What Are The Factors Of 87
Juapaving
Mar 05, 2025 · 6 min read
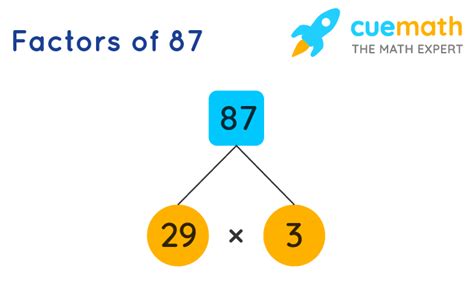
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 87? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization and Divisibility
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 87?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime factorization, and divisibility rules. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, exploring the concept deeply reveals underlying mathematical principles crucial for understanding more complex numerical relationships. This article will not only answer the question but also delve into the broader context of factor identification, providing a comprehensive guide for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of this fundamental concept in mathematics.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we tackle the factors of 87 specifically, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a factor. A factor (or divisor) of a number is any integer that divides the number without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if you can divide a number by another number and the result is a whole number, then the second number is a factor of the first. This concept is intrinsically linked to divisibility. A number is divisible by another number if the result of the division is a whole number (integer).
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly. This means 12/1 = 12, 12/2 = 6, 12/3 = 4, 12/4 = 3, 12/6 = 2, and 12/12 = 1.
Finding the Factors of 87: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's apply this knowledge to find the factors of 87. We can approach this systematically:
-
Start with 1 and the number itself: Every number is divisible by 1 and itself. Therefore, 1 and 87 are factors of 87.
-
Check for divisibility by small prime numbers: The next step involves checking for divisibility by prime numbers. Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that have only two factors: 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.). We can test divisibility by these numbers sequentially.
-
Divisibility by 2: 87 is not divisible by 2 because it's an odd number (doesn't end in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8).
-
Divisibility by 3: The divisibility rule for 3 states that a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. In the case of 87, 8 + 7 = 15, and 15 is divisible by 3 (15/3 = 5). Therefore, 87 is divisible by 3. 87/3 = 29. This gives us two more factors: 3 and 29.
-
Divisibility by 5: 87 is not divisible by 5 because it doesn't end in 0 or 5.
-
Divisibility by 7: We can perform the division: 87/7 ≈ 12.43. Not a whole number, so 7 is not a factor.
-
Divisibility by 11: Similarly, 87/11 ≈ 7.91. 11 is not a factor.
-
-
Consider the factors we've found: We've identified the factors 1, 3, 29, and 87. Since 29 is a prime number, we've found all the factors of 87.
Therefore, the factors of 87 are 1, 3, 29, and 87.
Prime Factorization of 87
The process of finding the factors also leads us to the prime factorization of 87. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. In this case:
87 = 3 × 29
This representation shows that 87 is composed of the prime numbers 3 and 29. This is a unique representation for any given number (excluding the order of the factors). Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory and has numerous applications in cryptography and other areas of mathematics.
Divisibility Rules: A Helpful Tool
Understanding divisibility rules significantly speeds up the process of identifying factors. Here are some key divisibility rules:
-
Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if it's an even number (ends in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8).
-
Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
-
Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if it ends in 0 or 5.
-
Divisibility by 9: A number is divisible by 9 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 9.
-
Divisibility by 10: A number is divisible by 10 if it ends in 0.
-
Divisibility by 11: This rule is a bit more complex. Alternately add and subtract the digits from right to left. If the result is divisible by 11, the original number is as well.
Mastering these rules will help you quickly determine whether a number is divisible by a smaller number without performing lengthy divisions.
Applications of Factorization
Understanding factors and factorization has numerous applications across various fields:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator of a fraction allows for simplification.
-
Solving Algebraic Equations: Factorization is crucial in solving quadratic and other higher-order polynomial equations.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization is the foundation of many modern encryption algorithms. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is what secures these systems.
-
Computer Science: Factorization plays a role in various algorithms and data structures.
-
Combinatorics and Probability: Understanding factors is important when working with permutations and combinations.
Expanding on Factor Concepts: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Beyond simply identifying factors, two important concepts build upon this foundation:
-
Greatest Common Factor (GCF): The GCF of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. For example, the GCF of 12 and 18 is 6.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. For example, the LCM of 12 and 18 is 36.
Finding the GCF and LCM is often done using prime factorization. By expressing numbers as products of their prime factors, it becomes easier to identify common factors and determine the GCF and LCM.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Factors
The seemingly simple question regarding the factors of 87 has led us on a journey into the fundamental principles of number theory. Understanding factors, divisibility, prime factorization, and related concepts like GCF and LCM is essential for a strong grasp of mathematics. These concepts are not merely abstract mathematical exercises; they have real-world applications across various fields, underscoring their importance in education and beyond. By mastering these concepts, you build a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems and appreciate the elegance and power of number theory. The next time you encounter a number, remember the rich mathematical landscape that lies beneath its surface.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Total Degree Of Angles For All Squares
Mar 05, 2025
-
What Is The Chemical Formula For Zinc Sulfite
Mar 05, 2025
-
How Many Centimeters Are In One Meter
Mar 05, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True
Mar 05, 2025
-
On A Solubility Curve Solids Are Sometimes Referred To As
Mar 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 87 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
