What Is The Formula For Iron Ii Sulfate
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
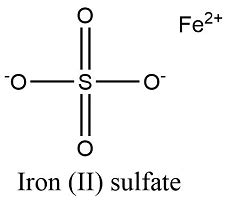
Table of Contents
What is the Formula for Iron(II) Sulfate? A Deep Dive into its Chemistry, Properties, and Applications
Iron(II) sulfate, also known as ferrous sulfate, is a fascinating chemical compound with a wide array of applications, from medicine to agriculture and beyond. Understanding its chemical formula is key to unlocking its properties and uses. This article will delve deep into the formula, exploring its structure, properties, production methods, applications, and safety considerations.
Understanding the Chemical Formula: FeSO₄
The chemical formula for iron(II) sulfate is FeSO₄. This simple formula tells us a great deal about the compound's composition:
-
Fe: This represents the element iron (ferrum). Iron exists in several oxidation states, most commonly +2 and +3. In iron(II) sulfate, iron is in its +2 oxidation state, also known as ferrous iron. This is crucial because iron(III) sulfate (ferric sulfate) has a different formula and properties.
-
S: This represents the element sulfur.
-
O₄: This represents four oxygen atoms. These atoms, along with sulfur, form the sulfate anion (SO₄²⁻), a polyatomic ion with a -2 charge.
Therefore, the formula FeSO₄ indicates that one iron(II) ion (Fe²⁺) is bonded to one sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻), resulting in a neutral compound.
Different Forms of Iron(II) Sulfate: Hydrates
While FeSO₄ represents the anhydrous form of iron(II) sulfate, it's more commonly found as a hydrate. Hydrates are compounds that incorporate water molecules into their crystal structure. The most common hydrate is iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate, with the formula FeSO₄·7H₂O. This means each formula unit of iron(II) sulfate incorporates seven water molecules.
Other hydrates exist, such as the tetrahydrate (FeSO₄·4H₂O) and monohydrate (FeSO₄·H₂O), but the heptahydrate is the most prevalent and readily available form. The presence of water molecules affects the compound's physical properties, such as its color and solubility.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Iron(II) Sulfate
Understanding the physical and chemical properties of iron(II) sulfate is vital for its safe handling and application.
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Anhydrous iron(II) sulfate is a white or pale-green powder. The heptahydrate is a pale blue-green crystalline solid.
- Solubility: Iron(II) sulfate is readily soluble in water, particularly the heptahydrate form. Solubility decreases slightly with increasing temperature.
- Melting Point: The melting point varies significantly depending on the hydration level. The heptahydrate loses water upon heating, eventually decomposing.
- Density: The density also varies with hydration.
- Odor: Odorless.
Chemical Properties:
- Oxidation: Iron(II) sulfate is susceptible to oxidation by air, slowly converting to iron(III) sulfate. This oxidation is accelerated in the presence of moisture and heat. This tendency is an important consideration for storage and usage.
- Reactions with Acids and Bases: Iron(II) sulfate reacts with acids and bases in typical acid-base reactions.
- Reactions with Oxidizing Agents: It reacts readily with strong oxidizing agents, undergoing a change in oxidation state.
- Formation of Complexes: Iron(II) can form coordination complexes with various ligands.
Production of Iron(II) Sulfate
Iron(II) sulfate can be produced through several methods, including:
-
Reaction of Iron with Sulfuric Acid: This is the most common industrial method. Iron metal reacts with dilute sulfuric acid to produce iron(II) sulfate and hydrogen gas:
Fe(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) → FeSO₄(aq) + H₂(g)
-
Oxidation of Pyrite: Pyrite (iron disulfide, FeS₂) can be oxidized in the presence of air and water to produce iron(II) sulfate:
2FeS₂(s) + 7O₂(g) + 2H₂O(l) → 2FeSO₄(aq) + 2H₂SO₄(aq)
-
Other Methods: Other methods involve the treatment of various iron-containing materials with sulfuric acid or other suitable reagents.
Applications of Iron(II) Sulfate
The versatile nature of iron(II) sulfate leads to its use in a diverse range of applications:
1. Medicine:
- Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia: Iron(II) sulfate is a common iron supplement used to treat iron deficiency anemia, a condition characterized by low levels of iron in the blood. The iron in the compound is readily absorbed by the body.
2. Agriculture:
- Soil Amendment: It is used as a soil amendment to correct iron deficiencies in plants. Iron is an essential micronutrient for plant growth, and iron(II) sulfate provides a readily available source.
- Herbicide: In some applications, it's used as a herbicide to control weeds.
3. Water Treatment:
- Coagulant: In water treatment plants, it's used as a coagulant to help remove suspended solids from water. It aids in the flocculation process.
- Reducing Agent: It can act as a reducing agent in specific water treatment processes.
4. Industry:
- Dyeing and Printing: Iron(II) sulfate has been used historically in the dyeing and printing industries as a mordant to fix dyes to fabrics.
- Wood Preservation: It has found some application in wood preservation due to its ability to inhibit the growth of certain microorganisms.
- Pigment Production: It can be used in the production of some pigments and inks.
Safety Precautions and Handling
While iron(II) sulfate is generally considered safe when used appropriately, certain precautions should be taken:
- Ingestion: Ingestion of large quantities can cause nausea, vomiting, and other gastrointestinal issues.
- Skin and Eye Contact: Contact with skin and eyes can cause irritation. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and eye protection, when handling.
- Inhalation: Inhalation of dust can irritate the respiratory system.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place, away from oxidizing agents and moisture. Properly sealed containers should be used to minimize oxidation.
Conclusion: The Importance of Iron(II) Sulfate
Iron(II) sulfate, with its simple yet significant chemical formula FeSO₄, plays a critical role in various sectors. From addressing iron deficiencies in humans and plants to its applications in industrial processes and water treatment, its importance is undeniable. Understanding its properties, production, and safety considerations is essential for its responsible use and handling. Further research into its applications continues to unlock its potential in various fields, underscoring its continued relevance in modern chemistry and beyond. Remember always to consult safety data sheets (SDS) and appropriate guidelines before handling any chemical substance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Purpose Of Commutator
Mar 22, 2025
-
How To Work Out Tensile Stress
Mar 22, 2025
-
Two Angles With Measures That Have A Sum Of 90
Mar 22, 2025
-
The Concentration Of Solutions Can Be Expressed As
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Kingdom Does The Euglena Belong To
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Formula For Iron Ii Sulfate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
