What Is The Step Down Transformer
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 7 min read
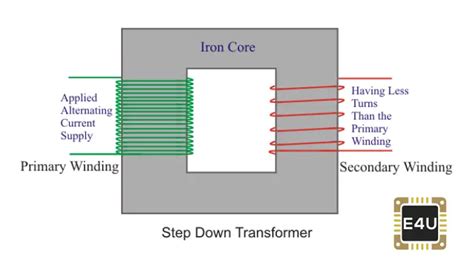
Table of Contents
What is a Step-Down Transformer? A Comprehensive Guide
A step-down transformer is a crucial component in various electrical systems, playing a vital role in reducing voltage levels while increasing current. Understanding its function, operation, and applications is essential for anyone working with electricity or interested in electrical engineering. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of step-down transformers, providing a detailed explanation for both beginners and experienced professionals.
Understanding the Basics of Transformers
Before diving into step-down transformers specifically, let's establish a foundational understanding of transformers in general. A transformer is a passive electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. This transfer occurs without a change in frequency, making transformers invaluable for efficient power management.
The core functionality of a transformer relies on two key components:
- Primary Winding: This coil receives the input voltage.
- Secondary Winding: This coil delivers the output voltage.
These windings are typically wound around a common ferromagnetic core, often made of laminated steel, which facilitates the magnetic coupling between them.
How a Step-Down Transformer Works
A step-down transformer, as its name suggests, reduces the voltage from a higher level to a lower level. This is achieved by having a higher number of turns in the primary winding compared to the lower number of turns in the secondary winding.
The relationship between the input voltage (V<sub>p</sub>), output voltage (V<sub>s</sub>), primary turns (N<sub>p</sub>), and secondary turns (N<sub>s</sub>) is governed by the following equation:
V<sub>p</sub> / V<sub>s</sub> = N<sub>p</sub> / N<sub>s</sub>
This fundamental equation illustrates the core principle: a smaller number of turns on the secondary winding results in a proportionally smaller output voltage. Conversely, the current increases proportionally in the secondary winding. This is because power (P) remains relatively constant (ignoring minor losses):
P = V<sub>p</sub> * I<sub>p</sub> ≈ V<sub>s</sub> * I<sub>s</sub>
Where:
- I<sub>p</sub> = Primary current
- I<sub>s</sub> = Secondary current
This equation highlights the inverse relationship between voltage and current in a transformer. As voltage decreases, current increases, and vice-versa, maintaining a relatively constant power level.
The Role of Electromagnetic Induction
The magic behind transformer operation lies in electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a fluctuating magnetic field within the core. This fluctuating field then induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary winding, generating an AC voltage at the output. The magnitude of this induced EMF is directly proportional to the ratio of the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings.
Key Components of a Step-Down Transformer
Beyond the primary and secondary windings, several other critical components contribute to the overall functionality and performance of a step-down transformer:
-
Core: The core, typically made of laminated silicon steel, provides a low-reluctance path for the magnetic flux, minimizing energy losses due to eddy currents and hysteresis. The lamination process helps reduce these losses significantly.
-
Insulation: Proper insulation is crucial to prevent short circuits and electrical shocks. Insulation materials vary depending on voltage and operating conditions.
-
Housing/Enclosure: The housing protects the internal components from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and physical damage. The material and design of the housing depend on the application and operating environment.
-
Terminals: These provide convenient connection points for the input and output circuits. The type of terminals (e.g., screw terminals, solder terminals) depends on the application and required current carrying capacity.
Applications of Step-Down Transformers
Step-down transformers are ubiquitous in modern electrical systems, finding applications across a wide range of industries and everyday devices. Some key applications include:
1. Power Distribution:
Large-scale power distribution networks rely heavily on step-down transformers to reduce the high voltage used for long-distance transmission to safer and more usable voltages for homes and businesses. High-voltage transmission minimizes energy losses during transmission over long distances.
2. Household Appliances:
Many household appliances, such as televisions, computers, and chargers, require lower voltages than the standard mains voltage. Step-down transformers ensure that these appliances receive the appropriate voltage for safe and efficient operation.
