What Is Prime Factorization Of 225
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
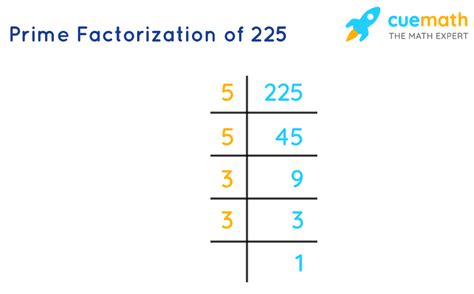
Table of Contents
What is Prime Factorization of 225? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, involves breaking down a composite number into its prime constituents. Understanding this process unlocks deeper insights into mathematical relationships and problem-solving. This article delves into the prime factorization of 225, explaining the method, its applications, and exploring related concepts in number theory.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Composite Numbers
Before diving into the factorization of 225, let's establish a foundational understanding of prime and composite numbers.
Prime Numbers: These are natural numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. They are the building blocks of all other numbers.
Composite Numbers: These are natural numbers greater than 1 that are divisible by numbers other than 1 and themselves. 225, for instance, is a composite number.
The number 1 is neither prime nor composite. This seemingly simple distinction forms the basis for many complex mathematical theorems and applications.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 225: Step-by-Step
To find the prime factorization of 225, we'll employ a systematic method, often using a factor tree. Here's how it works:
-
Start with the smallest prime number, 2: Is 225 divisible by 2? No, it's an odd number.
-
Move to the next smallest prime number, 3: Is 225 divisible by 3? Yes! 225 ÷ 3 = 75.
-
Continue with 75: Is 75 divisible by 3? Yes! 75 ÷ 3 = 25.
-
Now consider 25: Is 25 divisible by 3? No. Let's try the next prime number, 5. Is 25 divisible by 5? Yes! 25 ÷ 5 = 5.
-
Finally, we have 5: 5 is a prime number. We've reached the end of our factorization.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 225 is 3 x 3 x 5 x 5, which can be written more concisely as 3² x 5².
This means that 225 can be expressed as the product of only prime numbers: three squared multiplied by five squared. This representation is unique to each composite number; every composite number has only one unique prime factorization (Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic).
Visualizing Prime Factorization with a Factor Tree
A factor tree provides a visual representation of the factorization process:
225
/ \
3 75
/ \
3 25
/ \
5 5
Starting with 225, we branch out to its factors (3 and 75). We continue branching until we reach only prime numbers at the end of each branch.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The concept of prime factorization isn't merely a theoretical exercise; it has practical applications across various mathematical fields and even in computer science:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM): Prime factorization simplifies finding the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers.
-
Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization aids in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. By finding the prime factors of both the numerator and denominator, we can cancel out common factors.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers and their properties form the basis of many cryptographic systems, such as RSA encryption, which secures online transactions and data communication. The difficulty in factoring large numbers into their prime components underpins the security of these systems.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Understanding prime factorization is crucial in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory with applications in cryptography, computer science, and other areas.
-
Solving Diophantine Equations: Certain types of Diophantine equations (equations where only integer solutions are sought) can be solved using techniques that involve prime factorization.
Exploring Related Concepts in Number Theory
Several interconnected concepts in number theory build upon the foundation of prime factorization:
-
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (up to the order of the factors). This uniqueness is a fundamental property of prime numbers and forms the basis for many other results in number theory.
-
Divisibility Rules: Understanding prime factorization helps us better understand divisibility rules. For example, a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. This rule can be derived from the properties of prime factorization.
-
Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (divisors excluding the number itself). Prime factorization plays a role in identifying and understanding perfect numbers.
-
Abundant and Deficient Numbers: These are numbers where the sum of their proper divisors is greater than (abundant) or less than (deficient) the number itself. Prime factorization helps analyze the properties of these numbers.
Advanced Techniques for Prime Factorization
While the factor tree method is effective for smaller numbers, more sophisticated algorithms are needed for factoring very large numbers. These algorithms are crucial in cryptography, where the security of systems relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers.
-
Trial Division: A straightforward method, but inefficient for large numbers.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: An algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. Useful for pre-calculating primes to be used in other factorization methods.
-
Pollard's Rho Algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm, meaning it's not guaranteed to find a factor but is often efficient for finding smaller factors.
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): Currently the most efficient algorithm for factoring very large numbers. This is a sophisticated algorithm used in tackling numbers with hundreds of digits. It uses techniques from algebraic number theory.
Conclusion
The prime factorization of 225, while seemingly simple, serves as a gateway to understanding fundamental concepts in number theory. This seemingly straightforward calculation—3² x 5²—underpins significant mathematical ideas, impacting diverse fields from cryptography to computer science. The systematic approach and the various algorithms discussed demonstrate the depth and importance of prime factorization within the broader context of mathematics. As we explore deeper into number theory, the significance of prime numbers and their factorization becomes ever clearer. They are not just abstract concepts; they are the building blocks of arithmetic itself, shaping our understanding of numbers and their properties.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Water Is A Element Compound Or Mixture
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Heart Chambers Does A Frog Have
Mar 10, 2025
-
Why Is The Earth Referred To As The Blue Planet
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Fraction Is Equal To 3 6
Mar 10, 2025
-
Two Or More Elements Chemically Combined
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 225 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
