What Is The Electronic Configuration Of Barium
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
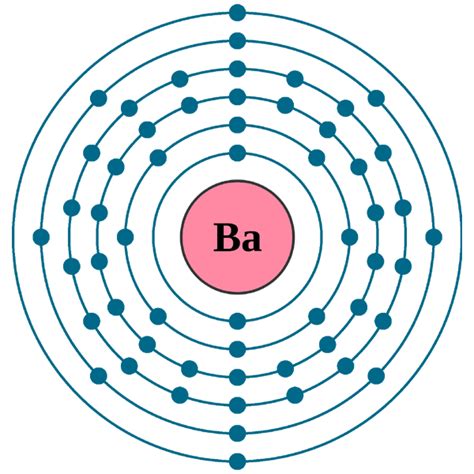
Table of Contents
What is the Electronic Configuration of Barium? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Barium, a fascinating alkaline earth metal, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic configuration is crucial to grasping its chemical properties, reactivity, and its role in various applications. This in-depth article will explore the electronic configuration of barium, delving into the principles of atomic structure, the Aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and the exceptions that sometimes occur. We'll also examine how this configuration influences barium's behavior and its significance in different fields.
Understanding Electronic Configuration
The electronic configuration of an element describes how electrons are arranged in the various energy levels and sublevels within an atom. These arrangements directly dictate the atom's chemical behavior and its interactions with other elements. Electrons occupy orbitals, regions of space around the nucleus where there's a high probability of finding an electron. Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, according to the Pauli Exclusion Principle.
Energy Levels and Sublevels
Electrons are distributed across different energy levels, often represented by the principal quantum number (n). These levels are further divided into sublevels, designated by the letters s, p, d, and f. Each sublevel has a specific number of orbitals and can therefore hold a specific number of electrons:
- s sublevel: One orbital, holding a maximum of 2 electrons.
- p sublevel: Three orbitals, holding a maximum of 6 electrons.
- d sublevel: Five orbitals, holding a maximum of 10 electrons.
- f sublevel: Seven orbitals, holding a maximum of 14 electrons.
The Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule
Two fundamental principles govern the filling of electrons into orbitals:
-
Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill orbitals starting from the lowest energy level and moving upwards. This means the orbitals are filled in a specific order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, and 7p.
-
Hund's Rule: Within a sublevel, electrons will individually occupy each orbital before pairing up. This minimizes electron-electron repulsion and leads to a more stable configuration. Each orbital gets one electron before any orbital gets two.
Determining Barium's Electronic Configuration
Barium (Ba) has an atomic number of 56, meaning it has 56 protons and 56 electrons in a neutral atom. Using the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, we can systematically fill the orbitals:
- 1s²: The first energy level (n=1) has only an s sublevel, which holds two electrons.
- 2s² 2p⁶: The second energy level (n=2) contains an s sublevel and a p sublevel, holding a total of 8 electrons (2 + 6).
- 3s² 3p⁶: The third energy level (n=3) also has an s and a p sublevel, accommodating another 8 electrons.
- 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶: The fourth energy level (n=4) has s, p, and d sublevels, holding 18 electrons in total.
- 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶: The fifth energy level (n=5) similarly contains s, p, and d sublevels, accommodating another 18 electrons.
- 6s²: Finally, the sixth energy level (n=6) contains only two electrons in the s sublevel.
Therefore, the complete electronic configuration of barium is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶ 6s².
Simplified Notation: Noble Gas Configuration
For convenience, we can also express barium's electronic configuration using a noble gas shorthand notation. The noble gas preceding barium in the periodic table is Xenon (Xe), which has an electronic configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶. Therefore, barium's configuration can be simplified to: [Xe] 6s². This notation clearly indicates that barium's outermost electrons occupy the 6s orbital.
The Significance of Barium's Electronic Configuration
Barium's electronic configuration profoundly influences its chemical and physical properties:
Reactivity:
The two electrons in the 6s orbital are relatively loosely held. This makes barium highly reactive, readily losing these two electrons to form a +2 ion (Ba²⁺). This reactivity is characteristic of alkaline earth metals. Barium readily reacts with water, oxygen, and acids, often with vigorous reactions.
Oxidation States:
Barium almost exclusively exhibits a +2 oxidation state due to the ease with which it loses its two valence electrons. Higher oxidation states are extremely rare and unlikely under normal conditions.
Chemical Bonding:
The +2 charge of the barium ion leads to the formation of ionic bonds with electronegative elements like oxygen, chlorine, and sulfur. These bonds form the basis of various barium compounds.
Applications:
Barium's unique properties, stemming directly from its electronic configuration, lead to various applications:
- Barium Sulfate (BaSO₄): Used as a contrast agent in medical imaging (X-rays and CT scans) due to its high atomic number and opacity to X-rays. Its low solubility ensures it's non-toxic when ingested.
- Barium Carbonate (BaCO₃): Used in the manufacturing of glass and ceramics, improving their optical properties and durability.
- Barium Titanate (BaTiO₃): A ferroelectric material used in capacitors and other electronic components due to its high dielectric constant.
- Barium Nitrate (Ba(NO₃)₂): Used in pyrotechnics to produce a bright green color in fireworks.
Exceptions to the Aufbau Principle: A Deeper Look
While the Aufbau principle provides a generally accurate prediction of electronic configurations, certain exceptions exist, particularly in transition metals and lanthanides/actinides. These exceptions often arise due to the close energy levels of certain orbitals and the effects of interelectronic repulsion. Although barium doesn't directly exhibit an exception to the Aufbau principle in its ground state configuration, understanding such exceptions helps provide a more complete picture of electronic structure.
Factors influencing deviations from the Aufbau Principle:
- Shielding effects: Inner electrons shield outer electrons from the full nuclear charge. This shielding effect varies among orbitals.
- Inter-electronic repulsion: Repulsive forces between electrons affect orbital energies.
- Relativistic effects: At high atomic numbers, relativistic effects become significant, altering electron velocities and orbital energies.
The energy differences between orbitals are crucial. A small energy difference might mean that it becomes energetically favorable for an electron to jump to a higher energy orbital. In such instances, the filling order predicted by the Aufbau principle would be slightly altered.
Conclusion
Barium's electronic configuration, [Xe] 6s², is fundamental to understanding its chemical reactivity, bonding behavior, and numerous applications. This configuration, determined by the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule, highlights the importance of atomic structure in predicting and explaining the properties of elements. While exceptions to the Aufbau principle exist in other elements, barium's configuration follows the standard filling pattern, providing a clear example of how electronic structure dictates chemical behavior. The study of barium's electronic configuration serves as an excellent foundation for exploring the intricacies of atomic structure and the periodic trends across the entire periodic table. Its importance in various fields, from medical imaging to pyrotechnics, underscores the practical relevance of understanding the fundamental principles of chemistry. Further exploration of the electronic structure of elements can lead to a deeper appreciation for the diversity and complexity of the chemical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Quantity That Has Magnitude And Direction
Mar 19, 2025
-
Most Tubular Reabsorption Occurs In The
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is 98 A Prime Or Composite Number
Mar 19, 2025
-
Greatest Common Divisor Of 20 And 30
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization For 300
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Electronic Configuration Of Barium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
