What Is Most Abundant Metal In Earth's Crust
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
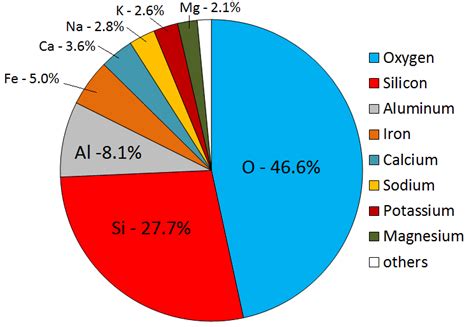
Table of Contents
What is the Most Abundant Metal in Earth's Crust? Unveiling the Reign of Aluminum
The Earth's crust, that thin, outermost layer of our planet, is a treasure trove of minerals and metals. While precious metals like gold and silver often capture our imaginations, the true abundance lies elsewhere. The answer to the question, "What is the most abundant metal in Earth's crust?" is a resounding aluminum. This seemingly ubiquitous metal, found in everything from soda cans to airplanes, significantly outweighs all other metallic elements in the Earth's surface layer. Let's delve deeper into the fascinating world of aluminum and its dominance in the Earth's crust.
Understanding Earth's Crustal Composition
Before we focus solely on aluminum, it's essential to appreciate the overall composition of the Earth's crust. The crust isn't a uniform entity; it's divided into two major types: continental crust and oceanic crust. Continental crust, thicker and less dense, is primarily composed of granite and other felsic rocks. Oceanic crust, thinner and denser, is largely composed of basalt and other mafic rocks. The relative proportions of elements differ between these two types of crust. However, even considering these variations, aluminum consistently reigns supreme among metals.
The Significance of Abundance
Understanding the abundance of elements is crucial for various scientific disciplines, including:
- Geology: Predicting the distribution of ore deposits, understanding plate tectonics, and modeling the Earth's formation.
- Material Science: Developing new alloys and materials with desired properties, influencing the choice of materials for various applications.
- Environmental Science: Assessing the environmental impact of mining and industrial processes, understanding geochemical cycles.
- Economic Geology: Identifying potential locations for mining operations, determining the economic viability of extraction processes.
The abundance of aluminum directly impacts these fields, influencing our understanding of the Earth and shaping our technological advancements.
Aluminum: The Unsung King of Metals
Aluminum, represented by the symbol Al and atomic number 13, is a lightweight, silvery-white metal. Its remarkable properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and malleability, make it incredibly versatile. However, these properties are not the only reason for its dominance. Its sheer abundance in the Earth's crust is a primary factor driving its widespread use.
Abundance and Prevalence
Aluminum constitutes approximately 8.1% of the Earth's crust by weight, far surpassing other metals in terms of abundance. To put this in perspective, iron, the next most abundant metal, makes up around 5%. This significant difference underlines aluminum's prominent role in the Earth's geological composition. It's not just abundant; it's ubiquitous, found in a vast array of minerals.
Key Aluminum-Bearing Minerals
Aluminum rarely exists in its native form (pure metal) in nature. Instead, it occurs primarily within various silicate minerals. Some of the most significant aluminum-bearing minerals include:
- Feldspars: These are the most abundant minerals in the Earth's crust and contain significant amounts of aluminum. Different types of feldspars exist, including orthoclase, plagioclase, and others, all contributing to the overall aluminum reservoir.
- Micas: These sheet silicates, such as muscovite and biotite, also incorporate considerable amounts of aluminum within their crystal structures.
- Clay Minerals: These are formed through the weathering of other silicate minerals and are important components of soils. Clays, such as kaolinite and montmorillonite, contain significant aluminum.
- Bauxite: While not as abundant as the previous minerals, bauxite is the primary ore from which aluminum is commercially extracted. Bauxite is an aluminum hydroxide mineral, making it a relatively concentrated source of the metal.
The Extraction of Aluminum: A Technological Marvel
Despite its abundance, extracting aluminum from its ore is not a trivial task. Unlike some metals that occur in relatively pure forms, aluminum is strongly bound within its mineral structures. The process requires significant energy input and sophisticated technology.
The Hall-Héroult Process: The Cornerstone of Aluminum Production
The most widely used method for aluminum production is the Hall-Héroult process. This electrolytic process involves dissolving bauxite in molten cryolite, an aluminum fluoride mineral, and then passing an electric current through the solution. This process reduces aluminum ions (Al3+) to metallic aluminum, which is then collected at the cathode.
The high energy demands of the Hall-Héroult process are a significant factor in the cost of aluminum production. However, advancements in technology and energy efficiency are constantly being made to reduce the environmental impact and cost associated with aluminum extraction.
The Environmental Impact of Aluminum Production
The production of aluminum has an undeniable environmental footprint. The process is energy-intensive, and the mining and processing of bauxite can lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, and water pollution. However, considerable efforts are being made to minimize these impacts through:
- Improved energy efficiency: Reducing energy consumption per unit of aluminum produced.
- Recycling: Aluminum is highly recyclable, and recycling significantly reduces energy consumption compared to primary production.
- Sustainable mining practices: Implementing responsible mining techniques to minimize environmental damage.
Aluminum's Versatility: Applications Across Industries
The remarkable combination of aluminum's abundance, properties, and relatively accessible extraction methods has led to its widespread use across numerous industries. Some of its key applications include:
- Transportation: Aluminum alloys are extensively used in automobiles, airplanes, and trains due to their lightweight nature and high strength.
- Packaging: Aluminum foil and cans are ubiquitous in food and beverage packaging.
- Construction: Aluminum is used in building materials such as roofing, siding, and window frames.
- Electrical Industry: Aluminum's excellent electrical conductivity makes it valuable in power transmission lines and electrical components.
- Consumer Goods: Aluminum is found in countless consumer products, from cookware to electronic devices.
Aluminum's Future: Sustainability and Innovation
With increasing concerns about climate change and resource sustainability, the future of aluminum production will likely be shaped by a focus on:
- Recycling: Improving aluminum recycling rates to reduce reliance on primary production.
- Sustainable mining practices: Minimizing the environmental impact of bauxite mining.
- Innovation in production technologies: Developing more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly aluminum extraction methods.
- Developing new aluminum alloys: Creating materials with enhanced properties for specific applications.
The journey of aluminum, from its abundant presence in the Earth's crust to its versatile applications in modern society, is a testament to human ingenuity and the power of materials science. As we move towards a more sustainable future, aluminum's role as a crucial metal will likely become even more pronounced, demanding innovative solutions for responsible extraction, processing, and utilization. The reign of aluminum as the most abundant metal in Earth's crust is not just a geological fact; it's a cornerstone of our modern technological world and a driving force for future innovations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Most Abundant Metal In Earth's Crust . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
