What Is The Largest Endocrine Gland In An Adult
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
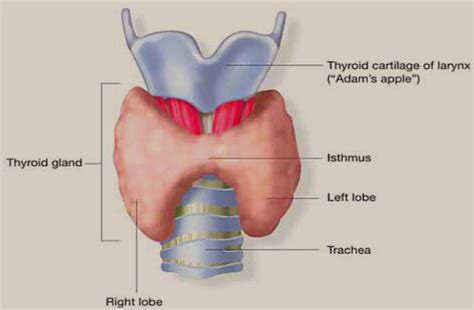
Table of Contents
What is the Largest Endocrine Gland in an Adult? The Thyroid's Crucial Role
The human body is a marvel of intricate systems working in perfect harmony. Among these, the endocrine system stands out, a complex network of glands that produce and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones then travel throughout the body, regulating a vast array of functions, from metabolism and growth to reproduction and mood. While many glands contribute to this intricate system, one stands out as the largest: the thyroid gland.
Understanding the Endocrine System
Before diving into the specifics of the thyroid, let's establish a foundational understanding of the endocrine system itself. This system relies on hormones, chemical messengers that act on target cells or organs to initiate specific responses. These responses can be immediate or take place over a longer period, depending on the hormone and its target.
The endocrine glands involved include:
- Pituitary gland: Often referred to as the "master gland," it regulates many other endocrine glands.
- Thyroid gland: Responsible for metabolism regulation and other vital processes.
- Parathyroid glands: Control calcium levels in the blood.
- Adrenal glands: Produce hormones that manage stress, blood pressure, and metabolism.
- Pancreas: Secretes hormones like insulin and glucagon, controlling blood sugar.
- Ovaries (in females) and testes (in males): Produce sex hormones.
- Pineal gland: Produces melatonin, regulating sleep cycles.
These glands, working in concert, maintain homeostasis – the body’s internal equilibrium. Any disruption in this delicate balance, often caused by hormonal imbalances, can lead to a variety of health issues.
The Thyroid Gland: A Detailed Look
The thyroid gland, located in the neck just below the Adam's apple, is indeed the largest endocrine gland in an adult. Shaped like a butterfly, it consists of two lobes connected by an isthmus. Its size varies slightly between individuals, but it typically measures around 5cm in length and 2-3cm in width.
Its primary function is the production and release of two crucial hormones:
- Thyroxine (T4): The main hormone produced by the thyroid. While less active than T3, it serves as a precursor to T3 and is vital for maintaining the body's metabolic rate.
- Triiodothyronine (T3): A more active form of thyroid hormone, T3 directly influences cellular metabolism, impacting almost every system in the body.
These hormones are essential for:
- Metabolism: Regulating the body's rate of energy expenditure. This impacts weight management, body temperature, and heart rate.
- Growth and Development: Crucial for normal growth and development, especially during childhood and adolescence. Thyroid hormones are vital for brain development in fetuses and infants.
- Cellular Function: Influencing the function of virtually every cell in the body. This includes protein synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and lipid metabolism.
- Nervous System Function: Maintaining the normal function of the nervous system. Thyroid hormones affect nerve transmission and brain function.
- Cardiac Function: Thyroid hormones influence the heart rate and contractility.
Thyroid Hormone Production: A Step-by-Step Process
The production of thyroid hormones is a fascinating process. It begins with the uptake of iodine from the bloodstream. Iodine is crucial; without sufficient iodine, the thyroid can't produce adequate amounts of T3 and T4. Inside the thyroid follicles, iodine is combined with tyrosine, an amino acid, to form T3 and T4. These hormones are then stored within the follicles before being released into the bloodstream as needed.
The production and release of T3 and T4 are tightly regulated by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland through a feedback mechanism. The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release T3 and T4. When levels of T3 and T4 are high enough, they inhibit the release of TRH and TSH, creating a balance.
Conditions Affecting the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland, despite its small size, plays a significant role in maintaining overall health. Consequently, malfunctions can lead to a range of conditions, broadly categorized into:
Hypothyroidism: Underactive Thyroid
This occurs when the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough thyroid hormones. Symptoms can be subtle and often develop gradually, including fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dry skin, and intolerance to cold. Untreated hypothyroidism can lead to serious complications, affecting the heart, brain, and other organs.
Hyperthyroidism: Overactive Thyroid
This condition occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Symptoms often include weight loss, nervousness, irritability, increased heart rate, and heat intolerance. Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to serious complications, including heart problems and osteoporosis.
Goiter: Enlarged Thyroid
A goiter refers to an enlargement of the thyroid gland. This enlargement can be associated with both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, or it can occur independently due to iodine deficiency or other causes.
Thyroid Nodules and Cancer
Thyroid nodules are lumps that develop within the thyroid gland. Most nodules are benign, but some can be cancerous. Regular screenings and medical evaluations are important for early detection and treatment.
Maintaining Thyroid Health
Maintaining a healthy thyroid is essential for overall well-being. Here are some key steps you can take:
- Maintain a balanced diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Ensure adequate iodine intake: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. Iodized salt is a good source of iodine.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively affect thyroid function. Practice stress-management techniques such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
- Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your doctor can help detect thyroid issues early. Blood tests can measure TSH, T3, and T4 levels.
- Avoid excessive exposure to radiation: Exposure to radiation can damage the thyroid gland.
The Thyroid's Importance: A Recap
The thyroid gland, as the largest endocrine gland in an adult, plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Its hormones regulate a wide range of bodily functions, influencing everything from metabolism and growth to mood and heart function. Understanding its crucial role and the potential consequences of thyroid disorders underscores the importance of regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms. Early detection and appropriate management are vital for preventing serious complications and ensuring a high quality of life. The thyroid's intricate mechanisms and crucial influence on overall health emphasize its status as a truly vital organ. By understanding its role and prioritizing its health, we can contribute significantly to our overall well-being.
This comprehensive overview highlights the significance of the thyroid gland and its profound impact on various aspects of human health. From the intricacies of hormone production to the implications of thyroid disorders, the information presented serves as a valuable resource for understanding this critical endocrine gland and its indispensable contribution to the overall functioning of the human body. Remember, maintaining thyroid health is crucial for a healthy and vibrant life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Largest Endocrine Gland In An Adult . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
