What Is A Factor Of 86
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
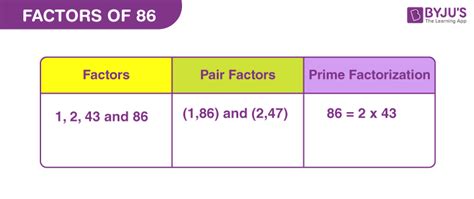
Table of Contents
- What Is A Factor Of 86
- Table of Contents
- What is a Factor of 86? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
- Understanding Factors and Divisors
- Finding the Factors of 86: A Step-by-Step Approach
- Prime Factorization and its Significance
- Implications of Prime Factorization for 86
- Divisibility Rules and their Application to 86
- Factors and their Applications in Different Mathematical Contexts
- Conclusion: The Significance of Factors and the Case of 86
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is a Factor of 86? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers. However, understanding the process and its implications delves into the fascinating world of number theory, revealing underlying principles that govern arithmetic and algebra. This article will explore the factors of 86 in detail, providing a comprehensive understanding not just of its divisors but also the broader mathematical concepts involved.
Understanding Factors and Divisors
Before we delve into the specific factors of 86, let's solidify our understanding of the fundamental terms. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a results in a whole number. This means there are no fractions or decimals involved.
Consider the number 12. Its factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Each of these numbers divides 12 evenly. We can express this mathematically as:
- 12 ÷ 1 = 12
- 12 ÷ 2 = 6
- 12 ÷ 3 = 4
- 12 ÷ 4 = 3
- 12 ÷ 6 = 2
- 12 ÷ 12 = 1
This simple example illustrates the concept of factors. Now, let's apply this understanding to the number 86.
Finding the Factors of 86: A Step-by-Step Approach
To find the factors of 86, we systematically check each whole number to see if it divides 86 without leaving a remainder. We can start with 1 and work our way up:
- 1: 86 ÷ 1 = 86 (1 is always a factor of any number)
- 2: 86 ÷ 2 = 43 (2 is a factor because 86 is an even number)
- 3: 86 ÷ 3 = 28.666... (3 is not a factor because it leaves a remainder)
- 4: 86 ÷ 4 = 21.5 (4 is not a factor)
- 5: 86 ÷ 5 = 17.2 (5 is not a factor)
- 6: 86 ÷ 6 = 14.333... (6 is not a factor)
- 7: 86 ÷ 7 = 12.285... (7 is not a factor)
- 8: 86 ÷ 8 = 10.75 (8 is not a factor)
- 9: 86 ÷ 9 = 9.555... (9 is not a factor)
- 10: 86 ÷ 10 = 8.6 (10 is not a factor)
- 11: 86 ÷ 11 = 7.818... (11 is not a factor)
- 12: 86 ÷ 12 = 7.166... (12 is not a factor)
- 13: 86 ÷ 13 = 6.615... (13 is not a factor)
- 14: 86 ÷ 14 = 6.142... (14 is not a factor)
- 17: 86 ÷ 17 = 5.058... (17 is not a factor)
- 17: 86 ÷ 17 ≈ 5.05 (17 is not a factor)
- 43: 86 ÷ 43 = 2 (43 is a factor)
- 86: 86 ÷ 86 = 1 (86 is always a factor of itself)
Therefore, the factors of 86 are 1, 2, 43, and 86.
Prime Factorization and its Significance
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. Prime factorization provides a unique representation of a number, regardless of the order of the factors.
To find the prime factorization of 86, we start by dividing it by its smallest prime factor:
86 = 2 × 43
Since 2 and 43 are both prime numbers, this is the prime factorization of 86. This representation is crucial in various mathematical applications, including simplifying fractions, finding the greatest common divisor (GCD), and the least common multiple (LCM) of numbers.
Implications of Prime Factorization for 86
The prime factorization of 86 (2 x 43) reveals several important characteristics:
- Even Number: The presence of the factor 2 indicates that 86 is an even number.
- Composite Number: Because 86 has more than two factors, it's classified as a composite number. Composite numbers are the opposite of prime numbers; they have more than two factors.
- Relationship between Factors: The factors 2 and 43 are directly related through the prime factorization. They are the building blocks of 86.
Divisibility Rules and their Application to 86
Divisibility rules are shortcuts that help determine whether a number is divisible by another number without performing long division. These rules can significantly speed up the process of finding factors. For 86, we can apply some common divisibility rules:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, or 8). Since 86 ends in 6, it's divisible by 2.
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. For 86, the sum of the digits (8 + 6 = 14) is not divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5. 86 doesn't end in 0 or 5, so it's not divisible by 5.
Applying these rules helps efficiently eliminate potential factors, reducing the number of divisions required.
Factors and their Applications in Different Mathematical Contexts
Understanding factors extends beyond simply identifying divisors. They are fundamental in various mathematical concepts:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them exactly. For example, finding the GCD is essential when simplifying fractions.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all the numbers. This is crucial in solving problems related to cycles and periodic events.
-
Algebraic Equations: Factors play a crucial role in solving quadratic and higher-degree equations by factoring expressions.
-
Number Theory: Factorization is a cornerstone of number theory, with profound implications in cryptography and other advanced mathematical fields.
Conclusion: The Significance of Factors and the Case of 86
The seemingly simple task of finding the factors of 86 opens a gateway to a deeper understanding of number theory and its far-reaching applications. While the factors of 86 – 1, 2, 43, and 86 – might appear straightforward, the process of finding them and understanding their implications within the broader context of mathematics highlights the fundamental role of factorization in numerous mathematical concepts and real-world applications. From divisibility rules to prime factorization, the exploration of factors offers a valuable insight into the elegance and interconnectedness of mathematical principles. Understanding these principles is crucial for success in various mathematical fields and provides a solid foundation for advanced studies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Volume Of One Drop Of Water
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 2
Mar 21, 2025
-
2 Cubic Feet Is How Many Quarts
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is A Row In The Periodic Table
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Degrees Is In A Rectangle
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Factor Of 86 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
