How Much Is A Straight Angle
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
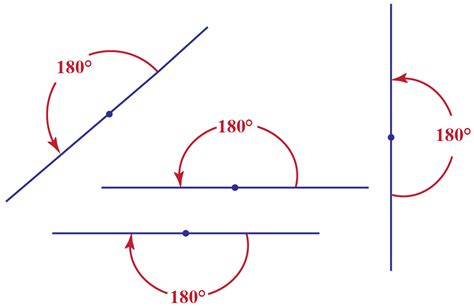
Table of Contents
How Much is a Straight Angle? A Comprehensive Guide to Angles and Their Measurement
Understanding angles is fundamental to various fields, from geometry and mathematics to engineering, architecture, and even computer graphics. Among the many types of angles, the straight angle holds a unique position, representing a fundamental concept in angular measurement. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the definition, properties, and applications of straight angles, clarifying exactly "how much" a straight angle truly is.
Defining a Straight Angle
A straight angle is an angle that measures exactly 180 degrees. It's formed by two rays that extend from a common point (the vertex) in opposite directions, forming a straight line. Think of it as a perfectly flat, unfolded line. This seemingly simple definition underpins a wealth of geometric concepts and calculations.
Visualizing a Straight Angle
Imagine a perfectly straight road extending infinitely in both directions. The road itself represents a straight angle. Another example is a perfectly folded piece of paper; when unfolded, it creates a straight angle at the crease. These visual representations help solidify the understanding of what a straight angle actually looks like.
Measuring Angles: Degrees and Radians
Angles are measured using two primary units: degrees and radians. While degrees are more commonly used in everyday applications, radians are crucial in higher-level mathematics and physics.
Degrees
The degree is a unit of angular measurement where a full circle is divided into 360 degrees. Therefore, a straight angle, representing half a circle, measures exactly 180 degrees. This is a fundamental relationship that underpins many geometric calculations.
Radians
Radians, on the other hand, are based on the radius of a circle. One radian is the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. A straight angle, in radians, is equal to π (pi) radians, which is approximately 3.14159 radians. This is because the circumference of a circle is 2πr, and a straight angle represents half the circumference.
Properties of a Straight Angle
Straight angles possess several key properties:
-
180-degree Measurement: The most fundamental property is its measurement of exactly 180 degrees or π radians. This is the defining characteristic that distinguishes a straight angle from other types of angles.
-
Linear Pair: Straight angles form linear pairs. A linear pair is formed when two adjacent angles share a common vertex and their non-common sides form a straight line. The sum of angles in a linear pair always equals 180 degrees. This property is invaluable in solving geometric problems.
-
Supplementary Angles: A straight angle can be divided into two supplementary angles. Supplementary angles are two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. This property is frequently used in proving geometric theorems and solving problems involving angles.
-
Formation of a Line: The rays forming a straight angle always create a straight line. This seemingly obvious property highlights the close relationship between straight angles and straight lines in geometry.
Straight Angles in Geometry: Theorems and Applications
Straight angles are not just a standalone concept; they are integral to numerous geometric theorems and applications.
Linear Pair Theorem
The Linear Pair Theorem states that if two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary (their measures add up to 180 degrees). This theorem is frequently used in proofs and problem-solving within geometry.
Angle on a Straight Line
The concept of a straight angle directly relates to the theorem stating that the sum of angles on a straight line is 180 degrees. This principle is frequently applied to solve problems involving angles formed by intersecting lines.
Vertically Opposite Angles
When two lines intersect, they form four angles. Vertically opposite angles are the angles that are directly opposite each other. Due to the properties of straight angles and linear pairs, vertically opposite angles are always equal.
Straight Angles in Real-World Applications
Straight angles are not merely abstract concepts confined to textbooks. They have numerous real-world applications across diverse fields.
Architecture and Construction
Architects and construction engineers utilize the concept of straight angles extensively in designing and building structures. From ensuring straight walls and floors to calculating precise angles for roof structures and bridges, straight angles are crucial for structural integrity and stability. The precise measurement of angles is vital for accurate construction, preventing structural weaknesses and potential collapses.
Engineering and Design
Engineers in various disciplines, including mechanical, civil, and aerospace engineering, rely on straight angles for accurate calculations and designs. This includes designing roadways, bridges, and other infrastructure, where precise angular measurements are essential for safe and effective functionality.
Computer Graphics and Animation
In the world of computer graphics and animation, straight angles are essential for creating realistic and accurate representations of objects and environments. The accurate calculation and manipulation of angles are crucial for the smooth animation of characters and objects, enabling lifelike movement and realistic interactions.
Navigation and Surveying
Navigation and surveying also heavily depend on straight angles. Precise angular measurements are vital for determining locations, charting courses, and mapping geographical features. Whether it's aerial surveying or land-based mapping, accurate angular measurements ensure the precision necessary for these critical tasks.
Other Applications
The concept of straight angles extends to many other fields, including:
-
Robotics: Programming robotic movements and actions often involves precise calculations of angles, including straight angles, to ensure accurate and efficient performance.
-
Physics: Straight angles play a role in understanding various physical phenomena, such as the trajectory of projectiles and the reflection and refraction of light.
Solving Problems Involving Straight Angles
Numerous problems involve applying the properties of straight angles. Here's an example:
Problem: Two angles, Angle A and Angle B, form a linear pair. If Angle A measures 75 degrees, what is the measure of Angle B?
Solution: Since angles A and B form a linear pair, their sum is 180 degrees. Therefore, Angle B = 180 degrees - 75 degrees = 105 degrees.
Conclusion: Understanding the Significance of the Straight Angle
The seemingly simple straight angle is a cornerstone of geometry and various applications across numerous fields. Understanding its properties, measurement in degrees and radians, and its role in theorems and real-world scenarios is crucial for anyone working with angles and spatial relationships. From the foundation of geometrical principles to the sophisticated designs of modern infrastructure and technology, the straight angle's influence is undeniable. Its consistent 180-degree measurement provides a reliable benchmark for numerous calculations and applications, solidifying its place as a fundamental concept in mathematics and beyond. This comprehensive exploration hopefully clarifies the question of "how much is a straight angle" and highlights its importance within the wider context of angular measurement and geometrical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are 3 Advantages Of Fossil Fuels
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is A Vertices In A Triangle
Mar 13, 2025
-
Five Letter Words Ending E R
Mar 13, 2025
-
Which Gas Do Plants Expel In The Troposphere During Photosynthesis
Mar 13, 2025
-
Resources Owned By A Business Are Referred To As
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Much Is A Straight Angle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
