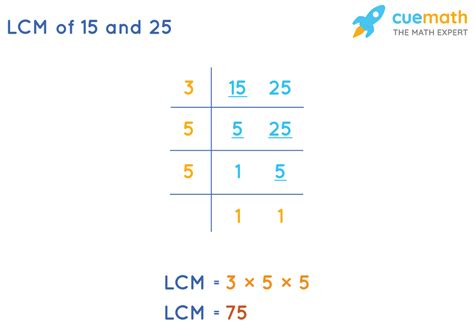
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 25 and 15? A Deep Dive into Finding the LCM
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple mathematical task, but understanding the underlying concepts and various methods for calculating it is crucial for a solid foundation in mathematics and its applications. This article will explore the LCM of 25 and 15 in detail, examining different approaches and highlighting the importance of LCM in various fields. We'll go beyond simply stating the answer and delve into the "why" and "how" behind the calculation, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for all readers.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we jump into calculating the LCM of 25 and 15, let's define what the LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the original numbers as factors.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
The LCM is a fundamental concept in mathematics with applications in various fields, including:
- Fractions: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions.
- Scheduling: Determining when events with different repeating cycles will occur simultaneously.
- Music: Understanding musical intervals and harmonies.
- Engineering: Solving problems related to gear ratios and cyclical processes.
Methods for Calculating the LCM
There are several methods to calculate the LCM, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. We will explore the most common ones, focusing on their application to find the LCM of 25 and 15.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. It is a straightforward approach, particularly useful for smaller numbers.
- Multiples of 25: 25, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 175...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105...
As we can see, the smallest common multiple in both lists is 75. Therefore, the LCM of 25 and 15 is 75.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the concept. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then building the LCM from the highest powers of each prime factor.
- Prime factorization of 25: 5 x 5 = 5²
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 5: 5² = 25
Therefore, the LCM of 25 and 15 is 3 x 25 = 75.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
This method uses the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The formula is:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
First, we need to find the GCD of 25 and 15. The GCD is the largest number that divides both 25 and 15 without leaving a remainder. We can use the Euclidean algorithm to find the GCD:
- Divide the larger number (25) by the smaller number (15): 25 ÷ 15 = 1 with a remainder of 10.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (15) and the smaller number with the remainder (10): 15 ÷ 10 = 1 with a remainder of 5.
- Repeat the process: 10 ÷ 5 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
The last non-zero remainder is the GCD, which is 5.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(25, 15) = (25 x 15) / 5 = 375 / 5 = 75
Why is Understanding LCM Important?
Understanding the LCM is crucial for several reasons:
Real-World Applications
The LCM has numerous real-world applications beyond the classroom. Consider these examples:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses arrive at a stop at different intervals. One bus arrives every 25 minutes, and the other every 15 minutes. The LCM (75 minutes) tells us how long it will take before both buses arrive at the stop simultaneously.
-
Construction: In construction projects, materials might be delivered at different intervals. Understanding the LCM can help optimize scheduling and resource allocation.
-
Manufacturing: Production lines often operate at different speeds. Knowing the LCM can help coordinate the processes and prevent bottlenecks.
Enhancing Mathematical Skills
Mastering the concept of LCM improves overall mathematical skills, particularly in areas such as:
-
Fraction Arithmetic: Finding a common denominator is essential for adding and subtracting fractions. The LCM provides the smallest common denominator, simplifying calculations.
-
Algebra: LCM plays a role in solving algebraic equations and simplifying expressions.
-
Number Theory: The LCM is a fundamental concept in number theory, which has broad applications in cryptography and computer science.
Improving Problem-Solving Abilities
The ability to calculate and apply LCM enhances problem-solving skills in various scenarios. It encourages systematic thinking, the ability to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps, and the application of appropriate mathematical tools to achieve a solution.
Conclusion: The LCM of 25 and 15 is 75
We've explored various methods to calculate the least common multiple of 25 and 15, consistently arriving at the answer: 75. This seemingly simple calculation underscores a fundamental concept with significant applications across diverse fields. Understanding the LCM enhances mathematical proficiency, fosters effective problem-solving abilities, and provides a valuable tool for tackling real-world challenges. This in-depth exploration goes beyond a simple numerical answer, providing a comprehensive understanding of the LCM's significance and practical implications. From scheduling to manufacturing, the LCM plays a vital role in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. By mastering this concept, you equip yourself with a powerful tool for both mathematical problem-solving and navigating the complexities of the real world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 25 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
