What Are Vertices Of A Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
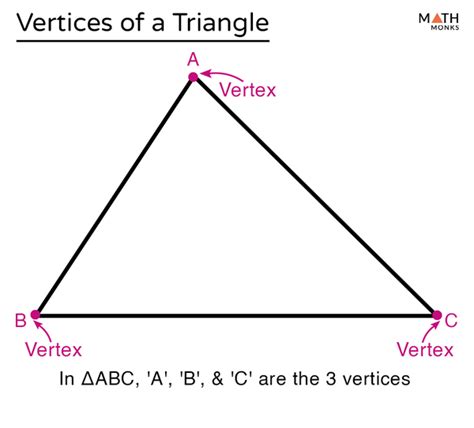
Table of Contents
What Are the Vertices of a Triangle? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the fundamental components of a triangle is crucial for anyone studying geometry, whether at a high school, undergraduate, or even graduate level. While seemingly simple, a deep dive into the concept of a triangle's vertices reveals intricate connections to various geometric theorems and applications across diverse fields. This comprehensive guide will explore the vertices of a triangle, their properties, and their significance in various mathematical and real-world contexts.
Defining the Vertices of a Triangle
A triangle, the simplest polygon, is a closed two-dimensional figure defined by three straight line segments that connect three non-collinear points. These three points are known as the vertices of the triangle. In simpler terms, a vertex is a corner point of the triangle where two sides meet. Each vertex is uniquely identified and plays a vital role in defining the triangle's shape and properties.
We typically label the vertices of a triangle with uppercase letters, such as A, B, and C. The sides opposite to these vertices are usually denoted by the corresponding lowercase letters, a, b, and c, respectively. This labeling convention simplifies discussions and proofs related to the triangle.
Think of it like this: Imagine three nails hammered into a piece of wood. These nails represent the vertices. When you stretch a string around these nails, forming a closed loop, you've created a triangle. The strings themselves represent the sides of the triangle.
Key Properties of Vertices:
-
Intersection of Sides: Vertices are the points where two sides of the triangle intersect. This intersection forms an interior angle, which is a crucial characteristic of the triangle.
-
Defining Angles: Each vertex defines an interior angle. The sum of these three interior angles is always 180 degrees (in Euclidean geometry). This is a fundamental property of triangles.
-
Coordinates in Coordinate Geometry: In coordinate geometry, each vertex can be represented by its coordinates (x, y) on a Cartesian plane. These coordinates are essential for calculating distances, areas, and other properties of the triangle.
-
Centroids and Other Centers: Various points within a triangle, such as the centroid, circumcenter, incenter, and orthocenter, are defined using the vertices as reference points. These points are crucial for understanding a triangle's various geometric properties.
Types of Triangles and Their Vertices
Triangles are classified based on their side lengths and angles. The vertices play a pivotal role in determining this classification:
1. Based on Side Lengths:
-
Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal in length. Consequently, all three interior angles are equal (60 degrees each). The vertices of an equilateral triangle are equidistant from each other.
-
Isosceles Triangle: At least two sides are equal in length. This results in two equal angles opposite the equal sides. The vertices of an isosceles triangle have a specific relationship: two vertices have equal angles, while the third vertex sits opposite the unequal side.
-
Scalene Triangle: All three sides are of different lengths. All three angles are also different. The vertices of a scalene triangle represent distinct points in space with unique angular properties.
2. Based on Angles:
-
Acute Triangle: All three angles are less than 90 degrees. The vertices of an acute triangle define three acute angles.
-
Right Triangle: One angle is exactly 90 degrees. The vertex forming the right angle is particularly significant as it is crucial in various geometric calculations (e.g., Pythagorean theorem).
-
Obtuse Triangle: One angle is greater than 90 degrees. The vertex forming the obtuse angle plays a significant role in the triangle's properties and calculations.
Significance of Vertices in Geometric Theorems
Vertices are fundamental to many important geometric theorems related to triangles:
1. The Angle Sum Theorem:
As mentioned earlier, the sum of the interior angles of any triangle (formed at its vertices) is always 180 degrees. This theorem is a cornerstone of Euclidean geometry and has numerous applications.
2. Pythagorean Theorem (for right-angled triangles):
This theorem relates the lengths of the sides of a right-angled triangle to the lengths of its sides. The vertices are crucial here because the theorem is applied specifically to the sides that meet at the right angle (90-degree vertex).
3. Triangle Inequality Theorem:
This theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side. This is directly related to the vertices because the sides are defined by the distances between the vertices.
Applications of Vertices and Triangles
Understanding vertices and their properties extends far beyond theoretical geometry. They find applications in various fields:
-
Engineering and Architecture: Triangles are incredibly strong geometric shapes. Many structures, from bridges to buildings, utilize triangular frameworks due to their stability. The vertices of these triangles are the critical points that hold the structure together.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: Triangles are the fundamental building blocks of 3D models in computer graphics. The vertices of these triangles define the shape and position of the objects displayed on the screen.
-
Cartography and Surveying: Triangulation is a technique used to determine the position of points by measuring angles to known points. The vertices play a crucial role in these calculations.
-
Navigation and GPS: GPS systems use triangulation to determine the location of a device by measuring the distance to several satellites. The vertices (positions of the satellites) are essential inputs in these calculations.
-
Physics and Engineering: Many physical phenomena can be modeled using triangles and their vertices. For example, stress analysis in structural engineering often involves analyzing force vectors acting on the vertices of triangular elements.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
The study of triangles and their vertices extends into more advanced topics in mathematics:
-
Trigonometry: Trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) are fundamentally defined using the ratios of sides and angles in a right-angled triangle. The vertices are crucial in defining the reference angles used in trigonometric calculations.
-
Linear Algebra: Vertices can be represented as vectors, allowing for the application of linear algebra techniques to analyze and manipulate triangles and their properties.
-
Vector Geometry: Vectors can be used to define the position of the vertices, and vector operations can be used to calculate various properties of the triangle.
-
Non-Euclidean Geometry: In non-Euclidean geometries (like spherical geometry), the properties of triangles and their vertices differ from those in Euclidean geometry. The study of these differences provides a deeper understanding of geometric concepts.
Conclusion
The vertices of a triangle are not merely corner points; they are fundamental components defining the entire triangle's shape, properties, and relationships with other geometric elements. Understanding their significance unlocks a deeper understanding of various geometric theorems, and the applications extend far beyond theoretical mathematics into the realms of engineering, computer science, and other fields. This comprehensive exploration highlights the simple yet profound importance of the seemingly basic concept of a triangle's vertices. A thorough grasp of these foundational concepts opens doors to exploring more intricate mathematical ideas and their applications in the real world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Letters Does Not Suffer Lateral Inversion
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is 53 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 24 And 15
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Percent Is 2 3 Of A Circle
Mar 28, 2025
-
Ray Diagrams Of A Concave Mirror
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Vertices Of A Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
