Find The Missing Values In The Ratio Table
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
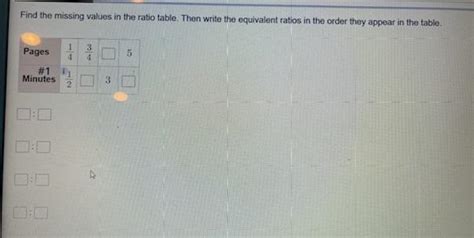
Table of Contents
Finding Missing Values in Ratio Tables: A Comprehensive Guide
Ratio tables are fundamental tools in mathematics, used to represent proportional relationships between two or more quantities. Understanding how to find missing values in these tables is crucial for solving a wide range of problems in various fields, from simple cooking recipes to complex engineering calculations. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to master this essential skill.
Understanding Ratio Tables
A ratio table displays equivalent ratios. Equivalent ratios are ratios that represent the same proportional relationship. For example, the ratios 1:2, 2:4, and 3:6 are all equivalent because they all simplify to the same fundamental ratio, 1:2. The table organizes these ratios in a structured format, making it easier to identify patterns and solve for missing values.
A typical ratio table has columns representing different quantities, with rows showing equivalent ratios. Missing values are represented by blanks or placeholders. The goal is to determine the values that maintain the consistent proportional relationship across the table.
Methods for Finding Missing Values
Several methods can be employed to find missing values in ratio tables. The choice of method often depends on the complexity of the table and the information provided.
1. Using Equivalent Ratios
This is the most fundamental method. It relies on the understanding that equivalent ratios are obtained by multiplying or dividing both parts of a ratio by the same non-zero number.
Example:
Let's consider a simple ratio table:
| Quantity A | Quantity B |
|---|---|
| 2 | 6 |
| 4 | x |
| y | 18 |
To find the missing value 'x', we observe that the ratio in the first row is 2:6, which simplifies to 1:3. To obtain the second row, we multiplied both parts of the 1:3 ratio by 4 (2 x 2 = 4 and 3 x 2 = 6). Therefore, x = 12. To find the missing value 'y', we notice that 18 is 6 multiplied by 3. Applying this same multiplication to the 'Quantity A' column, we get y = 6. The complete table is:
| Quantity A | Quantity B |
|---|---|
| 2 | 6 |
| 4 | 12 |
| 6 | 18 |
2. Using the Unit Rate
The unit rate is the ratio of one quantity to one unit of another quantity. Finding the unit rate can simplify the process of determining missing values, especially when dealing with more complex tables.
Example:
Consider this table:
| Number of Apples | Cost ($) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 6 |
| 5 | x |
| y | 24 |
First, find the unit rate (cost per apple): 6$/3 apples = 2$/apple.
To find 'x', multiply the unit rate by the number of apples: 5 apples * 2$/apple = 10$.
To find 'y', divide the cost by the unit rate: 24$ / 2$/apple = 12 apples.
The complete table is:
| Number of Apples | Cost ($) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 6 |
| 5 | 10 |
| 12 | 24 |
3. Using Cross-Multiplication
Cross-multiplication is a powerful technique, especially useful when dealing with more complex ratio tables or when other methods prove less efficient. It is based on the principle that the product of the means equals the product of the extremes in a proportion.
Example:
Let's consider the table:
| Quantity A | Quantity B |
|---|---|
| 5 | 15 |
| 7 | x |
This can be written as a proportion: 5/15 = 7/x.
Cross-multiplying, we get: 5x = 15 * 7.
Solving for x: 5x = 105, x = 21.
The complete table:
| Quantity A | Quantity B |
|---|---|
| 5 | 15 |
| 7 | 21 |
4. Using Proportions
Similar to cross-multiplication, setting up a proportion is a versatile method. A proportion equates two ratios. Once the proportion is set up, you can use cross-multiplication or other algebraic techniques to solve for the missing values.
Example:
Consider this table:
| Distance (km) | Time (hours) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 2 |
| x | 5 |
The proportion can be set up as: 100/2 = x/5
Cross-multiplying: 2x = 500
Solving for x: x = 250
The complete table:
| Distance (km) | Time (hours) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 2 |
| 250 | 5 |
Handling More Complex Ratio Tables
More complex tables may involve more than two quantities or multiple missing values. The strategies discussed above can still be applied, but often require a more systematic approach.
Example of a complex table:
| Ingredients A | Ingredients B | Total Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| 2 cups | 3 cups | 5 cups |
| x cups | 9 cups | y cups |
| 8 cups | z cups | 20 cups |
Solving this table requires a step-by-step approach. We can find the ratio between Ingredients A and Ingredients B from the first row (2:3). Using this ratio, we can solve for 'x' and 'z' by setting up proportions:
-
For 'x': 2/3 = x/9 => x = 6
-
For 'z': 2/3 = 8/z => z = 12
Finally, we can calculate 'y' by summing Ingredients A and Ingredients B in the second row: y = 6 + 9 = 15
The completed table is:
| Ingredients A | Ingredients B | Total Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| 2 cups | 3 cups | 5 cups |
| 6 cups | 9 cups | 15 cups |
| 8 cups | 12 cups | 20 cups |
Practical Applications of Ratio Tables
The ability to solve for missing values in ratio tables is invaluable in many real-world applications:
- Cooking: Scaling recipes up or down.
- Construction: Calculating material quantities based on blueprints.
- Finance: Determining interest rates or investment returns.
- Science: Analyzing experimental data and creating dilutions.
- Mapping: Calculating distances and scales.
Troubleshooting and Common Mistakes
- Incorrect simplification of ratios: Always simplify ratios to their lowest terms to make calculations easier and avoid errors.
- Mixing units: Ensure consistent units throughout the table.
- Inconsistent ratios: Double-check your work if the ratios within the table appear inconsistent. An error has likely been made in your calculations.
- Algebraic errors: Be meticulous in your algebraic manipulations to avoid simple mistakes.
Conclusion
Finding missing values in ratio tables is a fundamental skill with broad applications. By mastering the techniques outlined in this guide, including using equivalent ratios, unit rates, cross-multiplication, and proportions, you can effectively tackle a wide range of problems involving proportional relationships. Remember to always approach problem-solving systematically, double-checking your work to ensure accuracy. Practice is key to building proficiency and confidence in this essential mathematical skill. Through consistent practice and understanding of these methods, you'll become proficient in solving even the most complex ratio table problems. This skill will undoubtedly prove beneficial in numerous academic and professional contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Milliliters In 1 75 Liters
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is Thirty Nine A Prime Number
Mar 15, 2025
-
Volume Is The Amount Of An Object Occupies
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Major Organic Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 15, 2025
-
One Of The Physical Properties Of Bases Is That They
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Find The Missing Values In The Ratio Table . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
