What Is The Area Of The Figure
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
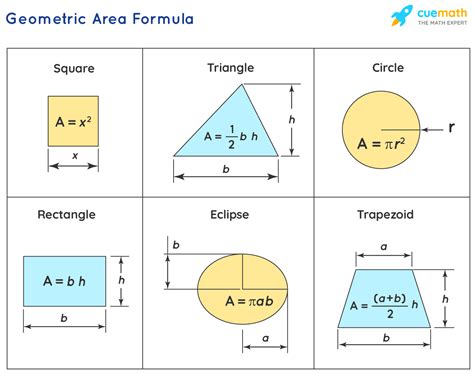
Table of Contents
What is the Area of the Figure? A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Area
Determining the area of a figure is a fundamental concept in geometry with widespread applications in various fields, from architecture and engineering to art and design. Understanding how to calculate the area of different shapes is crucial for solving real-world problems and mastering more advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will explore various methods for calculating the area of different figures, focusing on both common and less familiar shapes. We'll also delve into the importance of understanding units and the application of area calculations in practical scenarios.
Understanding Area: The Basics
Before we dive into specific shapes, let's establish a clear understanding of what "area" means. Simply put, the area of a two-dimensional figure is the amount of space enclosed within its boundaries. We typically measure area in square units, such as square centimeters (cm²), square meters (m²), square feet (ft²), or square miles (mi²). The choice of unit depends on the scale of the figure being measured.
The fundamental concept is that area represents the number of unit squares that can fit inside the figure. Visualizing this helps to grasp the meaning of area calculations.
Calculating the Area of Common Shapes
Let's start with some commonly encountered shapes and their respective area formulas:
1. Rectangle
A rectangle is a four-sided polygon with four right angles. The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length (l) by its width (w):
Area of a rectangle = l * w
For example, a rectangle with a length of 5 cm and a width of 3 cm has an area of 15 cm².
2. Square
A square is a special type of rectangle where all four sides are equal in length (s). Therefore, the area of a square is simply the side length squared:
Area of a square = s²
A square with a side length of 4 inches has an area of 16 square inches.
3. Triangle
The area of a triangle is calculated using its base (b) and height (h):
Area of a triangle = (1/2) * b * h
The height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex. Note that this formula applies to all types of triangles – right-angled, equilateral, isosceles, and scalene.
4. Circle
The area of a circle is determined using its radius (r), which is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference:
Area of a circle = π * r²
Where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
5. Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon with opposite sides parallel and equal in length. Its area is calculated using its base (b) and height (h):
Area of a parallelogram = b * h
The height is the perpendicular distance between the two parallel bases.
6. Trapezoid
A trapezoid (or trapezium) is a four-sided polygon with at least one pair of parallel sides (bases). The area is calculated using the lengths of the two parallel sides (b₁ and b₂) and the height (h):
Area of a trapezoid = (1/2) * (b₁ + b₂) * h
Calculating the Area of More Complex Figures
Many figures are not simple shapes. Calculating their area often requires breaking them down into smaller, simpler shapes whose areas can be individually calculated and then summed.
1. Composite Figures
Composite figures are made up of two or more simple shapes combined. To find the area, you must:
- Identify the individual shapes: Carefully dissect the composite figure into rectangles, triangles, circles, etc.
- Calculate the area of each shape: Use the appropriate formula for each shape.
- Sum the areas: Add the areas of all the individual shapes to find the total area of the composite figure.
2. Irregular Shapes
Calculating the area of irregular shapes can be more challenging. Approximation methods are often necessary. These include:
- Grid method: Overlay a grid of squares over the irregular shape and count the number of squares completely or partially inside the shape. This provides an estimate of the area.
- Planimeter: A planimeter is a mechanical or digital instrument used to measure the area of an irregular shape by tracing its perimeter.
Units and Conversions
It's crucial to maintain consistency in units throughout the calculation process. If the dimensions are given in centimeters, the area will be in square centimeters. If you're working with different units, you must convert them to a common unit before performing the calculations. For example, if the length is in meters and the width is in centimeters, convert both to either meters or centimeters before calculating the area.
Remember standard unit conversions:
- 1 meter (m) = 100 centimeters (cm)
- 1 foot (ft) = 12 inches (in)
- 1 mile (mi) = 5280 feet (ft)
Practical Applications of Area Calculation
Understanding how to calculate area has many practical applications:
- Construction and Engineering: Determining the amount of material needed for a building project, calculating the surface area of walls for painting, and designing floor plans.
- Agriculture: Calculating the size of a field for planting, determining fertilizer requirements, and estimating crop yields.
- Real Estate: Calculating the size of a property, determining property taxes, and assessing land value.
- Art and Design: Creating scaled drawings, designing patterns, and calculating the amount of material needed for a craft project.
- Cartography: Calculating the area of countries, states, or other geographical regions.
- Physics: Calculating various physical quantities such as pressure and force.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For more advanced applications, consider exploring:
- Calculus: Calculus provides powerful tools for calculating the area of irregular shapes and surfaces that cannot be easily broken down into simpler shapes. Integration techniques are particularly useful.
- Solid Geometry: Extending area calculations to three-dimensional shapes involves calculating surface area and volume.
- Computer-aided design (CAD) software: CAD software can automatically calculate the area of complex shapes, simplifying the process considerably.
Conclusion
Calculating the area of a figure is a fundamental skill with a wide range of practical applications. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the methods used to calculate the area of various shapes, from simple rectangles to more complex composite figures and irregular shapes. Mastering these techniques is essential for success in many fields, allowing for accurate measurements, efficient resource allocation, and informed decision-making. Remember to always double-check your calculations and pay close attention to units for accurate results. Further exploration of advanced concepts will enhance your understanding and broaden the applicability of this essential mathematical skill. By understanding the fundamentals and utilizing the techniques described, you'll be well-equipped to tackle area calculations confidently and accurately in any context.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Difference Between Endothermic And Exothermic
Mar 21, 2025
-
Lowest Common Factor Of 15 And 20
Mar 21, 2025
-
Simple Compound And Complex Sentences Worksheet
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Functional Unit Of The Kidney Is The
Mar 21, 2025
-
During What Moon Phase Is A Solar Eclipse
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Area Of The Figure . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
