What Can 25 Be Divided By
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
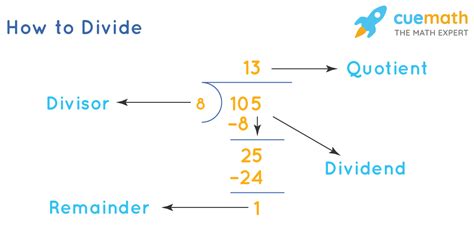
Table of Contents
What Can 25 Be Divided By? A Deep Dive into Divisibility and Factors
The seemingly simple question, "What can 25 be divided by?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, specifically divisibility rules and factors. While the immediate answer might seem obvious, a deeper understanding reveals valuable insights into mathematical concepts applicable far beyond this single number. This article will not only answer the question comprehensively but will also delve into the underlying principles, providing a robust understanding of divisibility and its significance.
Understanding Divisibility
Divisibility refers to the ability of a number to be divided by another number without leaving a remainder. In other words, the result of the division is a whole number (integer). For instance, 25 is divisible by 5 because 25 divided by 5 equals 5 (a whole number). However, 25 is not divisible by 3 because 25 divided by 3 equals 8 with a remainder of 1.
This seemingly basic concept forms the foundation for numerous mathematical operations and applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex equations. Understanding divisibility rules allows for quicker calculations and a deeper appreciation of numerical relationships.
Finding the Divisors of 25: A Step-by-Step Approach
To determine all the numbers that 25 can be divided by, we can systematically explore its factors. Factors are numbers that divide evenly into a given number without leaving a remainder. Let's break down the process:
1. The Obvious Ones:
- 1: Every number is divisible by 1. This is a fundamental rule of divisibility.
- 25: Every number is divisible by itself. This is also a fundamental rule.
- 5: We know that 25 divided by 5 equals 5, so 5 is a factor of 25.
2. Exploring Other Possibilities:
To find other potential divisors, we can consider the divisibility rules for different numbers. However, since 25 is a relatively small number, we can systematically check the numbers smaller than 25. We've already covered 1 and 5. Let's consider the rest:
- 2: 25 is not divisible by 2 because it's an odd number (divisibility rule for 2: even numbers are divisible by 2).
- 3: 25 is not divisible by 3 (divisibility rule for 3: sum of digits must be divisible by 3; 2 + 5 = 7, which is not divisible by 3).
- 4: 25 is not divisible by 4 (divisibility rule for 4: last two digits must be divisible by 4; 25 is not).
- 6: 25 is not divisible by 6 (divisibility rule for 6: must be divisible by both 2 and 3; it's not divisible by 2).
- 7: 25 is not divisible by 7. (Long division confirms this.)
- 8: 25 is not divisible by 8. (Long division confirms this.)
- 9: 25 is not divisible by 9 (divisibility rule for 9: sum of digits must be divisible by 9; 2+5=7).
- 10: 25 is not divisible by 10 (divisibility rule for 10: last digit must be 0; the last digit is 5).
3. The Complete List of Divisors:
After checking all the numbers up to the square root of 25 (which is 5), we have found all the divisors. Therefore, the numbers that 25 can be divided by are 1, 5, and 25.
Prime Factorization and Divisibility
A powerful tool for understanding divisibility is prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
The prime factorization of 25 is 5 x 5, or 5². This tells us a lot about its divisors. Any combination of these prime factors (including using them zero times) will result in a divisor of 25:
- 5⁰ = 1
- 5¹ = 5
- 5² = 25
This method clearly shows us that 1, 5, and 25 are the only divisors of 25.
Applications of Divisibility: Real-World Examples
Understanding divisibility isn't just an abstract mathematical exercise; it has numerous practical applications:
-
Fraction Simplification: Divisibility helps us simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, we can simplify 25/50 by dividing both the numerator (25) and the denominator (50) by their greatest common divisor (GCD), which is 25, resulting in the simplified fraction 1/2.
-
Scheduling and Grouping: Divisibility plays a crucial role in scheduling and grouping tasks or items. If you have 25 students and want to divide them into equal groups, you could divide them into groups of 1, 5, or 25.
-
Data Organization: In computer science and data management, understanding divisibility is crucial for optimizing data structures and algorithms.
Beyond 25: Exploring Divisibility of Other Numbers
While we've focused on 25, the principles discussed here can be applied to any number. The same systematic approach – considering divisibility rules, prime factorization, and checking for factors – can be used to find the divisors of any integer.
For example, let's consider the number 36:
- Obvious divisors: 1 and 36.
- Divisibility rules: 36 is divisible by 2 (even number), 3 (sum of digits is 9, divisible by 3), 4 (last two digits are 36, divisible by 4), 6 (divisible by both 2 and 3), 9 (sum of digits is 9, divisible by 9), and 12.
- Prime factorization: 36 = 2² x 3². This reveals divisors 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 36.
This example demonstrates how the same principles can be applied to find the divisors of any integer, no matter how large or small.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Divisibility
The question of what 25 can be divided by leads us on a journey through fundamental concepts in number theory. Understanding divisibility is not just about finding factors; it’s about grasping the underlying relationships between numbers, which have far-reaching implications in various fields. From simplifying fractions to optimizing algorithms, the principles of divisibility are essential tools for mathematical problem-solving and real-world applications. Mastering these concepts empowers us to approach numerical challenges with greater efficiency and insight. The seemingly simple question of "What can 25 be divided by?" thus serves as a gateway to a deeper appreciation of the elegance and practicality of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is All The Factors Of 17
Mar 23, 2025
-
Sodium Carbonate Hydrochloric Acid Balanced Equation
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Parts Of Earth Where Life Exists
Mar 23, 2025
-
Orbitals With The Same Energy Are Called
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Chambers Are In A Frogs Heart
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Can 25 Be Divided By . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
