What Are The Factors Of 58
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
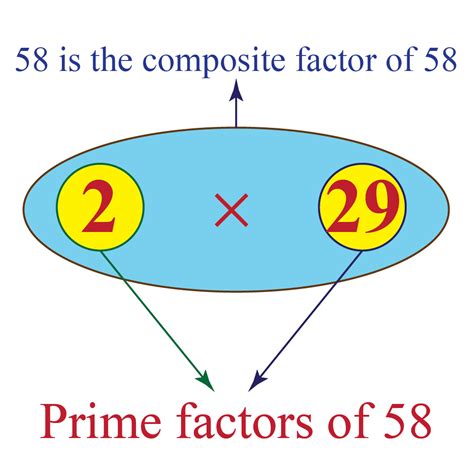
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 58? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization and Divisibility
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple mathematical task, but understanding the underlying principles reveals a fascinating world of number theory. This article delves into the factors of 58, exploring different methods to identify them, discussing the concepts of prime factorization and divisibility rules, and expanding on their applications in various mathematical contexts. We'll go beyond simply listing the factors and uncover the rich mathematical landscape surrounding this seemingly basic problem.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we tackle the factors of 58 specifically, let's solidify our understanding of fundamental concepts. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. Divisibility refers to the ability of one number to be divided evenly by another. For instance, 2 is a factor of 6 because 6 divided by 2 equals 3 with no remainder.
The Language of Factors
It's crucial to use precise mathematical language. When we say "factor," we're referring to a whole number. While decimals can divide a number evenly, they aren't considered factors in this context. We are focused on integers, the positive and negative whole numbers.
Finding the Factors of 58: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's determine the factors of 58. The most straightforward approach is to systematically test each whole number starting from 1, checking if it divides 58 without a remainder.
- Start with 1: 1 is a factor of every positive integer because any number divided by 1 equals itself.
- Check 2: 58 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. (58 / 2 = 29)
- Check 3: The divisibility rule for 3 states that a number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. 5 + 8 = 13, which is not divisible by 3.
- Check 4: 58 is not divisible by 4 because it's not divisible by both 2 and 2.
- Check 5: 58 doesn't end in 0 or 5, so it's not divisible by 5.
- Check 6: A number is divisible by 6 if it's divisible by both 2 and 3. 58 is divisible by 2 but not by 3.
- Check 7: There isn't a simple divisibility rule for 7, but we can test it: 58 / 7 ≈ 8.28, so it's not divisible by 7. We continue this process until we reach a number greater than the square root of 58 (which is approximately 7.6). Once we've passed this point, any remaining factors will be found by dividing 58 by the factors we've already discovered.
By following this systematic approach, we find that the factors of 58 are 1, 2, 29, and 58.
Prime Factorization: Unveiling the Building Blocks
Prime factorization is a powerful technique to decompose a number into its prime factors – prime numbers that, when multiplied, result in the original number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself.
To perform the prime factorization of 58, we start by dividing it by the smallest prime number, 2:
58 = 2 × 29
Both 2 and 29 are prime numbers. Therefore, the prime factorization of 58 is 2 × 29. This representation shows the fundamental building blocks of the number 58.
The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization
A remarkable property of prime factorization is its uniqueness. Every positive integer greater than 1 can be expressed as a product of prime numbers in only one way (disregarding the order of the factors). This fundamental theorem of arithmetic is a cornerstone of number theory.
Divisibility Rules: Shortcuts to Factor Identification
Knowing divisibility rules can significantly speed up the process of finding factors. Here are some useful rules:
- Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if it's an even number (ends in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8).
- Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 4: A number is divisible by 4 if its last two digits are divisible by 4.
- Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if it ends in 0 or 5.
- Divisibility by 6: A number is divisible by 6 if it's divisible by both 2 and 3.
- Divisibility by 9: A number is divisible by 9 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 9.
- Divisibility by 10: A number is divisible by 10 if it ends in 0.
These rules are valuable for quickly eliminating potential factors and focusing on those that are more likely to be divisors.
Applications of Factors and Prime Factorization
Understanding factors and prime factorization isn't just an academic exercise; it has widespread applications in various fields:
Cryptography
Prime factorization plays a critical role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components forms the basis of the security of many online transactions.
Modular Arithmetic and Number Theory
Factors are essential in modular arithmetic, a branch of mathematics where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus). This concept is fundamental in cryptography and computer science.
Algebra and Polynomial Factoring
The concept of factoring extends beyond integers to polynomials. Factoring polynomials is a crucial technique in algebra for solving equations and simplifying expressions. The principles are analogous to factoring integers.
Combinatorics and Probability
Understanding factors is important when working with combinations and permutations, often used in probability and statistics to calculate the number of ways to arrange or select items from a set.
Computer Science and Algorithms
Efficient algorithms for finding prime factors and testing divisibility are crucial in computer science for optimizing various processes, from cryptography to database management.
Conclusion: More Than Just a List of Numbers
This exploration of the factors of 58 has revealed that finding factors is more than just a simple division problem. It involves understanding fundamental concepts like divisibility, prime factorization, and the unique properties of prime numbers. These concepts are building blocks for more advanced mathematical fields, highlighting the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and their practical applications in various disciplines. The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 58?" opens a door to a deeper appreciation of number theory and its significance in the world around us. The systematic approach detailed here, combining direct division with divisibility rules and prime factorization, provides a robust methodology applicable to finding the factors of any positive integer. Remember, understanding the underlying principles allows for a more profound understanding of mathematics and its various applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Object Is An Example Of A Mechanical Wave
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is 0 75 As A Percentage
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is A Response In Biology
Mar 13, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 12 And 21
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Much Is A Straight Angle
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 58 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
