What Is The Lcm Of 32 And 48
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
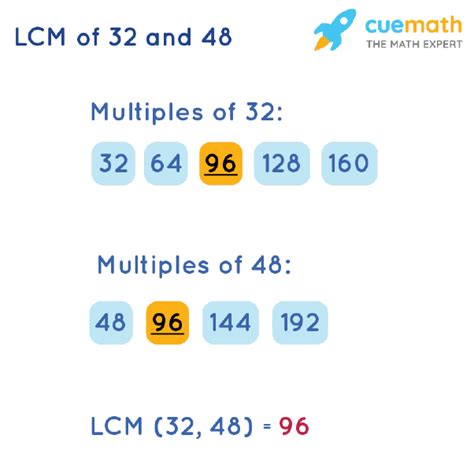
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 32 and 48? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with applications spanning various fields, from simple fraction arithmetic to complex scheduling problems. This article will explore the LCM of 32 and 48, providing multiple methods for calculation and demonstrating its practical significance. We'll delve into the theoretical underpinnings, offering a comprehensive understanding suitable for students and anyone seeking to refresh their mathematical skills.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 32 and 48, let's establish a solid understanding of what LCM actually means. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of each of the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that both numbers divide into evenly.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Calculating LCM
There are several effective methods for determining the LCM of two numbers. Let's examine the most common approaches, applying them to find the LCM of 32 and 48:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, particularly for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
Multiples of 32: 32, 64, 96, 128, 160, 192, 224, 256, 288, 320...
Multiples of 48: 48, 96, 144, 192, 240, 288, 336, 384...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple is 96. Therefore, the LCM of 32 and 48 is 96. This method is simple to understand but becomes less efficient when dealing with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method leverages the prime factorization of each number. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
- Prime factorization of 32: 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2<sup>5</sup>
- Prime factorization of 48: 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 2<sup>4</sup> x 3
To find the LCM using prime factorization:
-
Identify the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization. In this case, the prime factors are 2 and 3. The highest power of 2 is 2<sup>5</sup> (from 32), and the highest power of 3 is 3<sup>1</sup> (from 48).
-
Multiply the highest powers together. This gives us 2<sup>5</sup> x 3 = 32 x 3 = 96.
Therefore, the LCM of 32 and 48 is 96. This method is more efficient for larger numbers than listing multiples.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers evenly. The relationship is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
-
Find the GCD of 32 and 48. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- 48 = 32 x 1 + 16
- 32 = 16 x 2 + 0
The GCD is 16.
-
Apply the formula: LCM(32, 48) x GCD(32, 48) = 32 x 48
LCM(32, 48) x 16 = 1536
LCM(32, 48) = 1536 / 16 = 96
Therefore, the LCM of 32 and 48 is 96. This method is efficient and relies on a well-established algorithm for finding the GCD.
Practical Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple mathematical exercises. It has numerous real-world applications:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses departing from the same station at different intervals. One bus departs every 32 minutes, and the other every 48 minutes. To find out when both buses will depart simultaneously again, we need the LCM. The LCM (96 minutes) represents the time interval after which both buses will depart at the same time.
-
Fraction Operations: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, we need to find a common denominator. The LCM of the denominators is the least common denominator (LCD), simplifying the calculation.
-
Project Management: In project management, tasks might have different completion cycles. The LCM can help determine the optimal time to synchronize or review multiple tasks.
-
Cyclic Processes: In engineering and other fields dealing with cyclical processes (like rotating machinery or periodic signals), the LCM can help determine when cycles align or overlap.
-
Music Theory: In music, the LCM is used to find the least common denominator for different time signatures, helping in rhythmic coordination.
Conclusion: The Power of the LCM
The calculation of the LCM, in this case, for 32 and 48, demonstrates a core concept in number theory with far-reaching practical applications. Whether using the listing method, prime factorization, or the GCD method, the result remains consistent: the LCM of 32 and 48 is 96. Understanding these methods and their applications equips you with valuable problem-solving skills applicable across diverse fields. The LCM is not just an abstract mathematical concept; it's a powerful tool with significant real-world implications. Mastering the LCM is a key step in developing a deeper understanding of mathematics and its practical utility. Remember to choose the method best suited to the numbers involved, prioritizing efficiency and accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Center Of Mass Of An Equilateral Triangle
Mar 24, 2025
-
Non Superimposable Mirror Images Are Called
Mar 24, 2025
-
The Amount Of Space Between Two Points
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Multiple Of 3 And 4
Mar 24, 2025
-
Is A Buffalo A Herbivore Carnivore Or Omnivore
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 32 And 48 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
