During What Moon Phase Is A Solar Eclipse
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
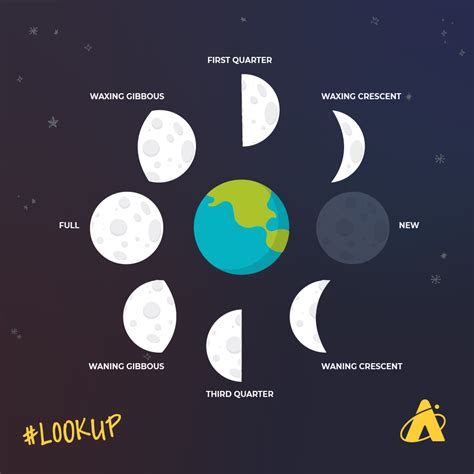
Table of Contents
During What Moon Phase is a Solar Eclipse? Understanding the Celestial Dance
A solar eclipse, a breathtaking celestial event, captivates audiences worldwide. But what cosmic alignment makes this spectacle possible? The simple answer is that a solar eclipse occurs only during a new moon phase. This article delves deep into the mechanics of solar eclipses, explaining the crucial role of the new moon, the different types of solar eclipses, and the fascinating science behind this awe-inspiring phenomenon.
The New Moon: A Necessary Condition for Solar Eclipses
The moon orbits the Earth, and as it does, its illuminated portion changes, creating the familiar phases we see from Earth. A new moon occurs when the moon is positioned between the Earth and the Sun. From our perspective, the sunlit side of the moon is facing away from us, rendering it invisible in the night sky. This seemingly simple positioning is the fundamental prerequisite for a solar eclipse.
Why a New Moon is Crucial
Imagine the Sun, the Earth, and the Moon aligned in a straight line. The Sun, the primary light source, shines its light onto the moon. However, during a new moon, the Moon sits directly between the Earth and the Sun, casting its shadow onto the Earth. This shadow is what we experience as a solar eclipse. Without the new moon's precise placement, the moon's shadow would miss the Earth entirely, and we wouldn't witness this spectacular event.
Types of Solar Eclipses: A Closer Look
While a new moon is essential, it's not the sole determining factor. The type of solar eclipse we see depends on the alignment and relative positions of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. Three main types exist:
1. Total Solar Eclipse: A Crown of Fire
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon completely blocks the Sun's disk from our perspective. This happens because the Moon's apparent size (as seen from Earth) is slightly larger than the Sun's. The resulting effect is dramatic: the sky darkens dramatically, stars may become visible, and the Sun's corona – its outer atmosphere – becomes visible as a breathtaking halo of light. This "crown of fire" is a truly unforgettable sight.
The path of totality, the area on Earth where the total eclipse is visible, is relatively narrow. People outside this path experience a partial eclipse.
2. Partial Solar Eclipse: A Bite Out of the Sun
A partial solar eclipse occurs when the Moon only partially obscures the Sun. This happens when the alignment isn't perfect, and the Moon's shadow only grazes the Earth. The Sun appears as a crescent, with a portion seemingly "missing." While impressive, it lacks the dramatic effect of a total eclipse. The degree of partial obscuration varies depending on the observer's location.
3. Annular Solar Eclipse: The Ring of Fire
An annular solar eclipse happens when the Moon is farther from Earth than usual in its elliptical orbit. Consequently, its apparent size is smaller than the Sun's. The Moon covers the Sun's center, but a bright ring of the Sun's disk remains visible around the Moon's silhouette. This ring of fire creates a mesmerizing visual effect, a unique spectacle distinct from both total and partial eclipses.
The Geometry of Eclipses: Orbital Mechanics and Alignment
The occurrence of solar eclipses isn't a random event. It's a result of the precise orbital mechanics of the Earth and Moon. Several factors contribute to the timing and type of solar eclipse:
-
The Moon's Orbit: The Moon's orbit around the Earth isn't perfectly circular but slightly elliptical. This varying distance influences the apparent size of the Moon in the sky, affecting whether the eclipse is total, partial, or annular.
-
The Earth's Orbit: The Earth's orbit around the Sun is also elliptical. This variation affects the apparent size of the Sun and influences the eclipse's visibility from different locations on Earth.
-
Orbital Planes: The Moon's orbital plane is tilted relative to the Earth's orbital plane around the Sun. Eclipses only happen when the Moon crosses the ecliptic plane (the Earth's orbital plane) during a new moon. This alignment is relatively rare, which is why solar eclipses aren't a monthly occurrence.
-
Saros Cycle: The cyclical nature of eclipses is explained by the Saros cycle, a period of approximately 18 years and 11 days. After this cycle, similar eclipses occur, although they appear at different locations on Earth.
Safety Precautions During Solar Eclipses: Protecting Your Eyes
Witnessing a solar eclipse is an awe-inspiring experience, but direct viewing of the Sun during an eclipse can cause serious and permanent eye damage. Never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection. Specialized solar viewing glasses, which meet the ISO 12312-2 safety standard, are crucial for safe viewing.
Improvised methods, such as sunglasses or exposed film, are insufficient and can still cause harm. Always prioritize your eye health and use appropriate safety equipment.
Predicting Solar Eclipses: The Science of Celestial Foresight
Predicting solar eclipses is a testament to our understanding of celestial mechanics. Astronomers use sophisticated calculations to pinpoint the date, time, and location of future eclipses, allowing for meticulous planning and observation. These predictions rely on precise knowledge of the orbital parameters of the Earth and Moon, accounting for gravitational interactions and other celestial influences. These accurate predictions allow people to prepare for and safely witness these magnificent events.
Cultural Significance and Historical Importance of Solar Eclipses
Throughout history, solar eclipses have held significant cultural and religious meaning for various civilizations. Often interpreted as omens or supernatural events, they have inspired awe, fear, and wonder. From ancient myths and legends to modern-day celebrations, solar eclipses have played a significant role in human history and continue to fascinate and intrigue us. Understanding their scientific basis, however, demystifies the phenomenon, enabling us to appreciate the remarkable interplay of celestial bodies that brings about this stunning spectacle.
Conclusion: The Marvel of a Solar Eclipse
The occurrence of a solar eclipse is a perfect example of the intricate dance between the Sun, Moon, and Earth. It's a reminder of the complex, yet beautiful, mechanisms that govern our solar system. The next time you witness a solar eclipse, remember the specific alignment required, the role of the new moon, and the fascinating science behind this incredible event. But most importantly, remember to prioritize safety and protect your vision with proper eye protection. The sight of a solar eclipse is truly a wonder to behold, but only when viewed responsibly. Enjoy the show, but always keep safety as your top priority.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Legs Does Ant Have
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Demand Curve For A Monopolist Is
Mar 21, 2025
-
Examples Of Complete And Incomplete Metamorphosis
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Are The Prime Factors Of 160
Mar 21, 2025
-
Definition Of Rotational Motion In Physics
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about During What Moon Phase Is A Solar Eclipse . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
