What Is The Chemical Formula Of Phosphorus Pentachloride
Juapaving
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
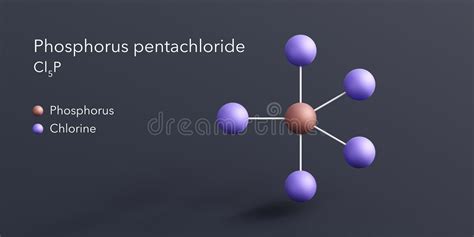
Table of Contents
What is the Chemical Formula of Phosphorus Pentachloride? A Deep Dive into its Properties and Reactions
Phosphorus pentachloride, a fascinating and important inorganic compound, plays a significant role in various chemical processes. Understanding its chemical formula, structure, properties, and reactions is crucial for anyone working with this substance or studying chemistry at an advanced level. This comprehensive article will delve into all aspects of phosphorus pentachloride, providing a detailed and informative overview.
The Chemical Formula: PCl<sub>5</sub>
The chemical formula of phosphorus pentachloride is PCl<sub>5</sub>. This formula clearly indicates that one molecule of phosphorus pentachloride consists of one phosphorus atom (P) covalently bonded to five chlorine atoms (Cl). This seemingly simple formula belies the complex chemistry and interesting properties of this compound.
Molecular Structure and Geometry
Understanding the structure of phosphorus pentachloride is key to grasping its reactivity. While the formula suggests a simple structure, the actual geometry is more intricate. In the gaseous and liquid states, PCl<sub>5</sub> adopts a trigonal bipyramidal geometry. This means that the phosphorus atom sits at the center, with three chlorine atoms arranged in a triangular plane around it (equatorial positions) and two other chlorine atoms positioned above and below this plane (axial positions).
Bond Lengths and Angles
The bond lengths and angles in phosphorus pentachloride are not all equal due to the geometry. The axial P-Cl bonds are longer than the equatorial P-Cl bonds. This difference in bond length arises from the different repulsive interactions experienced by the axial and equatorial chlorine atoms. The axial chlorine atoms experience greater repulsions from the equatorial chlorine atoms, resulting in a longer bond length. Similarly, the bond angles deviate from the ideal values expected for a perfect trigonal bipyramid.
Hybridisation
The hybridization of the phosphorus atom in PCl<sub>5</sub> is sp<sup>3</sup>d. This involves the mixing of one s orbital, three p orbitals, and one d orbital to form five hybrid orbitals, each of which is involved in a sigma bond with a chlorine atom.
Physical Properties of Phosphorus Pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride exhibits several characteristic physical properties:
- Appearance: It's a pale yellow-greenish crystalline solid at room temperature.
- Melting Point: Relatively low, around 160-161°C. It's important to note that it sublimes readily.
- Boiling Point: Decomposes before reaching its boiling point, preventing a typical boiling point observation.
- Solubility: Reacts violently with water, making it insoluble in typical solvents. It can dissolve in non-polar solvents like carbon disulfide (CS<sub>2</sub>) or benzene, but these solutions are often not stable.
- Odor: PCl<sub>5</sub> has a pungent, irritating odor, highlighting the importance of safety precautions during handling.
Chemical Reactions of Phosphorus Pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is a highly reactive compound, participating in a wide range of chemical reactions:
1. Hydrolysis: Reaction with Water
The reaction of PCl<sub>5</sub> with water is vigorous and exothermic, producing phosphoric acid (H<sub>3</sub>PO<sub>4</sub>) and hydrogen chloride (HCl). This reaction is summarized as follows:
PCl<sub>5</sub> + 4H<sub>2</sub>O → H<sub>3</sub>PO<sub>4</sub> + 5HCl
The extreme reactivity with water necessitates careful handling and storage in dry conditions.
2. Reaction with Alcohols
Phosphorus pentachloride reacts with alcohols to form alkyl chlorides and hydrogen chloride. This reaction is a useful method for converting alcohols to alkyl chlorides. A general representation is:
ROH + PCl<sub>5</sub> → RCl + POCl<sub>3</sub> + HCl
3. Reaction with Carboxylic Acids
Similar to its reaction with alcohols, PCl<sub>5</sub> reacts with carboxylic acids to form acyl chlorides. This is another significant application of PCl<sub>5</sub> in organic synthesis:
RCOOH + PCl<sub>5</sub> → RCOCl + POCl<sub>3</sub> + HCl
4. Chlorination Reactions
PCl<sub>5</sub> is a powerful chlorinating agent, capable of adding chlorine atoms to various organic compounds. For instance, it can convert ketones to gem-dichlorides:
R<sub>2</sub>C=O + PCl<sub>5</sub> → R<sub>2</sub>CCl<sub>2</sub> + POCl<sub>3</sub>
5. Dissociation and Ionization
In non-aqueous solvents, PCl<sub>5</sub> can undergo ionization and form ions. For example, in polar solvents, it can dissociate into the tetrachlorophosphonium cation ([PCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>+</sup>) and the hexachlorophosphate anion ([PCl<sub>6</sub>]<sup>−</sup>):
2PCl<sub>5</sub> ⇌ [PCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>+</sup> + [PCl<sub>6</sub>]<sup>−</sup>
Industrial Applications of Phosphorus Pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride finds diverse applications in various industries:
- Chlorinating Agent: Its primary use is as a chlorinating agent in the synthesis of organic and inorganic compounds, including pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
- Catalyst: In some reactions, it acts as a catalyst, speeding up the rate of chemical transformations.
- Dehydrating Agent: It can also act as a dehydrating agent, removing water molecules from certain substances.
- Synthesis of Other Phosphorus Compounds: PCl<sub>5</sub> serves as a starting material for the production of other valuable phosphorus-containing compounds.
Safety Precautions
Due to its high reactivity and corrosive nature, phosphorus pentachloride demands careful handling. The following safety precautions are essential:
- Eye Protection: Always wear safety goggles or a face shield.
- Respiratory Protection: Use a respirator to avoid inhalation of fumes.
- Gloves: Wear appropriate chemical-resistant gloves.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from moisture and incompatible materials.
Conclusion
Phosphorus pentachloride (PCl<sub>5</sub>), with its distinctive trigonal bipyramidal structure and potent reactivity, is a versatile compound with a wide array of applications in chemistry and industry. Understanding its chemical formula, properties, and reactions is crucial for safe and efficient handling and utilization in various chemical processes. The importance of safety precautions during handling cannot be overstated, emphasizing the need for proper protective equipment and procedures to prevent accidents and health hazards. Its role as a chlorinating agent and its involvement in various synthetic routes highlight its significance in chemical synthesis. Further research into its properties and applications continues to broaden our understanding of this fascinating compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Ph Given Pka
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Pitch Of A Sound Is Determined By What
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is 2 3 Less Than 1 2
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is 23 A Prime Number Or Composite
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is The Square Root Of 45 A Rational Number
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Chemical Formula Of Phosphorus Pentachloride . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
