Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 7
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
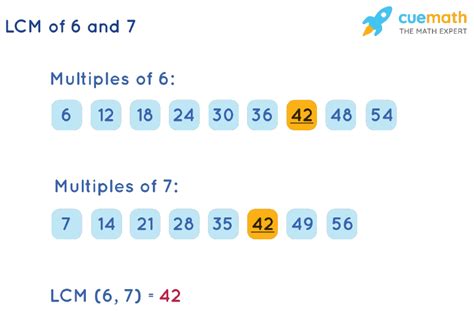
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 6 and 7: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in arithmetic and number theory. It represents the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of two or more integers. Understanding how to find the LCM is crucial for various mathematical applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex equations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods of calculating the LCM, focusing specifically on the LCM of 6 and 7, and exploring the broader implications of this concept.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 6 and 7, let's solidify our understanding of the underlying concept. The LCM is the smallest number that is divisible by both of the given numbers without leaving a remainder. For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21...
The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6. This signifies that 6 is the smallest number that can be divided evenly by both 2 and 3.
Methods for Finding the LCM
Several methods exist for determining the LCM of two or more numbers. Let's explore the most common approaches, illustrating each with examples relevant to our target LCM of 6 and 7.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60...
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63...
By examining the lists, we observe that the smallest number present in both sequences is 42. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 7 is 42.
This method is simple to understand but becomes less efficient when dealing with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method involves breaking down each number into its prime factors. The LCM is then constructed by multiplying the highest powers of all prime factors present in the numbers.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
Since 2, 3, and 7 are all prime factors present in either 6 or 7, we multiply them together: 2 x 3 x 7 = 42. Therefore, the LCM of 6 and 7 is 42.
This method is more efficient than listing multiples, particularly when dealing with larger numbers or a greater number of numbers. It provides a systematic approach for finding the LCM.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The formula connecting the LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we need to find the GCD of 6 and 7. The GCD is the largest number that divides both 6 and 7 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD(6, 7) = 1, as 1 is the only common divisor of 6 and 7.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(6, 7) x GCD(6, 7) = 6 x 7 LCM(6, 7) x 1 = 42 LCM(6, 7) = 42
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where finding the GCD is relatively easier than directly finding the LCM. Algorithms like the Euclidean algorithm efficiently calculate the GCD.
Applications of LCM
The LCM finds applications in various areas of mathematics and beyond:
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, we need to find a common denominator. The LCM of the denominators serves as the least common denominator (LCD), simplifying the calculation.
-
Scheduling Problems: LCM helps in solving scheduling problems, such as determining when two cyclical events will occur simultaneously. For instance, if two machines operate on cycles of 6 and 7 hours respectively, the LCM helps determine when they will both be at their starting point simultaneously.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCM plays a vital role in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory dealing with remainders after division.
-
Music Theory: LCM is used in music theory to determine the least common denominator for different rhythmic patterns.
-
Engineering and Physics: LCM has applications in various engineering and physics problems related to cyclical processes and synchronization.
The Significance of the LCM of 6 and 7
The LCM of 6 and 7, which we've established as 42, holds a specific significance in the context of these two numbers. It represents the smallest number that is both a multiple of 6 and a multiple of 7. This number serves as a crucial reference point for any operation or problem involving both 6 and 7 where a common multiple is required. The simplicity of this example allows for a clear demonstration of the LCM concept and its application.
Extending the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to calculate the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, we would find the prime factors of all the numbers and multiply the highest powers of each distinct prime factor. For the GCD method, we can use iterative approaches to find the LCM of multiple numbers.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
Understanding the least common multiple is essential for various mathematical computations and problem-solving. We’ve explored three primary methods for calculating the LCM, focusing on the LCM of 6 and 7 as a clear example. The prime factorization method generally provides the most efficient approach for larger numbers, while the listing multiples method remains intuitive for smaller numbers. Remember that mastering the LCM calculation is a fundamental step in developing strong mathematical skills. By understanding the concept and applying the methods correctly, you will be well-equipped to tackle more complex mathematical challenges. This knowledge extends beyond simple arithmetic, finding relevance in numerous practical applications across various disciplines. The seemingly simple task of finding the LCM of 6 and 7 opens a door to a deeper understanding of number theory and its multifaceted uses.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lowest Common Factor Of 6 And 10
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Examples Of Chemical Changes
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is 37 A Prime Or Composite
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is Tearing Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 06, 2025
-
Bile Is Stored And Concentrated In The
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
