What Is The Function Of The Arm In A Microscope
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
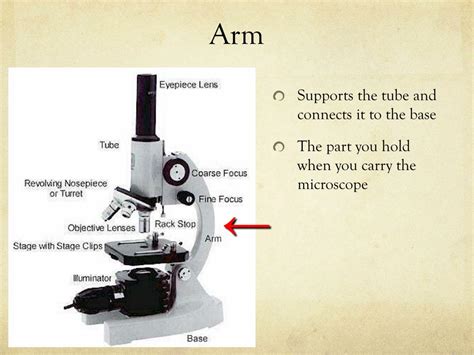
Table of Contents
What is the Function of the Arm in a Microscope? A Comprehensive Guide
The microscope, a cornerstone of scientific discovery, comprises several intricate components, each playing a crucial role in achieving magnification and clear visualization of specimens. While the lenses, stage, and light source are often the focal points of discussion, the often-overlooked microscope arm serves a vital, multifaceted function ensuring both stability and ease of use. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the arm's functionality, exploring its significance in various microscope types and emphasizing its contribution to optimal microscopy practices.
The Microscope Arm: More Than Just Support
The microscope arm, as its name suggests, acts as the primary structural support connecting the microscope's head (containing the eyepieces and objectives) to the base. However, its role extends far beyond mere structural integrity. The arm is ergonomically designed to facilitate several critical aspects of microscopy:
1. Stable Transportation and Handling
Perhaps the most immediately apparent function of the arm is its crucial role in the safe and secure transport of the microscope. The arm provides a sturdy grip point, allowing users to comfortably lift and carry the instrument without risk of damage or accidental breakage. This is particularly vital for larger, heavier microscopes. Incorrect handling can lead to misalignment, which compromises image quality and may even damage delicate internal components. The arm's design, often incorporating ergonomic curves and finger grips, minimizes strain on the user during transportation and manipulation.
2. Precise Adjustment and Focusing
While focusing is predominantly achieved through the focus knobs, the arm plays an indirect but crucial role in maintaining precision during adjustments. By securely supporting the microscope head, the arm prevents unwanted movement or vibration during the focusing process, especially at higher magnifications where even slight tremors can significantly impact image clarity. This stability is paramount for achieving sharp, detailed images, crucial for accurate observation and analysis of microscopic specimens.
3. Ergonomic Design and User Comfort
Modern microscope arms are meticulously designed with ergonomics in mind. The arm’s curvature and positioning often allow for comfortable viewing angles, reducing strain on the user’s neck and back during prolonged microscopy sessions. This is particularly important for professionals who spend extended periods examining specimens. Furthermore, the arm's location contributes to a balanced weight distribution, reducing fatigue and enhancing overall user comfort. A poorly designed arm can lead to discomfort and even repetitive strain injuries.
4. Integrated Controls and Accessibility
In some advanced microscope models, the arm also serves as a convenient housing for certain controls and accessories. This may include integrated illumination controls, allowing for easy adjustment of light intensity without reaching for separate controls. This integration enhances workflow efficiency and minimizes distractions during observation. The placement of such controls on the arm ensures optimal accessibility and user-friendliness.
5. Protection of Internal Components
The arm provides indirect protection to the delicate optical and mechanical components housed within the microscope head. By securely holding the head, it shields these components from accidental impacts and jarring movements. This protection is vital in maintaining the instrument's longevity and ensuring consistent performance over time.
The Arm's Role in Different Microscope Types
The function of the arm remains consistent across various microscope types, although the specific design and features may vary.
1. Compound Light Microscopes
In compound light microscopes, the arm is a critical component, connecting the sturdy base to the body tube containing the ocular and objective lenses. Its sturdy construction is essential for supporting the weight of the optical components and ensuring stable viewing, especially at higher magnifications where vibrations are more likely to affect image quality.
2. Stereomicroscopes (Dissecting Microscopes)
Stereomicroscopes also feature an arm, often incorporating a more robust design to accommodate the larger, heavier body and potentially additional accessories such as illumination systems. The arm's stability is vital for handling the often more intricate manipulation required in dissecting or examining larger specimens.
3. Inverted Microscopes
Inverted microscopes, used primarily for cell culture and tissue imaging, feature a unique arrangement where the light source is positioned above the stage and the objectives below. While the arm might appear less prominent, it still plays a vital role in supporting the inverted head and maintaining overall stability.
4. Electron Microscopes
Electron microscopes, while significantly different in design and functionality from optical microscopes, still incorporate structural components analogous to the arm. These components provide stability and support for the highly sensitive electron column and other components, ensuring the precision required for high-resolution imaging. However, the scale and construction are significantly different due to the vacuum environment and high voltage requirements of electron microscopy.
Maintaining and Caring for the Microscope Arm
Proper care and maintenance of the microscope arm are crucial for maintaining the instrument's overall performance and longevity. Avoid placing excessive pressure or force on the arm during handling or adjustments. Regular cleaning of the arm, using a soft, lint-free cloth, can help prevent dust and debris buildup. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as these can damage the finish and potentially compromise the arm's structural integrity.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Microscopy
While often overshadowed by the more prominent optical components, the microscope arm plays a crucial, multifaceted role in the efficient and accurate operation of the microscope. Its function extends beyond simple structural support; it directly impacts stability, user comfort, and the overall ease of use. Understanding the arm's significance is vital for any microscopist, ensuring proper handling, maintenance, and optimal performance of this invaluable scientific instrument. The arm’s robust design and strategic placement contribute significantly to the accuracy and reliability of microscopic observations, allowing researchers and scientists to unveil the microscopic world with confidence and precision. A well-designed and maintained arm enhances the overall user experience and contributes significantly to the long-term functionality of the microscope, ensuring years of reliable service and groundbreaking discoveries. Its seemingly simple function is in fact pivotal to the entire microscopy experience.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Digestion Of Starch Begins In The
Mar 14, 2025
-
Difference Between Ac And Dc Motors
Mar 14, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple 9 12 15
Mar 14, 2025
-
Difference Between Physical Map And Political
Mar 14, 2025
-
The Study Of Cell Structure And Function Is Called
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Function Of The Arm In A Microscope . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
