What Is A Suspension In Chemistry
Juapaving
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
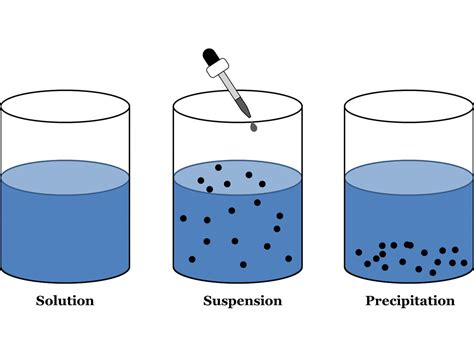
Table of Contents
What is a Suspension in Chemistry? A Comprehensive Guide
Suspensions are ubiquitous in our daily lives, from the mud stirred up in a puddle to the medications we take. Understanding what a suspension is in chemistry is crucial across various fields, from pharmaceuticals to environmental science. This comprehensive guide delves into the definition, properties, characteristics, types, applications, and preparation of suspensions, providing a thorough understanding of this fundamental chemical concept.
Defining a Suspension: A Heterogeneous Mixture
A suspension, in chemistry, is a heterogeneous mixture containing solid particles dispersed in a liquid medium. Unlike solutions where the solute dissolves completely, the particles in a suspension are relatively large (typically greater than 1 micrometer) and are not dissolved. These particles are visible to the naked eye or under a microscope and tend to settle out of the liquid over time if left undisturbed. This settling is a key characteristic that differentiates suspensions from other types of mixtures like solutions and colloids.
Think of it like this: if you mix sand into water, you create a suspension. The sand particles remain separate from the water, and eventually, they'll sink to the bottom. This contrasts with dissolving sugar in water, which forms a solution where the sugar particles are completely dispersed at a molecular level, invisible to the naked eye and don't settle.
Key Characteristics of Suspensions:
- Heterogeneous Nature: The components of a suspension are visibly distinct; you can see the solid particles separated from the liquid.
- Particle Size: Particles in a suspension are typically larger than 1 micrometer.
- Settling: Particles will settle out of the liquid if left undisturbed. This settling can be slow or fast, depending on factors such as particle size and density.
- Tyndall Effect: Suspensions exhibit the Tyndall effect, meaning they scatter light. If you shine a beam of light through a suspension, the path of the light becomes visible due to the scattering by the particles. This is unlike solutions which are transparent.
- Filterability: The solid particles in a suspension can be separated from the liquid using filtration.
Types of Suspensions: Exploring the Variations
Suspensions are classified based on different factors, including the nature of the dispersed phase and the dispersing medium. Some common classifications include:
1. Based on the Nature of the Dispersed Phase:
- Coarse Suspensions: These have relatively large particles that settle quickly. Examples include sand in water or clay in water.
- Fine Suspensions: These have smaller particles that settle more slowly. Many pharmaceutical suspensions fall under this category.
- Nano-suspensions: These contain particles in the nanoscale range (1-100 nanometers). These are increasingly important in drug delivery and other advanced applications.
2. Based on the Nature of the Dispersing Medium:
- Liquid Suspensions: The most common type, where solid particles are dispersed in a liquid. Examples range from mud to many pharmaceutical preparations.
- Gaseous Suspensions: Also known as aerosols, these are suspensions of solid or liquid particles in a gas. Examples include smoke, dust, and fog.
Applications of Suspensions: A Wide Range of Uses
Suspensions are incredibly versatile and find applications across diverse industries and fields.
1. Pharmaceuticals:
- Oral Suspensions: Many medications are formulated as suspensions for easier ingestion, particularly for children or patients who have difficulty swallowing pills. These suspensions often contain flavoring agents and sweeteners to improve palatability.
- Injectable Suspensions: Some vaccines and other injectable drugs are formulated as suspensions.
- Topical Suspensions: Creams and lotions are often suspensions of solid particles in a liquid or semi-solid base.
