What Is A Prime Factorization Of 24
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
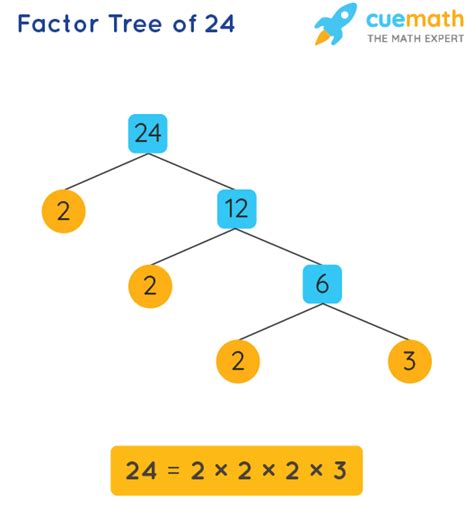
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 24? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 24?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding the why behind the process reveals fundamental concepts crucial to mathematics and computer science. This article will explore the prime factorization of 24 in detail, explaining the method, its significance, and its applications.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before delving into the prime factorization of 24, we need a firm grasp of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. They are the building blocks of all other numbers.
Key Characteristics of Prime Numbers:
- Divisibility: A prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This fundamental theorem has been proven and is a cornerstone of number theory.
- Uniqueness: Every composite number (a number that is not prime) can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This is the basis of prime factorization.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization (also known as prime decomposition) is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal a given number. This representation is unique for every composite number. It's like breaking down a number into its fundamental prime building blocks. Think of it as a recipe, where prime numbers are the ingredients, and the composite number is the final dish.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 24
Now, let's find the prime factorization of 24. We can achieve this using several methods:
Method 1: Factor Tree
The factor tree is a visual method that helps systematically break down the number into its prime factors.
-
Start with 24: We begin by finding any two factors of 24. Let's choose 2 and 12.
-
Branch Out: We draw branches from 24 to 2 and 12.
-
Continue Factoring: 2 is a prime number, so we circle it. 12 is not prime, so we continue factoring 12. Let's choose 2 and 6.
-
Repeat: We branch from 12 to 2 and 6. 2 is prime (circle it). 6 is not prime, so we factor it into 2 and 3.
-
Prime Factors: Both 2 and 3 are prime numbers, so we circle them.
The factor tree will look something like this:
24
/ \
2 12
/ \
2 6
/ \
2 3
Our prime factors are 2, 2, 2, and 3. Therefore, the prime factorization of 24 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 3, or 2³ x 3.
Method 2: Repeated Division
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number possible until you reach 1.
- Divide by 2: 24 divided by 2 is 12.
- Divide by 2 again: 12 divided by 2 is 6.
- Divide by 2 again: 6 divided by 2 is 3.
- Divide by 3: 3 divided by 3 is 1.
The prime factors used in the divisions are 2, 2, 2, and 3. Thus, the prime factorization is 2³ x 3.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of a number, seemingly a simple exercise, holds immense importance in various mathematical and computational fields:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Prime factorization is crucial for efficiently calculating the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides all the given numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the given numbers. By comparing the prime factorizations, finding the GCD and LCM becomes straightforward.
For example, let's find the GCD and LCM of 24 and 36:
-
Prime factorization of 24: 2³ x 3
-
Prime factorization of 36: 2² x 3²
-
GCD: We take the lowest power of each common prime factor: 2² x 3 = 12
-
LCM: We take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization: 2³ x 3² = 72
2. Cryptography
Prime factorization plays a fundamental role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptosystems like RSA. RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. The security of RSA hinges on this computational challenge; it's incredibly difficult to factor extremely large numbers, even with powerful computers.
3. Modular Arithmetic
Modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus), is widely used in computer science and cryptography. Prime numbers and their factorizations are essential to understanding and working with modular arithmetic.
4. Abstract Algebra
Prime factorization is a cornerstone of abstract algebra, particularly in ring theory and the study of ideals. Understanding the prime factorization of elements within various algebraic structures is crucial for analyzing their properties and relationships.
5. Number Theory Research
Prime factorization is central to many unsolved problems in number theory, such as the Riemann Hypothesis. Research into the distribution and properties of prime numbers continues to be a significant area of mathematical inquiry.
Beyond 24: Exploring Prime Factorization of Larger Numbers
The techniques used to factorize 24 can be applied to larger numbers, although the process can become more complex. For very large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are employed, as direct factorization becomes computationally expensive.
For example, let's consider the prime factorization of 100:
- Start with 100: We can choose 10 and 10.
- Factor 10: 10 is 2 x 5.
- Combine the primes: The prime factorization of 100 is 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 or 2² x 5².
Conclusion: The Enduring Power of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 24, while seemingly simple, unveils a world of mathematical depth. From its applications in cryptography and computer science to its fundamental role in number theory and abstract algebra, the concept of prime factorization demonstrates the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas. Understanding prime numbers and their ability to form the building blocks of all other numbers underscores their significance in various fields, showcasing the power of seemingly simple concepts in the wider landscape of mathematics. The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 24?", thus, leads us on a journey of discovery, highlighting the beauty and elegance of number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Stage Of Mitosis
Mar 09, 2025
-
How To Find The Area And Perimeter Of A Triangle
Mar 09, 2025
-
Smallest Particle Of An Element That Retains Its Properties
Mar 09, 2025
-
How To Know If A Number Is Divisible By 6
Mar 09, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons In P
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Prime Factorization Of 24 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