3. Electronic Circuits:
Step-down transformers are essential components in various electronic circuits, providing the necessary voltage levels for different parts of a system. This is particularly important in integrated circuits and microprocessors that operate at low voltages.
4. Battery Chargers:
Many battery chargers utilize step-down transformers to convert the higher mains voltage to the lower voltage required for charging a specific battery type. This ensures safe and efficient charging without damaging the battery.
5. Industrial Applications:
Numerous industrial applications, ranging from motors and control systems to welding equipment, require specific voltage levels. Step-down transformers are crucial in providing the required voltage for optimal performance and safety in these environments.
Types of Step-Down Transformers
Several types of step-down transformers exist, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions:
-
Power Transformers: These are designed for high power applications and typically used in power distribution networks and large industrial settings.
-
Isolation Transformers: These transformers provide electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits, enhancing safety by preventing ground faults and electrical shocks.
-
Audio Transformers: Used in audio equipment, these transformers match impedance levels between different components in an audio system.
-
Instrument Transformers: Used for measurement purposes, these transformers accurately step down voltage or current for measurement by instruments without significantly affecting the circuit being measured.
-
Miniature Transformers: These small transformers are often used in electronic devices and appliances where space is limited.
Step-Down Transformer Efficiency and Losses
While transformers are highly efficient devices, they are not perfect and experience some energy losses:
-
Copper Losses (I²R losses): These losses occur due to the resistance of the copper windings. They increase with current and are proportional to the square of the current.
-
Core Losses (Iron Losses): These losses are due to hysteresis and eddy currents within the transformer core. Hysteresis losses are caused by the energy required to magnetize and demagnetize the core material, while eddy current losses are due to circulating currents induced in the core.
-
Stray Losses: These losses occur due to leakage flux and other minor factors.
Selecting the Right Step-Down Transformer
Choosing the appropriate step-down transformer involves considering several critical factors:
-
Input Voltage: This must match the available power source.
-
Output Voltage: This should match the required voltage for the load.
-
Power Rating (VA): This determines the maximum power the transformer can handle without overheating. Always select a transformer with a power rating that exceeds the load's requirements.
-
Frequency: The transformer must operate at the correct frequency of the power source.
-
Operating Temperature: The transformer should be able to operate within the expected temperature range of the application.
Troubleshooting Common Step-Down Transformer Issues
While generally robust, step-down transformers can sometimes encounter problems. Common issues include:
-
Overheating: This usually indicates overloading, faulty windings, or poor ventilation.
-
No Output Voltage: This could be due to a blown fuse, faulty windings, or a problem with the power source.
-
Humming Noise: Excessive humming can suggest loose parts, core saturation, or problems with the magnetic circuit.
Addressing these issues may require professional assistance, depending on the complexity of the problem and safety considerations.
Safety Precautions when Working with Step-Down Transformers
Always prioritize safety when working with step-down transformers:
-
Never work on a live transformer. Always disconnect the power before attempting any repairs or maintenance.
-
Use appropriate safety equipment, including insulated tools and gloves.
-
Be aware of high voltages present in some transformers, even when disconnected.
-
Ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
-
Follow all manufacturer's instructions and safety guidelines.
Conclusion
Step-down transformers are essential components in modern electrical systems, enabling efficient and safe voltage reduction for a multitude of applications. Understanding their operation, components, applications, and safety precautions is critical for anyone involved in electrical engineering or working with electrical equipment. By carefully selecting the appropriate transformer and taking the necessary safety precautions, you can ensure reliable and efficient performance in your electrical systems. This comprehensive guide has provided a solid foundation for understanding and utilizing these vital devices. Remember always to prioritize safety and consult with qualified professionals when working with high voltage equipment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is The Poorest Conductor Of Electricity
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Name Of A 7 Sided Polygon
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is Difference Between Evaporation And Vaporization
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 4 9 As A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
-
Select All Of The Characteristics Of Phylum Echinodermata
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Step Down Transformer . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