2. Cosmetics and Personal Care:
- Sunscreens: Many sunscreens are suspensions of fine particles that help to block ultraviolet radiation.
- Face Powders: These are suspensions of finely milled powders in a liquid or cream base.
- Lotions and Creams: Many lotions and creams contain solid particles dispersed in a liquid base.
3. Food Industry:
- Milk: Milk is a natural suspension of fat globules in water.
- Fruit Juices with Pulp: These contain suspended fruit particles.
- Salad Dressings: Many salad dressings are emulsions which are closely related to suspensions.
4. Environmental Science:
- Soil: Soil is a complex suspension of mineral particles, organic matter, and water.
- Sediment in Rivers and Lakes: Suspended sediment plays a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems.
- Air Pollution: Airborne particulate matter, such as dust and smoke, represents gaseous suspensions (aerosols) and has significant environmental consequences.
5. Industrial Applications:
- Paints: Paints are suspensions of pigment particles in a liquid vehicle.
- Ceramics: Ceramic slurries are suspensions of ceramic particles used in manufacturing.
- Mining: The processing of ores often involves suspensions of mineral particles.
Preparation of Suspensions: Achieving Stability
The preparation of stable suspensions requires careful control of various parameters to prevent settling, caking, and other undesirable effects. Key aspects include:
- Particle Size Reduction: Smaller particles tend to settle more slowly, thus milling or other size reduction techniques are often employed.
- Wetting Agents: These reduce the surface tension between the solid particles and the liquid, preventing clumping and improving dispersion.
- Suspending Agents: These increase the viscosity of the suspension, slowing down the rate of settling. Common suspending agents include polymers, gums, and clays.
- Flocculating Agents: These promote the formation of loose aggregates (flocs) of particles, preventing dense packing and caking.
- Protective Colloids: These form a protective layer around the particles, preventing aggregation and promoting stability.
- pH Adjustment: Controlling the pH of the suspension can influence the stability of the particles and prevent degradation.
Stable suspensions require a balance of these factors. Improper preparation can lead to rapid settling, caking, and changes in the physical and chemical properties of the suspension, rendering it ineffective or unusable.
Distinguishing Suspensions from Other Mixtures: Solutions and Colloids
It is important to differentiate suspensions from solutions and colloids, other types of mixtures.
Suspensions vs. Solutions:
- Particle Size: Suspensions have larger particles (>1 micrometer) compared to solutions, where the solute particles are dissolved at a molecular level.
- Visibility: Particles in suspensions are visible, whereas solutions are transparent.
- Settling: Particles in suspensions settle, whereas dissolved solutes in solutions do not.
- Filtration: Suspensions can be filtered, while solutions cannot.
Suspensions vs. Colloids:
- Particle Size: Suspensions have larger particles (>1 micrometer) than colloids (1-1000 nanometers).
- Settling: Particles in suspensions settle more readily than particles in colloids.
- Tyndall Effect: Both suspensions and colloids exhibit the Tyndall effect, but the scattering intensity is usually greater in suspensions.
- Filtration: Suspensions can be filtered, while colloids generally cannot be filtered by standard methods.
Conclusion: The Significance of Suspensions
Suspensions are essential in various fields, playing a crucial role in diverse applications. Understanding the properties, characteristics, and preparation of suspensions is paramount for researchers, scientists, and engineers in numerous disciplines. From the development of life-saving medications to the manufacturing of everyday products, the significance of suspensions in chemistry cannot be overstated. This comprehensive exploration underscores the importance of this fundamental chemical concept and its far-reaching implications. Further research into specific applications and advancements in suspension technology continues to broaden our understanding and unlock new possibilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Are Renewable Resources
Apr 05, 2025
-
A Rectangular Prism Has How Many Edges
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Algebraic Expressions Are Polynomials Check All That Apply
Apr 05, 2025
-
A Substance Formed As A Result Of A Chemical Reaction
Apr 05, 2025
-
A Frequency Polygon Is Graphed Using
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Suspension In Chemistry . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
