What Does It Mean For A Solution To Be Saturated
Juapaving
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
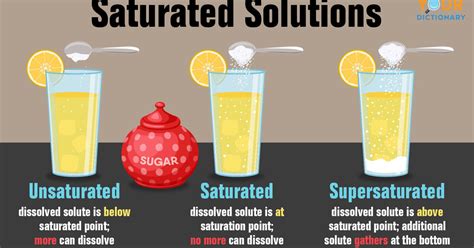
Table of Contents
What Does It Mean for a Solution to Be Saturated?
Understanding saturation in chemistry is crucial for various applications, from medicine and environmental science to industrial processes and everyday life. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the concept of saturated solutions, exploring its meaning, factors influencing it, and its practical implications. We'll cover everything from basic definitions to advanced concepts, ensuring you gain a complete understanding of this fundamental chemical principle.
Defining Saturation: A Solution at its Limit
A saturated solution is a chemical solution containing the maximum concentration of a solute dissolved in the solvent at a given temperature and pressure. In simpler terms, it's like a sponge that's completely full of water – no more water can be absorbed. Any additional solute added to a saturated solution will simply settle out of the solution as a precipitate, remaining undissolved. The point at which a solution becomes saturated is called the saturation point.
This definition highlights the key factors influencing saturation:
-
Temperature: Temperature plays a crucial role. Generally, increasing the temperature increases the solubility of most solids in liquids, allowing more solute to dissolve before reaching saturation. However, the relationship between temperature and solubility isn't always straightforward; some substances show a decrease in solubility with increasing temperature.
-
Pressure: Pressure significantly affects the solubility of gases in liquids. Increasing pressure increases the solubility of a gas, while decreasing pressure decreases it. This is why opening a carbonated beverage releases carbon dioxide gas – the pressure is reduced, and the solubility of CO2 decreases. The effect of pressure on the solubility of solids in liquids is typically negligible.
-
Nature of the Solute and Solvent: The chemical nature of both the solute (the substance being dissolved) and the solvent (the substance doing the dissolving) greatly influences the solubility and hence, the saturation point. Polar solvents tend to dissolve polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes. This is often summarized by the saying "like dissolves like." For example, salt (a polar compound) dissolves readily in water (a polar solvent), while oil (a nonpolar compound) doesn't.
Understanding Solubility and its Relationship to Saturation
Solubility refers to the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature and pressure to form a saturated solution. Solubility is often expressed in terms of grams of solute per 100 grams of solvent (g/100g) or moles of solute per liter of solution (mol/L). It's a crucial parameter in determining whether a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated.
Let's explore the different types of solutions based on their solute concentration relative to the saturation point:
-
Unsaturated Solution: An unsaturated solution contains less solute than the maximum amount that can dissolve at a given temperature and pressure. More solute can be added to an unsaturated solution and it will dissolve completely.
-
Saturated Solution: As previously defined, a saturated solution contains the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve at a given temperature and pressure. Any additional solute added will remain undissolved.
-
Supersaturated Solution: A supersaturated solution contains more solute than it can theoretically hold at a given temperature and pressure. These solutions are metastable, meaning they are in a state of unstable equilibrium. A small disturbance, such as adding a seed crystal or scratching the container, can cause the excess solute to precipitate out, returning the solution to a saturated state. Supersaturated solutions are often prepared by carefully cooling a saturated solution without disturbing it.
Factors Affecting Solubility and Saturation
Several factors, beyond temperature and pressure, influence the solubility of a substance and consequently, the saturation point of a solution. These include:
-
Particle Size: Smaller solute particles generally dissolve faster than larger particles because they have a greater surface area exposed to the solvent. While this affects the rate of dissolution, it doesn't change the ultimate saturation point.
-
Stirring or Agitation: Stirring or agitation increases the rate at which a solute dissolves by constantly bringing fresh solvent into contact with undissolved solute. Again, this impacts the rate of dissolution, not the final saturation point.
-
Presence of Other Solutes: The presence of other solutes in the solution can affect the solubility of a particular solute. This is known as the common ion effect, where the solubility of a sparingly soluble salt decreases in the presence of a common ion.
-
Intermolecular Forces: The strength of intermolecular forces between the solute and solvent molecules plays a significant role in solubility. Stronger attractive forces between solute and solvent molecules lead to greater solubility.
Practical Applications of Saturated Solutions
The concept of saturated solutions has numerous applications across various fields:
-
Crystallization: Saturated solutions are commonly used in crystallization processes to obtain pure solid substances. By carefully cooling a saturated solution, the excess solute precipitates out as crystals, leaving behind impurities in the solution.
-
Medicine: Many pharmaceutical formulations are prepared as saturated solutions to ensure a consistent and predictable drug delivery.
-
Environmental Science: Understanding saturation is essential for managing water quality, as saturated solutions can lead to the precipitation of harmful substances.
-
Industrial Processes: Saturated solutions play crucial roles in various industrial processes, such as electroplating, where a metal salt solution is used to deposit a layer of metal onto a substrate.
-
Food Science: Many food products utilize saturated solutions, like sugar syrups used in candies and preserves, where the high concentration of sugar prevents microbial growth.
Advanced Concepts: Solubility Product and Ion Product
For sparingly soluble ionic compounds, the concept of the solubility product (Ksp) becomes essential. Ksp is the equilibrium constant for the dissolution of a sparingly soluble ionic compound in water. It represents the product of the ion concentrations raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced dissolution equation.
The ion product (Q), on the other hand, is a measure of the actual ion concentrations in a solution at a given time. By comparing Q and Ksp, we can determine whether a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated:
- Q < Ksp: The solution is unsaturated.
- Q = Ksp: The solution is saturated.
- Q > Ksp: The solution is supersaturated.
Understanding Ksp and Q is crucial for predicting whether precipitation will occur when solutions are mixed.
Conclusion: Mastering the Concept of Saturation
Understanding the concept of saturated solutions is fundamental in chemistry and has wide-ranging practical implications. This comprehensive exploration has highlighted the definition of saturation, the factors influencing it, its relationship to solubility, and its application across diverse fields. From basic solubility to the advanced concepts of Ksp and Q, grasping these principles is crucial for anyone working with chemical solutions. The information provided here serves as a strong foundation for further exploration and application of this fundamental chemical concept in various contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Does An Electron Microscope Differ From A Light Microscope
Mar 31, 2025
-
Burning Of Paper Is A Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Represents A Physical Change
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Cell Placed In A Hypotonic Solution Will
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Does An Amoeba Get Its Food
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does It Mean For A Solution To Be Saturated . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
