What Is The Greatest Common Multiple Of 3 And 4
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
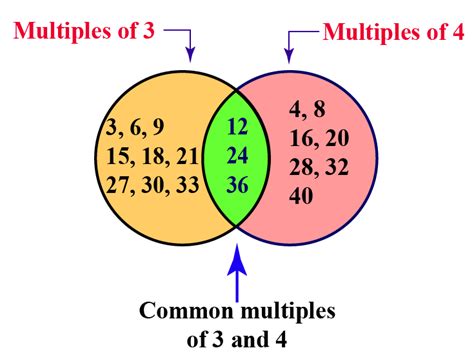
Table of Contents
What is the Greatest Common Multiple of 3 and 4? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the greatest common multiple (GCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple task, especially with small numbers like 3 and 4. However, understanding the underlying concepts of number theory and exploring different methods for finding the GCM provides a valuable foundation for more complex mathematical problems. This article will delve into the intricacies of finding the GCM of 3 and 4, exploring various approaches, and expanding on the broader significance of this concept in mathematics.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Factors, Multiples, and the GCM
Before jumping into the calculation, let's establish a clear understanding of the key terms.
Factors: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Factors are numbers that divide evenly into a given number without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Understanding factors is crucial because they represent the components that make up a number.
Multiples: The Extended Family of Numbers
Multiples are the results of multiplying a number by any integer (whole number). For instance, the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on. Similarly, the multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, and so on.
Greatest Common Multiple (GCM): Finding the Shared Maximum
The greatest common multiple (GCM), also known as the least common multiple (LCM), is the largest number that is a multiple of both numbers in question. It represents the highest value that both numbers divide into evenly. It's important to note that while the term "least common multiple" is often used, the concept remains the same: finding the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of both numbers.
Calculating the GCM of 3 and 4: Different Approaches
Now, let's explore different methods for finding the GCM of 3 and 4.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The simplest method, especially for smaller numbers, is to list the multiples of each number until you find the smallest multiple they share.
Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24...
Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32...
As you can see, the smallest multiple that appears in both lists is 12. Therefore, the GCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more robust and works well for larger numbers. Prime factorization involves breaking down each number into its prime factors—numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves.
- Prime factorization of 3: 3 (3 is already a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 4: 2 x 2 = 2²
To find the GCM using prime factorization, we identify the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
Multiply these highest powers together: 2² x 3 = 4 x 3 = 12
Therefore, the GCM of 3 and 4 is again 12.
Method 3: Using the Formula (For Two Numbers)
A convenient formula exists for calculating the GCM of two numbers (a and b) using their greatest common divisor (GCD):
GCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
First, we need to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 3 and 4. The GCD is the largest number that divides both 3 and 4 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD of 3 and 4 is 1 (because 1 is the only number that divides both 3 and 4).
Now, applying the formula:
GCM(3, 4) = (3 x 4) / GCD(3, 4) = 12 / 1 = 12
This method confirms, once again, that the GCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
The Significance of the GCM in Real-World Applications
The concept of the GCM extends far beyond simple mathematical exercises. It has numerous practical applications in various fields:
1. Scheduling and Timing:
Imagine you have two machines that perform different tasks. Machine A completes its cycle every 3 minutes, and Machine B completes its cycle every 4 minutes. To find out when both machines will complete their cycles simultaneously, you need to find the GCM. The GCM (12 minutes) indicates when both machines will be at the start of a new cycle at the same time.
2. Geometry and Measurement:
In geometric problems, the GCM can be used to find the size of tiles needed to cover a rectangular area with specific dimensions. For example, if a rectangle has dimensions of 3 units and 4 units, tiles with a side length equal to the GCM (12) would perfectly cover the area.
3. Music and Rhythm:
In music, the GCM helps determine the least common denominator in rhythmic patterns. Understanding the GCM of different note values allows musicians and composers to create harmonious and complex rhythms.
Expanding on the Concept: GCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be adapted to find the GCM of more than two numbers. However, the process becomes more complex. Here's a brief outline of how to approach this:
- Prime Factorization: Find the prime factorization of each number.
- Identify Common Factors: Identify the prime factors that are common to all numbers.
- Select the Lowest Power: For each common prime factor, select the lowest power that appears in any of the factorizations.
- Multiply: Multiply the selected lowest powers together to obtain the GCM.
For example, let's find the GCM of 3, 4, and 6:
- Prime factorization of 3: 3
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
The common prime factors are 2 and 3. The lowest power of 2 is 2¹ = 2, and the lowest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3. Therefore, the GCM of 3, 4, and 6 is 2 x 3 = 6.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Further Mathematical Exploration
Understanding the concept of the greatest common multiple, particularly how to calculate it using different methods, is a cornerstone of number theory. The seemingly simple problem of finding the GCM of 3 and 4 provides a springboard to explore more complex mathematical concepts, offering practical applications in a wide range of fields. The ability to find the GCM demonstrates a fundamental grasp of number relationships and their real-world implications, laying the groundwork for further mathematical exploration and problem-solving. Mastering this concept empowers you to tackle more challenging mathematical problems and opens doors to a deeper understanding of the underlying structure of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
30 Yards Is How Many Feet
Mar 25, 2025
-
Surface Area Of A Regular Pyramid Calculator
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Yards Are In 7 Feet
Mar 25, 2025
-
Calculate The Surface Area Of A Cuboid
Mar 25, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 18 And 6
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Greatest Common Multiple Of 3 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
