What Is The Prime Factorization For 300
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
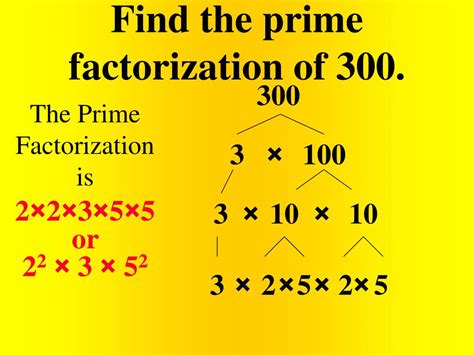
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization for 300? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Prime factorization. The phrase itself might conjure up memories of tedious math classes, but understanding prime factorization is fundamental to a deeper grasp of number theory and has practical applications in cryptography and computer science. This article will not only explain what the prime factorization of 300 is but also explore the broader concepts of prime numbers and factorization, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this important mathematical concept.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we delve into the factorization of 300, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered a prime number.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This was proven by Euclid centuries ago, a testament to their enduring mathematical significance.
- Distribution: While the distribution of prime numbers is seemingly random, there are patterns and conjectures (like the Riemann Hypothesis) that mathematicians continue to explore.
What is Factorization?
Factorization, in its simplest form, is the process of breaking down a number into smaller numbers that, when multiplied together, equal the original number. These smaller numbers are called factors. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because 1 x 12 = 12, 2 x 6 = 12, and 3 x 4 = 12.
Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
Prime factorization is a special type of factorization where a number is expressed as a product of only prime numbers. This process is unique for every composite number (a number that is not prime). This uniqueness is encapsulated by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every composite number can be represented as a unique product of prime numbers, regardless of the order. This theorem is a cornerstone of number theory, offering a fundamental way to understand the building blocks of numbers.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 300
Now, let's tackle the prime factorization of 300. We can use a variety of methods to achieve this:
Method 1: Factor Tree
A factor tree is a visual method to break down a number into its prime factors.
- Start with 300.
- Find any two factors of 300. Let's choose 2 and 150.
- Break down 150 into its factors: 2 and 75.
- Break down 75 into its factors: 3 and 25.
- Break down 25 into its factors: 5 and 5.
Now, let's represent this in a tree structure:
300
/ \
2 150
/ \
2 75
/ \
3 25
/ \
5 5
The prime factors at the end of the branches are 2, 2, 3, 5, and 5. Therefore, the prime factorization of 300 is: 2² x 3 x 5²
Method 2: Repeated Division
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until you reach 1.
- Start with 300.
- Divide by 2: 300 / 2 = 150
- Divide by 2 again: 150 / 2 = 75
- Divide by 3: 75 / 3 = 25
- Divide by 5: 25 / 5 = 5
- Divide by 5: 5 / 5 = 1
This shows that 300 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 5, which is equivalent to 2² x 3 x 5².
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization might seem like a purely mathematical exercise, but it has significant applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: RSA encryption, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors. The security of online transactions and data protection depends on this principle.
-
Computer Science: Prime factorization algorithms are crucial in areas like hashing, random number generation, and data compression.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory, with deep connections to other mathematical areas like modular arithmetic and algebraic number theory.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a crucial role in error correction codes, ensuring data integrity during transmission.
Beyond 300: Exploring Other Factorizations
Understanding the prime factorization of 300 provides a solid foundation for tackling the factorization of other numbers. The same methods – factor trees and repeated division – can be applied to any composite number. The key is to systematically break down the number into its prime constituents until you're left only with prime numbers.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those seeking a deeper dive into the world of prime numbers and factorization, here are some advanced concepts to explore:
- The Sieve of Eratosthenes: An ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
- The Riemann Hypothesis: One of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics, related to the distribution of prime numbers.
- Miller-Rabin Primality Test: A probabilistic test to determine if a number is prime. It's widely used in cryptography because of its efficiency.
- AKS Primality Test: A deterministic primality test, meaning it guarantees the correctness of its result.
Conclusion: The Importance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 300, as we've demonstrated, is 2² x 3 x 5². However, the significance extends far beyond this specific example. Understanding prime factorization provides a fundamental understanding of number theory, with practical applications spanning various fields. From securing online transactions to developing efficient algorithms, the ability to break down numbers into their prime factors remains a cornerstone of modern mathematics and computer science. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of this important concept, laying the groundwork for further exploration and a deeper appreciation of the fascinating world of prime numbers. Remember, the seemingly simple act of finding the prime factors of a number holds a world of mathematical complexity and practical utility within it.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Planet Is Called The Red Planet
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is Xlvi In Roman Numerals
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Inches Are 20 Cm
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 20
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Yards Is 300 Ft
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization For 300 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
