What Are The Least Common Multiples Of 3 And 4
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
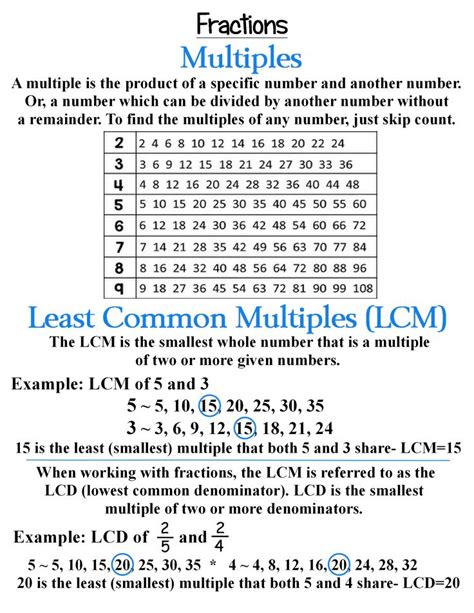
Table of Contents
What Are the Least Common Multiples of 3 and 4? A Deep Dive into LCM and its Applications
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications across various fields. This article will explore the LCM of 3 and 4 in detail, examining different methods for calculating it and demonstrating its practical relevance in solving real-world problems. We'll move beyond a simple answer and delve into the underlying principles, offering a comprehensive understanding of this crucial mathematical concept.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific case of 3 and 4, let's establish a firm understanding of LCMs. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that can be evenly divided by all the numbers in the set.
For example, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Calculating the LCM of 3 and 4: Three Methods
Now, let's focus on finding the LCM of 3 and 4. We can employ several methods to achieve this:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28...
By comparing the two lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple is 12. Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers or when dealing with multiple numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 4: 2² (4 = 2 x 2)
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations: 2² and 3. Multiplying these together, we get 2² x 3 = 4 x 3 = 12.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers themselves. The formula is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we need to find the GCD of 3 and 4. Since 3 is a prime number and 4 is not divisible by 3, the GCD of 3 and 4 is 1.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(3, 4) x GCD(3, 4) = 3 x 4 LCM(3, 4) x 1 = 12 LCM(3, 4) = 12
All three methods consistently show that the LCM of 3 and 4 is 12.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has significant practical applications in various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two machines that complete a cycle in 3 and 4 hours, respectively. To find out when both machines will complete a cycle simultaneously, you need to calculate the LCM of 3 and 4. The LCM, 12, indicates that both machines will complete a cycle together after 12 hours.
2. Fraction Operations
LCM plays a crucial role in adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add fractions like 1/3 and 1/4, you need to find a common denominator, which is the LCM of 3 and 4 (12). This allows you to rewrite the fractions as 4/12 and 3/12, facilitating easy addition (resulting in 7/12).
3. Construction and Engineering
In construction projects, materials might be delivered in quantities that are multiples of certain numbers. Determining the LCM can help optimize material ordering and minimize waste. For instance, if one type of brick is sold in packs of 3 and another in packs of 4, finding the LCM helps determine the smallest number of packs to buy to have an equal number of both types of bricks.
4. Music Theory
LCM is used in music theory to determine the least common multiple of the lengths of different musical phrases or patterns. This is helpful in understanding rhythmic relationships and creating harmonious compositions. Understanding the rhythmic cycles and when they will coincide requires an understanding of the LCM.
5. Computer Science
In computer programming, algorithms involving synchronization or periodic tasks often rely on LCM calculations to determine the optimal time intervals for processes to run concurrently or in a coordinated manner. This avoids conflicts and ensures efficient resource utilization.
6. Manufacturing and Production
Manufacturing processes often involve machines working at different cycles or speeds. Knowing the LCM can be useful in optimizing production lines, scheduling maintenance, and determining the most efficient intervals for quality checks.
7. Calendar Calculations
While not as direct, the concept of LCM underpins the calculations involved in determining when specific dates align in different calendar systems. Understanding cyclical events like leap years or the recurrence of certain astrological events requires similar mathematical reasoning.
Beyond the Basics: Extending LCM Concepts
The calculation of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. You can easily calculate the LCM of three or more numbers using the prime factorization method or other advanced techniques. Furthermore, exploring the relationship between LCM and GCD provides a deeper understanding of number theory and its applications.
Conclusion: The Power of the LCM
The seemingly simple calculation of the least common multiple of 3 and 4, which is 12, reveals a powerful mathematical concept with widespread applicability. From everyday scheduling challenges to complex engineering projects and even music composition, understanding and applying LCM provides efficient solutions and enhances our understanding of various systems and processes. By mastering this fundamental concept, we unlock a deeper understanding of mathematics and its profound impact on our world. It's a testament to the beauty and utility of seemingly simple mathematical ideas.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find A Coordination Number
Mar 09, 2025
-
Is 97 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 09, 2025
-
Give One Reason Mendel Chose Pea Plants For His Experiment
Mar 09, 2025
-
Does A Liquid Have A Definite Shape
Mar 09, 2025
-
Bronsted Lowry Acid Vs Lewis Acid
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Least Common Multiples Of 3 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
