What Is The Half Life Of Au-198
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
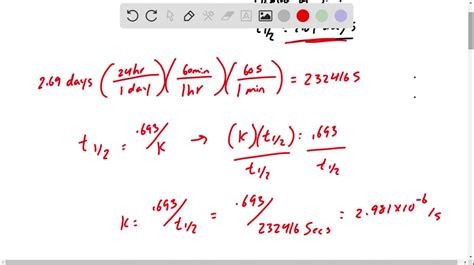
Table of Contents
What is the Half-Life of Au-198? Understanding Radioactive Decay and its Applications
Gold-198 (Au-198), a radioactive isotope of gold, plays a significant role in various scientific and medical applications. Understanding its properties, particularly its half-life, is crucial for safe and effective utilization. This comprehensive article delves into the intricacies of Au-198's half-life, exploring its implications in radioactive decay, medical applications, and safety protocols.
What is Half-Life?
Before diving into the specifics of Au-198, let's establish a clear understanding of half-life. Half-life is the time it takes for half of the atoms in a radioactive sample to decay into a different, more stable element. This decay process is governed by the laws of radioactive decay, a fundamental concept in nuclear physics. It's important to understand that half-life is a statistical measure; it doesn't predict the behavior of a single atom, but rather the overall behavior of a large number of atoms.
Understanding Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation. This radiation can take several forms, including alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. The type of radiation emitted depends on the specific isotope and its decay pathway. Au-198, for instance, primarily decays through beta decay, emitting beta particles and gamma rays.
Beta Decay in Au-198
In beta decay, a neutron in the Au-198 nucleus transforms into a proton, emitting an electron (beta particle) and an antineutrino. This transformation increases the atomic number by one, changing the element from gold (atomic number 79) to mercury (atomic number 80). The resulting mercury isotope is Hg-198, which is stable. The gamma rays emitted during this process are a significant factor in Au-198's applications in medicine.
The Half-Life of Au-198: 2.697 Days
The half-life of Au-198 is 2.697 days. This means that after 2.697 days, half of the initial amount of Au-198 in a sample will have decayed into Hg-198. After another 2.697 days (a total of 5.394 days), half of the remaining Au-198 will have decayed, leaving only one-quarter of the original amount. This process continues exponentially, with the amount of Au-198 decreasing by half every 2.697 days.
Calculating Remaining Au-198
The amount of Au-198 remaining after a certain time can be calculated using the following formula:
N(t) = N₀ * (1/2)^(t/T)
Where:
- N(t) is the amount of Au-198 remaining after time t
- N₀ is the initial amount of Au-198
- t is the elapsed time
- T is the half-life of Au-198 (2.697 days)
Practical Implications of the Half-Life
The relatively short half-life of Au-198 has both advantages and disadvantages. The short half-life means that the radiation exposure decreases rapidly over time, which is crucial for safety considerations. However, it also means that the isotope needs to be regularly replenished for applications requiring sustained radiation.
Applications of Au-198
Despite its short half-life, Au-198 finds several important applications, primarily in the medical field:
Medical Applications:
-
Radiotherapy: Au-198 is used in brachytherapy, a type of radiotherapy where radioactive sources are placed directly into or near a tumor. Its gamma rays effectively target cancerous cells, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. This is particularly useful in treating certain types of cancers.
-
Diagnostic Imaging: While less common than its use in radiotherapy, Au-198 can be used in some diagnostic procedures. Its gamma emissions can be detected by imaging equipment, providing information about the distribution and uptake of the isotope within the body.
-
Colloidal Gold: Au-198 is often prepared as a colloid for medical applications. Colloidal gold particles are suspended in a liquid, enabling easier administration and more targeted delivery to specific areas within the body.
Non-Medical Applications:
While primarily used in medicine, Au-198 also has limited applications in other fields, such as:
-
Industrial Gauging: Au-198's gamma emissions can be utilized in industrial gauging applications to measure the thickness of materials or detect flaws in production processes. This application is less prevalent than medical uses, due to the need for specialized handling and safety protocols.
-
Research: Au-198 plays a role in nuclear physics research, providing insights into radioactive decay processes and nuclear reactions. This research helps further our understanding of fundamental physics and has implications for various technological advancements.
Safety Precautions and Handling
Given the radioactive nature of Au-198, strict safety precautions are essential when handling this isotope:
Shielding:
Au-198 emits gamma radiation, which requires shielding to protect personnel. Lead shielding is commonly used to attenuate gamma rays and minimize radiation exposure.
Distance:
Maintaining a safe distance from the radioactive source is another crucial safety measure. The intensity of radiation decreases with the square of the distance from the source, minimizing exposure.
Time:
Minimizing the time spent near the radioactive source is critical. Reducing exposure time directly reduces the overall radiation dose received.
Monitoring:
Radiation monitoring devices, such as Geiger counters, are crucial for ensuring that radiation levels remain within safe limits. Regular monitoring helps prevent accidental exposure to harmful levels of radiation.
Waste Disposal:
Disposal of Au-198 waste must comply with strict regulations to protect the environment and public health. Specialized procedures and facilities are required to handle and dispose of radioactive materials properly.
Conclusion: Au-198 – A Powerful Tool with Cautious Handling
Au-198, with its characteristic half-life of 2.697 days and its unique decay properties, offers significant potential in various scientific and medical fields. Its applications in radiotherapy, particularly, highlight its importance in combating cancer. However, its radioactive nature necessitates strict adherence to safety protocols to mitigate risks associated with radiation exposure. Proper handling, shielding, and disposal practices are crucial for the safe and responsible use of this valuable isotope. Understanding the half-life of Au-198 is fundamental to these practices, enabling accurate calculations of radiation levels and appropriate safety measures. The ongoing research and development in this area continue to refine our understanding and application of this important radioactive material, furthering its potential benefits while mitigating associated risks. The continued responsible use of Au-198 highlights the critical balance between harnessing the power of nuclear technology and ensuring public health and safety.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Tap Water Pure Substance Or Mixture
Mar 28, 2025
-
Amount Of Matter That An Object Contains
Mar 28, 2025
-
As The Temperature Of A Gas Increases
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 17 25 As A Decimal
Mar 28, 2025
-
150 Is 25 Of What Number
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Half Life Of Au-198 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
