What Kingdom Does The Euglena Belong To
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
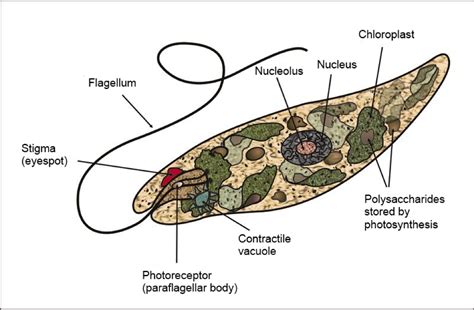
Table of Contents
What Kingdom Does the Euglena Belong To? A Deep Dive into the Controversial Classification of Euglena
The question of what kingdom Euglena belongs to is not a simple one. Unlike many organisms that fit neatly into established taxonomic classifications, Euglena presents a fascinating case study in the complexities of biological classification and the ever-evolving nature of scientific understanding. While traditionally placed in the kingdom Protista, its unique characteristics have led to ongoing debate and alternative classifications. This article delves deep into the intricacies of Euglena's classification, exploring its key features and why its placement remains a subject of scientific discussion.
The Protist Kingdom: A Diverse and Often Controversial Grouping
Before we dive into the specifics of Euglena, let's briefly discuss the kingdom Protista. This kingdom is a catch-all category for eukaryotic organisms that are not animals, plants, or fungi. This means it encompasses a vast array of organisms with incredibly diverse characteristics. This diversity is precisely what makes the Protista kingdom controversial. The sheer range of organisms included often leads to groupings based more on what they aren't rather than shared characteristics.
Many protists are unicellular, though some are multicellular. They exhibit a range of nutritional strategies: some are autotrophic (producing their own food through photosynthesis), some are heterotrophic (consuming other organisms), and some are mixotrophic (capable of both autotrophy and heterotrophy). Their reproductive strategies are similarly diverse, ranging from asexual to sexual reproduction. This lack of unifying characteristics has led many scientists to suggest that the Protista kingdom is paraphyletic, meaning it does not include all the descendants of a common ancestor.
Euglena: A Mixotrophic Master
Euglena is a genus of unicellular, eukaryotic organisms that embody the complexities of protist classification. These microscopic organisms are found in freshwater habitats worldwide and are often studied in introductory biology courses due to their unique blend of plant-like and animal-like characteristics.
Key Characteristics of Euglena: Why the Classification Debate?
-
Photosynthesis: Many species of Euglena possess chloroplasts, organelles that allow them to carry out photosynthesis, just like plants. This autotrophic capability is a key characteristic often associated with plants.
-
Motility: Euglena possess a flagellum, a whip-like appendage that allows them to move freely in their aquatic environment. This is a feature typically associated with animal-like organisms.
-
Heterotrophic Nutrition: While capable of photosynthesis, many Euglena species can also absorb nutrients from their surroundings, exhibiting heterotrophic nutrition. This ability to switch between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition, known as mixotrophy, further complicates its classification.
-
Eyespot (Stigma): Euglena have a unique eyespot, also known as a stigma, which functions as a light sensor, helping them move towards optimal light conditions for photosynthesis. This specialized structure adds another layer to their already complex characteristics.
-
Pellicle: Instead of a rigid cell wall, Euglena possess a pellicle, a flexible protein layer beneath the cell membrane. This pellicle allows for changes in cell shape, contributing to their motility and adaptability.
The Ongoing Debate: Beyond the Protist Kingdom
The presence of chloroplasts and photosynthetic capabilities led early taxonomists to place Euglena closer to plants. However, their motility, heterotrophic capabilities, and lack of a rigid cell wall clearly distinguish them from plants. The Protista kingdom provided a seemingly convenient solution, but the growing understanding of eukaryotic evolution has further fueled the debate. Some scientists argue that:
-
Euglena should belong to a separate kingdom: The unique combination of plant-like and animal-like features suggests that Euglena might represent a distinct evolutionary lineage, deserving of its own kingdom. This reflects the growing recognition that the traditional five-kingdom system of classification is an oversimplification.
-
Phylogenetic analyses are necessary: Modern molecular techniques allow scientists to analyze the genetic relationships between organisms with greater precision. Phylogenetic analyses based on DNA and RNA sequences can shed light on the evolutionary history of Euglena and its relationship to other eukaryotic lineages. This data could support placement within the Protista kingdom or suggest a revised classification entirely.
-
The Protista kingdom itself needs re-evaluation: The Protista kingdom remains a heterogeneous group, and its inherent ambiguity continues to challenge traditional taxonomic frameworks. A thorough reassessment of the entire kingdom may be necessary to address the ongoing controversies regarding the classification of many protists, including Euglena.
The Role of Endosymbiosis in Euglena's Evolutionary History
The presence of chloroplasts within Euglena cells is believed to be a result of endosymbiosis – a process where one organism lives within another, and over time, a symbiotic relationship develops. The chloroplasts in Euglena are thought to be derived from an ancient endosymbiotic event involving a green alga. This evolutionary event played a critical role in shaping Euglena's unique mixotrophic lifestyle. Understanding this evolutionary history is crucial in accurately placing Euglena within the broader context of eukaryotic evolution.
The Future of Euglena Classification
The classification of Euglena remains a dynamic area of research. As our understanding of eukaryotic evolution and phylogenetic relationships improves, further adjustments to its taxonomic placement are likely. The development of new molecular techniques and analyses will undoubtedly play a significant role in refining our understanding of Euglena's evolutionary history and its correct placement within the tree of life.
The ongoing debate surrounding Euglena's classification highlights the limitations of traditional taxonomic systems and the ongoing need for scientists to refine and update our understanding of the biological world. The unique characteristics of Euglena serve as a powerful reminder that the diversity of life on Earth is far more complex than our previous classifications often suggest.
Implications for Biological Education
The uncertainty surrounding Euglena's classification presents a valuable opportunity for educators. Teaching about Euglena not only imparts knowledge about a fascinating organism but also allows for discussions about the complexities of biological classification, the limitations of traditional systems, and the ever-evolving nature of scientific understanding. By presenting the ongoing debate, educators can encourage critical thinking and foster a deeper appreciation for the dynamic nature of scientific inquiry.
In conclusion, the question of what kingdom Euglena belongs to remains a fascinating and complex one. While currently placed within the Protista kingdom, its unique characteristics, including mixotrophy and its evolutionary history, have sparked continuous debate and highlight the ongoing challenges in classifying organisms that defy simple categorization. Further research utilizing advanced phylogenetic techniques will be essential in clarifying Euglena's place within the intricate web of life. This ongoing debate serves as a valuable example of the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of biological classification and our understanding of the diversity of life on Earth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
9 Is A Multiple Of 3
Mar 23, 2025
-
A Pair Of Angles That Add Up To 180
Mar 23, 2025
-
Work Is Scalar Or Vector Quantity
Mar 23, 2025
-
Round 62 To The Nearest Ten
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is Sugar Dissolves In Water A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Kingdom Does The Euglena Belong To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
