What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 16
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
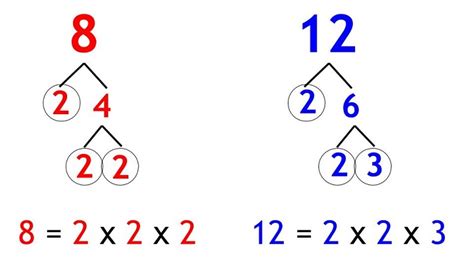
Table of Contents
- What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 16
- Table of Contents
- What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 12 and 16? A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- Methods for Calculating the LCM of 12 and 16
- 1. Listing Multiples Method
- 2. Prime Factorization Method
- 3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
- Applications of LCM: Real-World Examples
- LCM and its Relationship with GCD
- Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
- Conclusion: The Power of Understanding LCM
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 12 and 16? A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and different methods for calculation can be surprisingly beneficial in various mathematical fields and real-world applications. This in-depth guide will explore the LCM of 12 and 16, detailing multiple approaches, explaining the underlying principles, and highlighting the significance of LCM in broader mathematical contexts.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. It's a fundamental concept in number theory with practical applications in various areas, including:
-
Scheduling: Determining when events will occur simultaneously. For example, if two buses arrive at a stop every 12 and 16 minutes respectively, finding the LCM helps determine when they'll arrive together.
-
Fractions: Finding the least common denominator (LCD) when adding or subtracting fractions. The LCD is essentially the LCM of the denominators.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Used extensively in cryptography and computer science.
-
Music Theory: Determining the harmonic intervals between notes.
Methods for Calculating the LCM of 12 and 16
Several methods can be used to find the LCM of 12 and 16. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method is straightforward, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 96, 108, 120... Multiples of 16: 16, 32, 48, 64, 80, 96, 112, 128...
Observing the lists, we see that 48 and 96 are common multiples. The smallest common multiple is 48. Therefore, the LCM(12, 16) = 48. While simple for smaller numbers, this method becomes less efficient for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This is a more efficient and systematic method, particularly useful for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 16: 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2⁴
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2⁴ = 16
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
Therefore, LCM(12, 16) = 2⁴ x 3 = 16 x 3 = 48
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The formula connecting LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we need to find the GCD of 12 and 16. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide the larger number (16) by the smaller number (12): 16 ÷ 12 = 1 with a remainder of 4.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (12) and the smaller number with the remainder (4): 12 ÷ 4 = 3 with a remainder of 0.
- The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 4. Therefore, GCD(12, 16) = 4.
Now, using the formula:
LCM(12, 16) = (12 x 16) / GCD(12, 16) = (192) / 4 = 48
Applications of LCM: Real-World Examples
The concept of LCM isn't just confined to theoretical mathematics; it has many practical applications:
-
Scheduling Events: Imagine two trains departing from the same station, one every 12 minutes and the other every 16 minutes. To find when they depart simultaneously, you'd calculate the LCM(12, 16) = 48 minutes. They'll depart together every 48 minutes.
-
Production Planning: A factory produces two types of products, with production cycles of 12 and 16 hours respectively. The LCM helps determine when both production lines will complete a cycle at the same time, aiding in efficient resource allocation.
-
Music: The LCM is used in music theory to determine when different musical phrases or rhythms will align perfectly, creating harmonious sounds.
-
Calendars: Calculating when specific dates will coincide (e.g., determining when a specific day of the week will fall on a particular date).
-
Construction: In tasks like tiling or bricklaying, LCM helps determine the optimal size of tiles or bricks to avoid uneven patterns.
LCM and its Relationship with GCD
The greatest common divisor (GCD) and least common multiple (LCM) are intrinsically linked. As shown earlier, the product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers themselves. This relationship is crucial in simplifying calculations and solving problems involving both LCM and GCD. Understanding this interconnectedness provides a more holistic understanding of number theory.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, you would simply include all prime factors from all numbers, taking the highest power of each. For the GCD method, you would iteratively find the LCM of pairs of numbers.
Conclusion: The Power of Understanding LCM
Finding the least common multiple of 12 and 16, as demonstrated, is a seemingly simple task, but the underlying principles and the various methods for calculation are valuable tools in mathematics and numerous practical applications. Mastering LCM calculations strengthens fundamental mathematical skills and provides a framework for tackling more complex problems in diverse fields, from scheduling and production planning to music theory and beyond. By understanding the different methods and the relationship between LCM and GCD, one gains a powerful toolset for tackling various mathematical challenges effectively. The simplicity of the LCM calculation for 12 and 16 belies the significance and broad utility of this fundamental concept in mathematics and real-world problem-solving.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats The Difference Between Monohybrid And Dihybrid Crosses
Mar 28, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 12 15
Mar 28, 2025
-
Three Letter Words That Start With X
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 3 5 7
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Surface Area And Area
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 16 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
