Difference Between Physical Map And Political
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
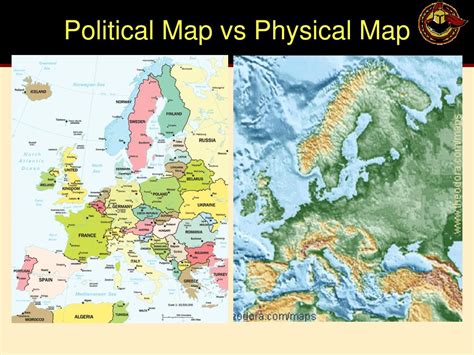
Table of Contents
Delving into the Differences: Physical vs. Political Maps
Maps are fundamental tools for understanding our world. They provide visual representations of geographical information, allowing us to navigate, analyze, and interpret spatial relationships. However, not all maps are created equal. Two prominent types, physical maps and political maps, serve distinct purposes and employ different methods of representation. Understanding the key differences between these two map types is crucial for anyone seeking to effectively utilize cartographic data. This article will explore the nuances of physical and political maps, highlighting their individual strengths, limitations, and applications.
What is a Physical Map?
A physical map primarily focuses on the natural features of a geographic area. It showcases the Earth's topography, including mountains, valleys, plains, rivers, lakes, oceans, and other landforms. The primary purpose of a physical map is to illustrate the physical geography of a region, providing a visual representation of its three-dimensional landscape. Think of it as a snapshot of the Earth's surface, highlighting its natural formations.
Key Characteristics of Physical Maps:
- Emphasis on Landforms: Mountains are depicted using shading, contour lines, or even three-dimensional rendering to show elevation. Valleys, plains, and plateaus are also clearly indicated, providing a comprehensive view of the terrain.
- Hydrographic Features: Rivers, lakes, oceans, and other bodies of water are prominently displayed, often using different shades of blue to indicate depth or water flow.
- Use of Color and Shading: Physical maps heavily rely on color and shading to represent elevation, with varying shades of green, brown, and tan indicating changes in altitude. Blues are reserved for bodies of water.
- Limited Human Influence: While human settlements might be shown, they're usually secondary to the emphasis on natural features. The focus remains firmly on the Earth's natural landscape.
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, offering a detailed representation of terrain's slope and shape, particularly useful for understanding the gradient of hills and mountains.
What is a Political Map?
In contrast to a physical map, a political map emphasizes human-created boundaries and divisions. Its primary focus is on the geopolitical organization of a region, showing countries, states, provinces, cities, and other administrative areas. Political maps provide a framework for understanding international relations, governmental structures, and the distribution of power. They are primarily concerned with illustrating human influence on the Earth's surface.
Key Characteristics of Political Map:
- National Boundaries: Clearly defined lines depict the borders between countries, marking territories under different sovereignties.
- State/Province Boundaries: Sub-national divisions, like states or provinces, are also delineated, showcasing the administrative structure within a country.
- Cities and Towns: Major urban centers are indicated, often with different sizes of markers or text representing population size or importance.
- Capital Cities: Often marked with a star or a specific symbol, capital cities highlight the centers of political power within each country or region.
- Water Bodies: While water bodies are included, they're usually simplified and play a less prominent role than in physical maps. The focus is on political divisions rather than geographical formations.
- Limited Topographical Detail: Topographical features like mountains and valleys are either absent or significantly simplified, prioritizing political boundaries.
Comparing Physical and Political Maps: A Side-by-Side Analysis
To further illustrate the differences, let's examine specific aspects side-by-side:
| Feature | Physical Map | Political Map |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Natural Features (landforms, water bodies) | Human-made Boundaries (countries, states, cities) |
| Color Scheme | Emphasizes elevation and terrain (greens, browns, blues) | Usually uses distinct colors for countries/states |
| Details | Detailed topographic information | Primarily focuses on political divisions |
| Symbols | Contour lines, shading, elevation markers | Country/state borders, city markers, capital city indicators |
| Purpose | Showcasing the Earth's physical geography | Illustrating political divisions and organization |
| Applications | Geology, environmental studies, geography | Social studies, politics, international relations |
Beyond the Basics: Hybrid Maps and Specialized Applications
While distinctly different, physical and political maps are not mutually exclusive. Many maps are hybrid maps, combining elements of both types. These hybrid maps provide a more comprehensive view by incorporating both natural and political features, allowing for a richer understanding of a region's characteristics.
Furthermore, both physical and political maps can be specialized for specific purposes. For example, a thematic map, built upon either a physical or political base, might overlay information about population density, climate, or economic activity. This adds another layer of data interpretation to the basic map framework.
The Importance of Map Scale and Projection
The scale of a map, representing the ratio between the map's distance and the actual distance on the Earth, is crucial for both physical and political maps. A large-scale map shows a small area in great detail, while a small-scale map displays a large area with less detail. The level of detail achievable on a physical map often dictates the scale, as showing intricate topographic information requires a larger scale.
Map projection, the method of transforming the three-dimensional Earth's surface onto a two-dimensional plane, also impacts both map types. Different projections distort the Earth's surface in various ways, affecting the accuracy of distances, shapes, and areas. Choosing an appropriate projection is crucial for minimizing distortion and ensuring that the map accurately represents the intended information.
Practical Applications and Everyday Relevance
The practical applications of physical and political maps extend far beyond academic settings. Their use permeates daily life and numerous professional fields:
- Navigation: Both map types are vital for navigation, whether planning a road trip or determining the location of a specific address. GPS systems utilize underlying map data, including both physical and political information.
- Urban Planning: Physical maps, showing topography and hydrology, are essential for urban planning, guiding the development of infrastructure and ensuring efficient resource allocation. Political maps define zoning regulations and administrative boundaries.
- Environmental Studies: Physical maps are invaluable in environmental studies, helping to identify areas susceptible to natural hazards, like flooding or landslides, and monitoring environmental changes.
- International Relations: Political maps are fundamental in understanding geopolitical dynamics, conflicts, and international collaborations.
- Education: Both map types are essential educational tools, helping to build spatial awareness, understand geographic concepts, and analyze data.
- Disaster Management: Understanding the physical geography of an area (using physical maps) and the location of settlements (political maps) is crucial for efficient disaster response and relief efforts.
- Military Strategy: Both types of maps play significant roles in military strategy, providing information on terrain, locations of troops, and potential battlefields.
Conclusion: Understanding the Nuances for Effective Interpretation
Physical and political maps, despite their differences, serve complementary purposes in representing the Earth's surface and human interaction with it. Understanding their unique characteristics, strengths, limitations, and appropriate applications is crucial for effective interpretation and utilizing the valuable information they provide. By recognizing the distinct focus of each map type – the natural environment versus human-created divisions – we can better analyze spatial information and draw more meaningful conclusions. Whether for navigating a city, understanding international relations, or studying environmental patterns, the appropriate choice and accurate interpretation of physical and political maps are key to insightful analysis and informed decision-making.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Bond Holds Nitrogen Bases Together
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Examples Of Plasmas
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Slime A Non Newtonian Fluid
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Type Of Triangle Has Two Equal Sides
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of Areolar Tissue
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Physical Map And Political . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
