What Color Does Litmus Paper Turn In Nuetral
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 7 min read
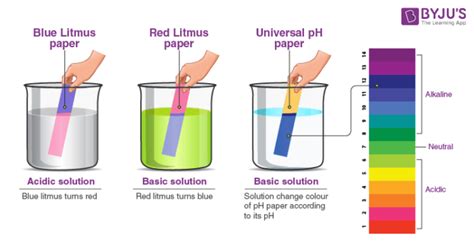
Table of Contents
What Color Does Litmus Paper Turn in Neutral? Understanding pH and Litmus Paper
Litmus paper, a simple yet powerful tool in chemistry, provides a quick and easy way to determine the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Understanding how litmus paper behaves in neutral solutions is crucial for interpreting its results and applying this knowledge in various contexts. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the intricacies of litmus paper, its interaction with neutral solutions, and its broader applications.
Understanding pH and the pH Scale
Before exploring the color change of litmus paper in neutral solutions, it's essential to grasp the concept of pH. The pH scale, ranging from 0 to 14, measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. A pH of 7 represents neutrality, indicating an equal concentration of H+ and hydroxide ions (OH-). Solutions with a pH below 7 are acidic, exhibiting a higher concentration of H+, while solutions with a pH above 7 are alkaline or basic, displaying a higher concentration of OH-.
The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning each whole number change represents a tenfold difference in H+ concentration. For example, a solution with a pH of 6 is ten times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 7, and a solution with a pH of 5 is one hundred times more acidic than a solution with a pH of 7.
The Importance of Neutrality
Neutrality, represented by a pH of 7, signifies a balanced state where the solution is neither acidic nor alkaline. Pure water, at 25°C, serves as a standard example of a neutral solution. However, it's important to note that the pH of pure water can slightly vary depending on temperature and other environmental factors. Maintaining neutrality is crucial in many biological and chemical processes, as extreme acidity or alkalinity can disrupt delicate equilibria and damage living organisms.
Litmus Paper: A Brief History and Composition
Litmus paper, derived from lichens, has a long history in chemistry. These complex organisms, symbiotic combinations of fungi and algae, produce a variety of chemical compounds, including the color-changing substances responsible for litmus paper's functionality. The extraction and processing of these compounds to create litmus paper involve a series of steps, ultimately resulting in thin strips of filter paper infused with a mixture of dyes extracted from these lichens.
The precise composition of the dye mixture in litmus paper is complex and proprietary, varying slightly depending on the manufacturer. However, the key characteristic is the presence of several different dyes that exhibit different color changes across the pH spectrum. These dyes are weak acids and bases, changing color as the solution they are in shifts the equilibrium of the dyes. This is a key aspect of understanding the subtle changes seen with litmus paper, as different dye components react at different points in the pH scale.
Litmus Paper's Color Change in Neutral Solutions: The Key to Understanding
The most critical aspect of litmus paper's use is its ability to indicate the pH of a solution through a color change. In a neutral solution (pH 7), litmus paper will typically show a purple or lavender color. This is the intermediate color between the red color exhibited in acidic solutions and the blue color seen in alkaline solutions.
The color change isn't an abrupt shift but rather a gradual transition. As the pH moves from slightly acidic (e.g., pH 6) to neutral (pH 7) to slightly alkaline (e.g., pH 8), the color of the litmus paper will change accordingly. This subtle shift in color is an important indicator of how close to neutrality a solution might be.
Factors Affecting Litmus Paper's Color Change
Several factors can influence the accuracy and reliability of litmus paper readings:
-
Temperature: Temperature affects the ionization of the dyes in the litmus paper, thus slightly influencing the color change. Results should always be considered within the context of the ambient temperature.
-
Concentration: The concentration of the solution being tested can impact the intensity of the color change. A highly concentrated acid or base might cause a more dramatic shift in color compared to a dilute solution. This can make assessing neutrality more difficult.
-
Interfering Substances: Certain substances in a solution can interfere with the color change of litmus paper, leading to inaccurate results. The presence of other colorants, strong oxidants, or reducing agents can make reading and interpreting the results of litmus paper testing complicated.
-
Paper Quality: The quality of the litmus paper itself can affect the accuracy and sensitivity of the test. High-quality litmus paper will provide more consistent and reliable results.
Beyond the Simple Color Change: Interpreting Litmus Paper Results
While the purple color indicates neutrality, it's important to understand that litmus paper offers only a rough estimation of pH. It does not provide a precise numerical pH value. For precise pH measurements, more sophisticated instruments like pH meters are required. Litmus paper should be considered as a qualitative indicator, giving a rapid, general indication of acidity or alkalinity.
The value of litmus paper lies in its simplicity and rapid response. It is often used as a preliminary test to quickly assess the pH of an unknown solution, guiding further investigation with more precise techniques if necessary. It can effectively distinguish between strongly acidic, neutral, and strongly alkaline solutions. However, it cannot differentiate between subtly differing pH values within a specific range.
Applications of Litmus Paper: A Wide Range of Uses
Litmus paper finds applications across various fields, including:
-
Chemistry Education: It's a fundamental tool in teaching basic chemistry concepts, especially pH and acid-base reactions. Students learn to test and interpret the color change to gauge pH.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Litmus paper can be used for quick, on-site assessments of water quality, assisting in identifying acidic or alkaline conditions in streams, lakes, or other water bodies.
-
Soil Testing: Gardeners and farmers use litmus paper to determine the pH of their soil, a crucial factor influencing plant growth. Different plants thrive under different pH levels; knowledge of soil acidity or alkalinity guides decisions on what to plant and how to amend the soil.
-
Medical and Health Applications: Although less common now, in some medical applications litmus paper tests might be used for quick pH assessments of bodily fluids. Modern medical practice relies more on sophisticated methods.
-
Food and Beverage Industry: While not a primary quality control measure, litmus paper can provide a rapid initial assessment for specific pH levels in food production or processing.
Distinguishing between Litmus Paper Types: Red and Blue
It’s important to note that litmus paper comes in two forms: red litmus paper and blue litmus paper. Red litmus paper turns blue in alkaline solutions (pH > 7), while blue litmus paper turns red in acidic solutions (pH < 7). Neither changes color significantly in a neutral solution (pH 7). The combined use of both red and blue litmus paper provides a more complete picture of a substance’s pH.
Conclusion: Litmus Paper – A Simple Tool with Broad Applications
Litmus paper, despite its simplicity, remains a valuable tool for rapidly determining whether a solution is acidic, alkaline, or neutral. While it doesn't provide the precision of a pH meter, its ease of use and quick results make it invaluable in educational settings, environmental monitoring, and various other applications. Understanding its color change in neutral solutions – a purple or lavender hue – is key to correctly interpreting its indications and applying this knowledge effectively. Remember to consider factors influencing color change, and consider the limitations of litmus paper's qualitative nature. When precise pH measurements are needed, more sophisticated instrumentation is necessary. However, for a quick initial assessment, litmus paper remains a valuable and readily accessible tool.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Sides In A Dodecagon
Mar 06, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 7
Mar 06, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 12
Mar 06, 2025
-
The Period Of Division Is Called
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is Water An Element Compound Or Mixture
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Color Does Litmus Paper Turn In Nuetral . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
