What Is A Response In Biology
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
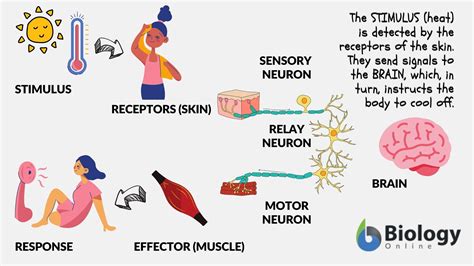
Table of Contents
What is a Response in Biology? A Comprehensive Guide
Biological responses are the cornerstone of life, shaping how organisms interact with their environments and ensuring survival. From the simple twitch of a plant towards sunlight to the complex cognitive processes of the human brain, responses are the dynamic interplay between stimulus and reaction. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the fascinating world of biological responses, exploring their various forms, mechanisms, and significance.
Defining Biological Responses: Stimulus and Reaction
At its core, a biological response is any change in an organism's behavior, physiology, or biochemistry in reaction to a stimulus. A stimulus is any detectable internal or external change in the environment that triggers a response. This could be anything from a change in temperature or light intensity to the presence of a predator or a nutrient-rich food source. The response itself is the organism's adaptive mechanism to deal with this stimulus, helping it to survive, reproduce, or maintain homeostasis.
Types of Stimuli and Corresponding Responses
The diversity of life on Earth translates into a vast spectrum of stimuli and responses. We can categorize these broadly as follows:
1. Environmental Stimuli: These are external factors influencing an organism.
- Light: Plants exhibit phototropism (growth towards light) in response to light stimuli, while animals use light for navigation and vision.
- Temperature: Organisms demonstrate thermoregulation, adjusting their body temperature to maintain optimal metabolic function. This can involve behavioral responses like seeking shade or basking in the sun.
- Water: Organisms respond to water availability through various mechanisms, including osmoregulation (regulation of water balance) and drought tolerance. Plants might wilt under drought conditions, while animals might migrate in search of water sources.
- Gravity: Plants exhibit gravitropism (growth in response to gravity), directing roots downwards and shoots upwards.
- Chemicals: Organisms respond to chemical stimuli through chemoreception, a process vital for finding food, avoiding predators, and communication (e.g., pheromones).
2. Internal Stimuli: These are factors within the organism itself.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormones act as chemical messengers, regulating various physiological processes, such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. Responses to hormonal changes can be widespread and complex.
- Neural Signals: The nervous system plays a critical role in coordinating rapid responses to stimuli. Neural signals allow for immediate reactions, like withdrawing a hand from a hot stove.
- Nutrient Levels: Internal nutrient levels influence metabolic processes. For instance, low blood sugar can trigger the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels.
Mechanisms of Biological Responses
The underlying mechanisms of biological responses vary greatly depending on the organism and the type of stimulus involved. However, some key mechanisms are common across different systems:
1. Signal Transduction: This is a fundamental process in which a stimulus is converted into an intracellular signal, ultimately leading to a specific cellular response. This often involves a cascade of molecular events, including receptor activation, enzyme activation, and gene expression changes.
2. Receptor Proteins: Specialized receptor proteins on the cell surface or within the cell detect stimuli. These receptors bind to specific molecules or sense changes in physical conditions, initiating the signal transduction pathway.
3. Effector Molecules: Effector molecules are the components that carry out the actual response. These can include enzymes, ion channels, or motor proteins.
Specific Examples of Response Mechanisms
- Plant Responses: Plants utilize a variety of mechanisms, including hormone signaling (e.g., auxin, gibberellins), changes in turgor pressure (cell swelling), and differential cell growth to respond to environmental stimuli.
- Animal Responses: Animals rely heavily on the nervous and endocrine systems to coordinate responses. Rapid responses are mediated by the nervous system, while slower, longer-lasting responses are often regulated by hormones.
- Microbial Responses: Microorganisms exhibit various responses to environmental changes, including chemotaxis (movement towards or away from chemicals), osmoregulation, and sporulation (formation of resistant spores).
The Significance of Biological Responses in Ecology and Evolution
Biological responses are crucial for an organism's survival and reproductive success. They enable organisms to adapt to changing environmental conditions, avoid predators, find food, and reproduce effectively. This adaptive capacity plays a vital role in shaping ecological interactions and evolutionary processes.
Adaptive Responses and Natural Selection
Natural selection favors individuals with responses that enhance their fitness. Organisms with more effective responses are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to future generations. This process drives the evolution of increasingly sophisticated response mechanisms.
Ecological Interactions and Responses
Biological responses are central to various ecological interactions. Predator-prey relationships are a prime example, with both predators and prey exhibiting specialized responses to enhance their survival. Competition for resources also drives the evolution of responses that optimize resource acquisition.
Studying Biological Responses: Techniques and Approaches
The study of biological responses employs a diverse range of techniques and approaches, ranging from simple behavioral observations to sophisticated molecular analyses.
- Behavioral observations: This involves observing and recording an organism's behavior in response to different stimuli. This is a fundamental approach in ethology, the study of animal behavior.
- Electrophysiology: This technique measures electrical signals in cells and tissues, providing insights into the neural and muscular responses to stimuli.
- Molecular biology techniques: These techniques, such as gene expression analysis, proteomics, and metabolomics, help to unravel the molecular mechanisms underlying biological responses.
- Imaging techniques: Microscopy and other imaging techniques are used to visualize responses at the cellular and tissue levels.
- Computational modeling: Mathematical and computational models are used to simulate biological responses and predict how organisms will react to different conditions.
Applications of Understanding Biological Responses
Understanding biological responses has significant implications across various fields:
- Agriculture: Optimizing crop yields involves understanding plant responses to environmental factors such as light, water, and nutrients.
- Medicine: Understanding how organisms respond to disease, injury, and drugs is essential for developing effective therapies.
- Environmental conservation: Understanding how organisms respond to environmental changes is crucial for developing conservation strategies.
- Biotechnology: Manipulating biological responses through genetic engineering and other techniques has significant applications in various industries.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Interaction
Biological responses are a dynamic and multifaceted process, essential for the survival and evolution of all living organisms. From the simplest unicellular organism to the most complex multicellular creature, the ability to respond to internal and external stimuli is fundamental to life itself. The continued investigation of these fascinating mechanisms promises to yield significant advancements across various scientific disciplines, contributing to our understanding of life's intricate tapestry and its remarkable adaptations. Further research continues to unravel the complexities of these responses, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge and shaping our ability to interact with and protect the living world around us. The study of biological responses is not just a scientific pursuit; it's a journey into the heart of life itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 500 Yards
Mar 14, 2025
-
No Of Subsets Of A Set
Mar 14, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 45 And 60
Mar 14, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 15 And 18
Mar 14, 2025
-
54 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Response In Biology . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
