What Happens To Volume When Temperature Increases
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
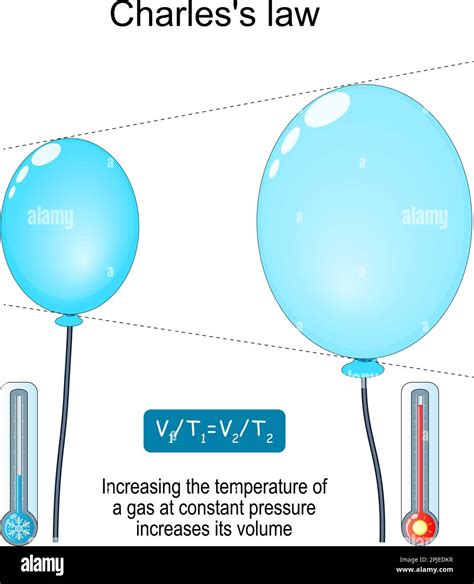
Table of Contents
What Happens to Volume When Temperature Increases? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the relationship between temperature and volume is fundamental in various scientific fields, from physics and chemistry to engineering and meteorology. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of thermal expansion, exploring its causes, effects, and applications across diverse materials and systems. We'll examine the ideal gas law, anomalous expansion of water, and practical implications of this fundamental principle.
The Fundamentals of Thermal Expansion
When the temperature of a substance increases, its particles gain kinetic energy, leading to increased vibrational motion. This heightened activity causes the particles to occupy more space, resulting in an expansion of the substance's volume. This phenomenon is known as thermal expansion. The magnitude of this expansion is dependent on several factors, including:
-
The material's nature: Different materials exhibit varying degrees of thermal expansion. Metals, for instance, generally expand more than ceramics or polymers. This difference is reflected in their coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE), a material property that quantifies the fractional change in size per degree change in temperature.
-
The initial temperature: The extent of expansion is often more significant at higher initial temperatures.
-
The temperature change: A larger temperature increase naturally leads to a greater volume expansion.
Types of Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is broadly classified into three types:
-
Linear Expansion: This describes the change in length of a solid object in response to a temperature change. The change in length (ΔL) is directly proportional to the original length (L), the temperature change (ΔT), and the linear coefficient of thermal expansion (α): ΔL = αLΔT.
-
Area Expansion: This refers to the change in surface area of an object due to a temperature change. The change in area (ΔA) is proportional to the original area (A), the temperature change (ΔT), and the area coefficient of thermal expansion (β), which is approximately twice the linear coefficient (β ≈ 2α): ΔA = βAΔT.
-
Volume Expansion: This accounts for the overall change in volume of a substance in response to a temperature change. The change in volume (ΔV) is proportional to the original volume (V), the temperature change (ΔT), and the volumetric coefficient of thermal expansion (γ), which is approximately three times the linear coefficient (γ ≈ 3α): ΔV = γVΔT.
The Ideal Gas Law and Thermal Expansion
For gases, the relationship between temperature and volume is most readily described by the ideal gas law: PV = nRT.
Where:
- P = pressure
- V = volume
- n = number of moles of gas
- R = the ideal gas constant
- T = temperature (in Kelvin)
This equation reveals a direct proportionality between volume (V) and temperature (T) when pressure (P) and the number of moles (n) remain constant. This means that if the temperature of an ideal gas increases while pressure remains constant, the volume will increase proportionally. This is known as Charles's Law.
Limitations of the Ideal Gas Law
It is crucial to remember that the ideal gas law is a simplification. Real gases deviate from ideal behavior, particularly at high pressures and low temperatures. Intermolecular forces and the finite volume of gas molecules become significant under these conditions, leading to deviations from the predicted linear relationship between temperature and volume.
Anomalous Expansion of Water
Water exhibits a unique behavior concerning thermal expansion. Unlike most substances, water's density is highest at 4°C (39.2°F). As the temperature increases or decreases from this point, the volume increases, meaning water expands both when heated above 4°C and when cooled below 4°C. This anomalous behavior is attributed to the hydrogen bonding in water molecules. This unusual expansion has significant implications for aquatic life and the overall environment. The ice formed on the surface of water bodies is less dense than the water beneath, acting as an insulating layer and preventing the freezing of the entire body of water.
Practical Implications and Applications of Thermal Expansion
Understanding and managing thermal expansion is crucial in numerous engineering and technological applications. Failure to account for these effects can lead to significant structural damage or malfunction. Some key examples include:
-
Civil Engineering: Bridges, buildings, and pavements are designed to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction to prevent cracking or buckling due to temperature fluctuations. Expansion joints are incorporated into structures to allow for this movement.
-
Mechanical Engineering: Engines and other mechanical systems must be designed to account for the expansion of components due to heat generated during operation. Precise tolerances are essential to ensure proper functionality and prevent jamming or damage.
-
Aerospace Engineering: The extreme temperature variations encountered in aerospace applications require careful consideration of thermal expansion in aircraft and spacecraft design. Materials with low coefficients of thermal expansion are often selected for critical components.
-
Precision Manufacturing: Thermal expansion needs to be accounted for in manufacturing processes that require high precision, such as semiconductor fabrication. Temperature control is essential to maintain the desired dimensions of components.
-
Thermometry: The principle of thermal expansion is utilized in various thermometers, where the expansion of a liquid (e.g., mercury or alcohol) is used to measure temperature.
-
Bimetallic Strips: These are made of two different metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion, bonded together. When heated, the strip bends due to the unequal expansion of the two metals, a principle used in thermostats and other temperature-sensitive devices.
Factors Affecting Thermal Expansion
Besides the inherent properties of the material, several other factors influence the extent of thermal expansion:
-
Pressure: Increased pressure generally reduces the extent of thermal expansion.
-
Phase Transitions: Phase changes (e.g., solid to liquid, liquid to gas) involve significant changes in volume and are not directly governed by the linear relationship expressed by the coefficients of thermal expansion.
-
Impurities and Alloying: The presence of impurities or alloying elements can alter the coefficient of thermal expansion of a material.
Conclusion
The relationship between temperature and volume is a fundamental principle with far-reaching implications. Understanding thermal expansion is crucial for engineers, scientists, and anyone involved in designing or working with materials and systems subject to temperature variations. From the design of bridges and buildings to the operation of precision machinery and the understanding of natural phenomena, the ability to predict and manage thermal expansion is essential for success. Further research continues to refine our understanding of thermal expansion across various materials and conditions, leading to innovations in materials science and engineering. The anomalous behavior of water and the deviations from ideal gas law behavior highlight the complex interplay of factors that can influence the response of a substance to changes in temperature, underscoring the continuous need for investigation and deeper understanding of this fundamental physical phenomenon.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is An Operator In Biology
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Happens To Volume When Temperature Increases . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
