What Are The Prime Factors Of 65
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
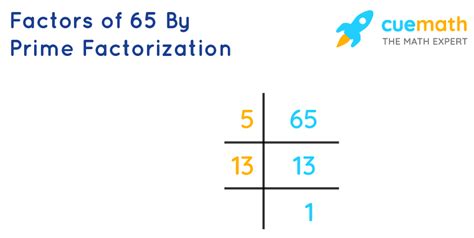
Table of Contents
What Are the Prime Factors of 65? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Finding the prime factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic exercise, but it's a fundamental concept in number theory with far-reaching applications in cryptography, computer science, and beyond. This article delves into the prime factorization of 65, exploring the method, its significance, and related concepts. We'll go beyond the simple answer and uncover the rich mathematical landscape surrounding prime numbers and factorization.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before tackling the prime factors of 65, let's establish a solid foundation. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. A number that is not prime is called a composite number.
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal the original number. Every composite number can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This uniqueness is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. This theorem is a cornerstone of number theory, providing a foundational truth about the structure of integers.
Finding the Prime Factors of 65: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's determine the prime factors of 65. We'll use a method often taught in elementary mathematics:
-
Start with the smallest prime number: We begin by checking if the smallest prime number, 2, is a factor of 65. Since 65 is an odd number, it's not divisible by 2.
-
Move to the next prime number: Next, we check if the next prime number, 3, is a factor. Adding the digits of 65 (6 + 5 = 11), which is not divisible by 3, confirms that 65 is not divisible by 3. Alternatively, we could perform the division: 65/3 ≈ 21.67, indicating it's not divisible.
-
Continue the process: We continue checking prime numbers. 5 is the next prime, and we find that 65 ÷ 5 = 13.
-
Identifying the Prime Factors: We've found that 65 = 5 × 13. Both 5 and 13 are prime numbers. Therefore, the prime factorization of 65 is 5 × 13.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
While finding the prime factors of 65 might seem trivial, the process and the result hold significant implications across various fields:
1. Cryptography: The Foundation of Secure Communication
Prime factorization is the backbone of many modern cryptographic systems. Algorithms like RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) rely on the difficulty of factoring very large composite numbers into their prime factors. The security of these systems hinges on the computational infeasibility of factoring numbers with hundreds or even thousands of digits. While factoring small numbers like 65 is easy, factoring large numbers requires immense computational power, making these cryptographic methods secure.
2. Computer Science and Algorithm Design
Prime factorization plays a crucial role in various computer science algorithms. For instance, efficient algorithms for prime factorization are essential for optimizing certain tasks related to data structures and network security. Understanding the properties of prime numbers helps in designing efficient and secure algorithms.
3. Number Theory and Abstract Algebra
Prime factorization is a central concept in number theory, which explores the properties of integers and their relationships. It serves as a building block for more advanced concepts like modular arithmetic, congruences, and abstract algebra.
4. Applications in Other Fields
The concept of prime factorization extends beyond the realm of pure mathematics. It finds applications in areas like:
- Coding Theory: Prime numbers and their properties are used in the design of error-correcting codes.
- Data Compression: Prime factorization can be used in developing efficient data compression algorithms.
- Physics: Prime numbers appear unexpectedly in certain physical phenomena, sparking ongoing research.
Exploring Related Concepts: Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Prime factorization is intimately linked to two other essential concepts in number theory: the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and the Least Common Multiple (LCM).
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. Prime factorization provides an efficient way to calculate the GCD. By finding the prime factorization of each number, we can identify the common prime factors and their lowest powers to determine the GCD.
Example: Let's find the GCD of 65 and 195.
- Prime factorization of 65: 5 × 13
- Prime factorization of 195: 3 × 5 × 13
The common prime factors are 5 and 13. The lowest power of each is 5¹ and 13¹. Therefore, the GCD(65, 195) = 5 × 13 = 65.
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. Again, prime factorization offers a straightforward method for calculating the LCM.
Example: Let's find the LCM of 65 and 195.
- Prime factorization of 65: 5 × 13
- Prime factorization of 195: 3 × 5 × 13
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations: 3¹, 5¹, and 13¹. Therefore, LCM(65, 195) = 3 × 5 × 13 = 195.
Beyond 65: Exploring Larger Numbers and Algorithms
While finding the prime factors of 65 is relatively straightforward, factoring larger numbers becomes increasingly challenging. For extremely large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are employed. Some notable algorithms include:
- Trial Division: This is the simplest method, but it becomes computationally expensive for large numbers.
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: This is an efficient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified limit.
- Pollard's Rho Algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm that is efficient for finding small prime factors.
- General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): The most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers, commonly used in cryptography.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple task of finding the prime factors of 65 opens a window into the fascinating world of number theory and its profound applications. Understanding prime factorization is not merely an academic exercise; it's a fundamental concept that underpins much of modern cryptography, computer science, and various other fields. The journey from finding the prime factors of a small number like 65 to grappling with the complexities of factoring large numbers highlights the beauty and power of mathematical principles in shaping our technological world. As we continue to explore the intricacies of prime numbers, their significance in shaping our digital landscape will only grow.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Melting Of Wax A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Is Carbon Tetrachloride Ionic Or Covalent
Mar 16, 2025
-
Write The Formula For Sulfurous Acid
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Raw Materials Required For Photosynthesis
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Prime Factors Of 65 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
